Communication Knowledge
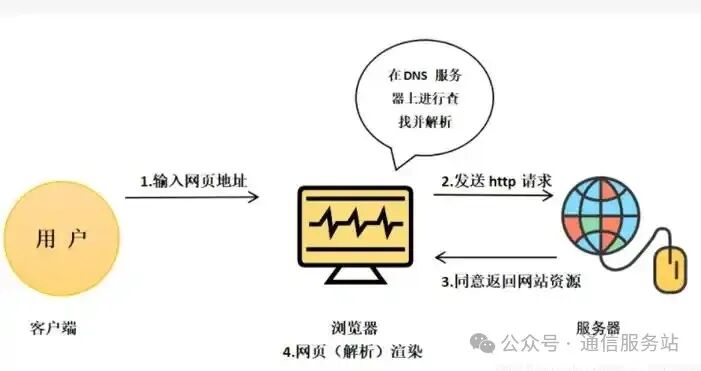
When browsing the internet, have you noticed that some websites have URLs starting with HTTP:// while others start with HTTPS://?
HTTP and HTTPS are two protocols used for transmitting information over the internet. Although they serve similar functions, there are significant differences in terms of security and application scenarios. This article will detail the concepts, characteristics, differences, and relationships between HTTP and HTTPS.
HTTP: The Pioneer of Fast Transmission
Introduction
HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) is one of the most commonly used protocols on the internet. It is responsible for transmitting hypertext data, such as HTML pages, between clients (like browsers) and servers. HTTP is a stateless protocol, meaning each request/response is independent and does not retain any state information.
Characteristics
-
Stateless: Each request is independent and does not retain session information.
-
Default Port: Uses port number 80.
-
Fast Speed: Due to the absence of encryption/decryption processes, HTTP’s transmission speed is relatively fast.
Uses
-
Accessing websites.
-
Transmitting web data.
HTTPS: The Guardian of Secure Transmission
Introduction
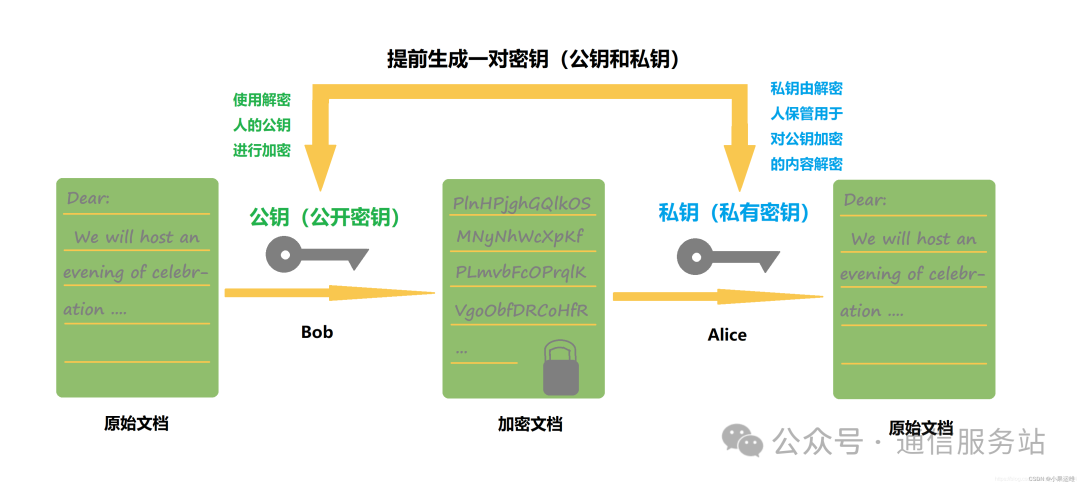
HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure) is built on HTTP and incorporates the SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security) protocol to encrypt data transmission, ensuring that data is not eavesdropped on or tampered with during transmission. HTTPS not only provides data encryption for websites but also verifies the server’s identity through SSL certificates, ensuring that the client connects to the real server.
Characteristics
-
High Security: Encrypts data transmission through SSL/TLS protocols, effectively preventing data from being eavesdropped on or tampered with.
-
Identity Verification: Verifies the server’s identity through SSL certificates, enhancing trust.
-
Default Port: Uses port number 443.
-
Slower Speed: Due to the encryption/decryption process, HTTPS’s transmission speed may be slightly slower than HTTP.
Uses
-
E-commerce websites.
-
Online banking.
-
Social media.
-
Any website that needs to protect sensitive information.
Differences and Relationships Between HTTP and HTTPS
Differences
-
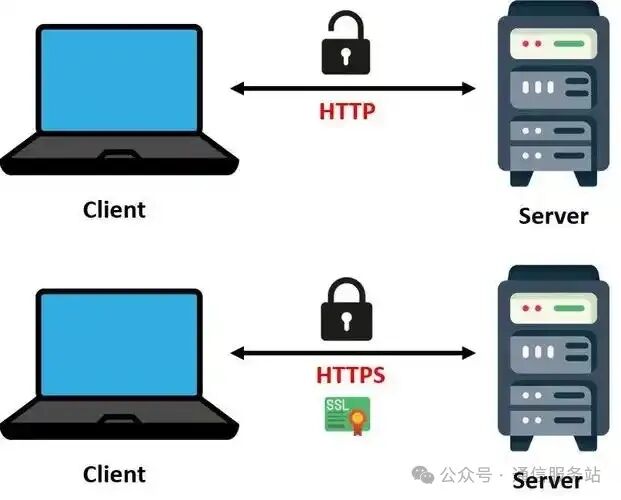
Security: HTTP does not encrypt data, making information vulnerable to eavesdropping and tampering during transmission; whereas HTTPS uses SSL/TLS protocols to encrypt data, ensuring confidentiality and integrity during transmission.
-
Ports: HTTP uses port 80 by default; HTTPS uses port 443 by default.
-
Performance: Due to the lack of encryption, HTTP’s transmission speed is faster; whereas HTTPS may be slightly slower due to the encryption and decryption processes.
-
Certificates: HTTP does not require any certificates; HTTPS requires the purchase and configuration of SSL certificates.
Relationships
-
Base Protocol: Both HTTP and HTTPS are based on the TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) for data transmission.
-
Application Scenarios: Both are used for data transmission between clients and servers, primarily for accessing web pages. HTTPS is essentially the application of the HTTP protocol over the SSL/TLS layer.
Conclusion
HTTP and HTTPS, as two important protocols on the internet, each play different roles. HTTP, with its fast transmission characteristics, is suitable for scenarios with low security requirements; while HTTPS, with its high security, has become the preferred choice for protecting sensitive information transmission. As the demand for network security continues to rise, HTTPS has gradually become the standard protocol on the internet. Therefore, for websites and applications that need to transmit sensitive information, it is recommended to prioritize the use of the HTTPS protocol to ensure user data security.