What is a map file?
In simple terms: a map file is a mapping file that integrates the program, data, and IO space after compilation by the compiler.
Program Size: Code=1112 RO-data=320 RW-data=0 ZI-data=1632
About the map file in Keil
How to open a map file
The most direct and simplest way: double-click the project target to open the map file (note to double-click the project target, not the project or file group). See the image below:
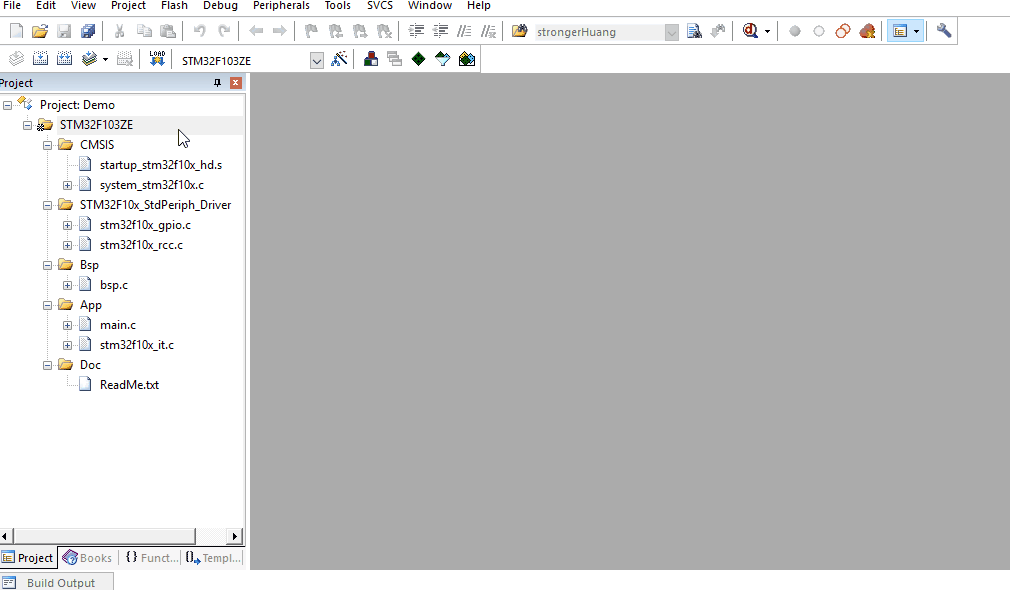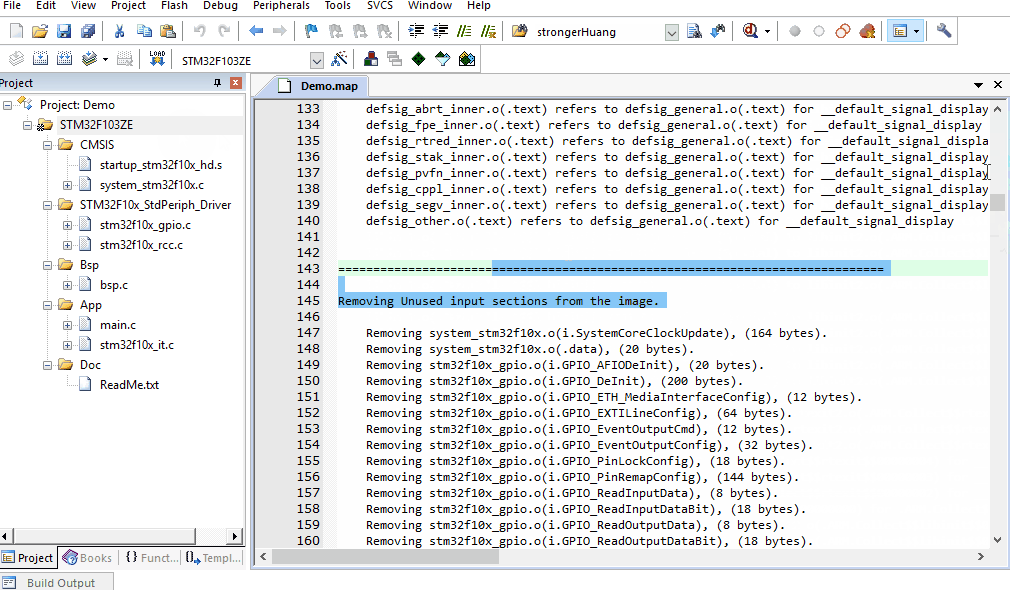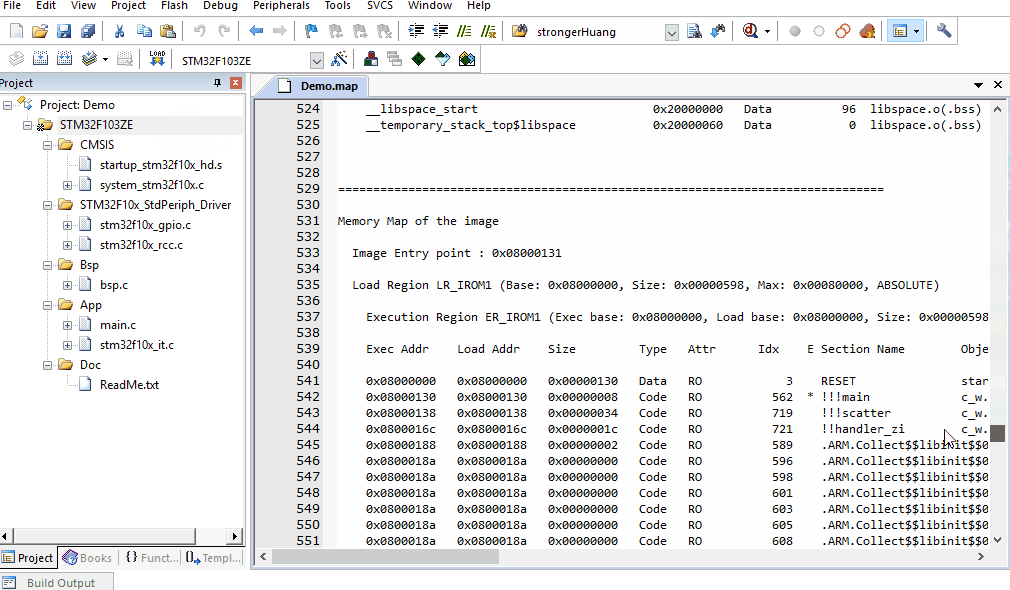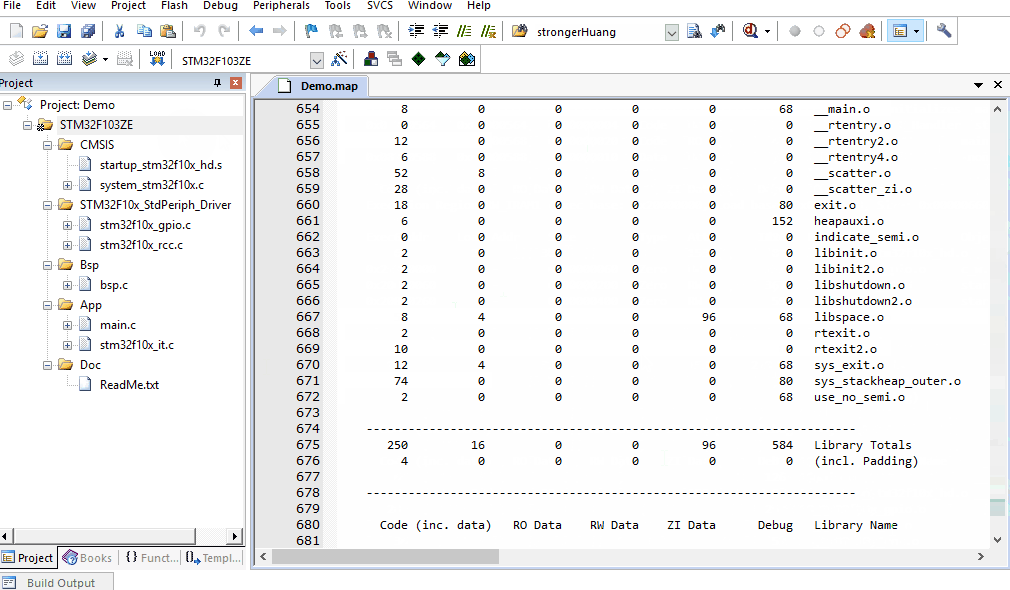
Map file output content configuration
Main configurations include:
Memory Map:Memory Mapping
Callgraph:Graph Mapping
Symbols:Symbols
Cross Reference:Cross References
Size Info:Size Information
Totals Info:Total Information
Unused Section Info:Unused Module Information
Veneers Info:Veneer Information
We can select the corresponding information based on our needs.
Note:
A.By default, all information is output;
B.These configurations are a combination relationship;
Classification of map file content
From the above output configuration, we can see what information the map file roughly contains. The map file is divided into the following five categories:
1.Section Cross References:Module and section (entry) cross-references
2.Removing Unused input sections from the image:Removing Unused Modules
3.Image Symbol Table:Mapping Symbol Table
4.Memory Map of the image:Memory (Mapping) Distribution
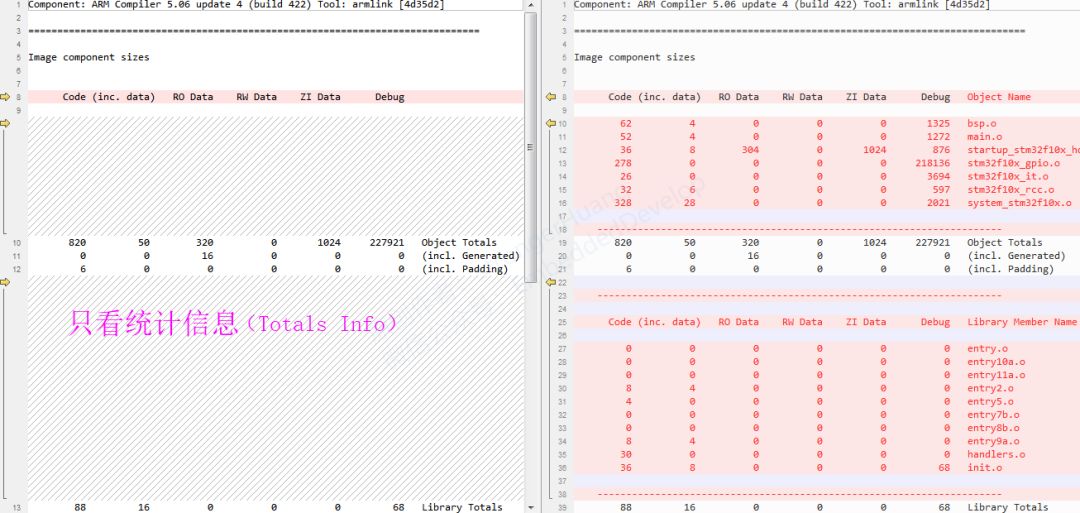
5.Image component sizes:Storage Composition Sizes
Descriptions of Each Module
Configuration needs to check: Cross Reference
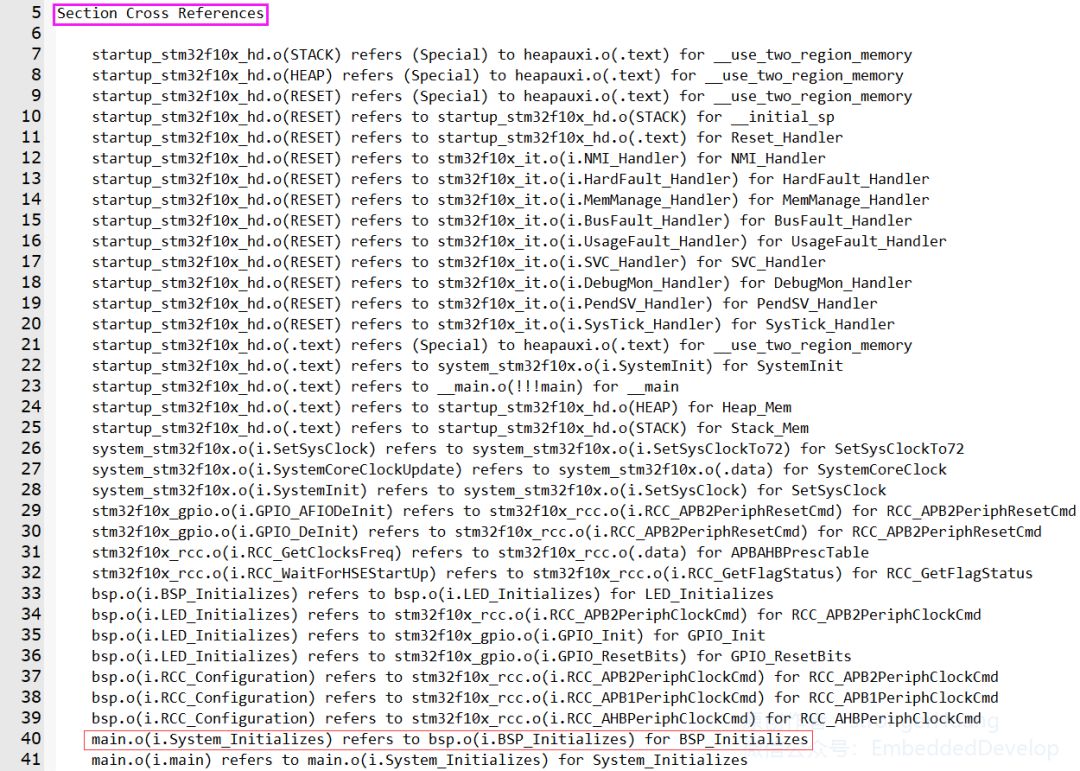
Section Cross References:Module and section (entry) cross-references refer to the relationship of mutual references between the modules and sections generated by various source files.
For example:
main.o(i.System_Initializes) refers to bsp.o(i.BSP_Initializes) for BSP_Initializes
Means:
The System_Initializes function (i.System_Initializes) in the main module (main.o) calls the BSP_Initializes function in the bsp module (bsp.o).
Note:
A.main.o is the target file module generated from the main.c source file;
B.I.System_Initializes is the entry of the System_Initializes function.
2、Removing Unused input sections from the image:Removing Unused Modules
Configuration needs to check: Unused Sections Info
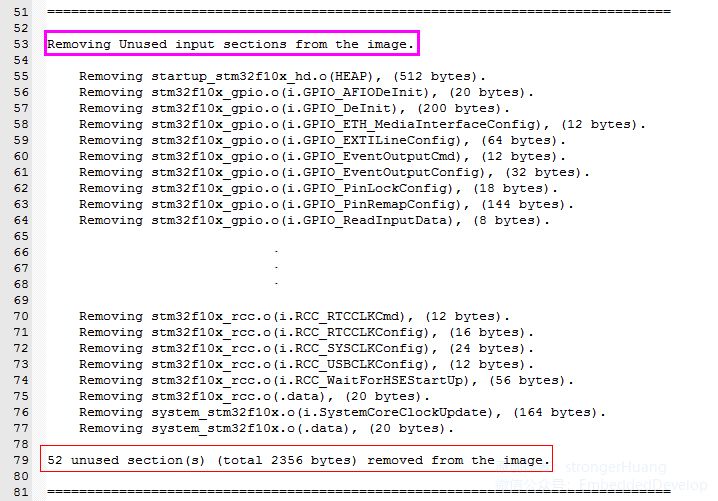
This category is easy to understand; it generates a list in the map file of modules (or functions) in our code that are not called.
For example:
Removing stm32f10x_gpio.o(i.GPIO_AFIODeInit), (20 bytes).
Means:
The GPIO_AFIODeInit module (function) in the stm32f10x_gpio.c file is not called and its code size is 20 bytes.
Lastly, there is a statistic:
52 unused section(s) (total 2356 bytes) removed from the image.
1.A total of 52 sections were not called;
2.The total size of the unused sections is 2356 bytes;
3、Image Symbol Table:Mapping Symbol Table
Configuration needs to check: Symbols
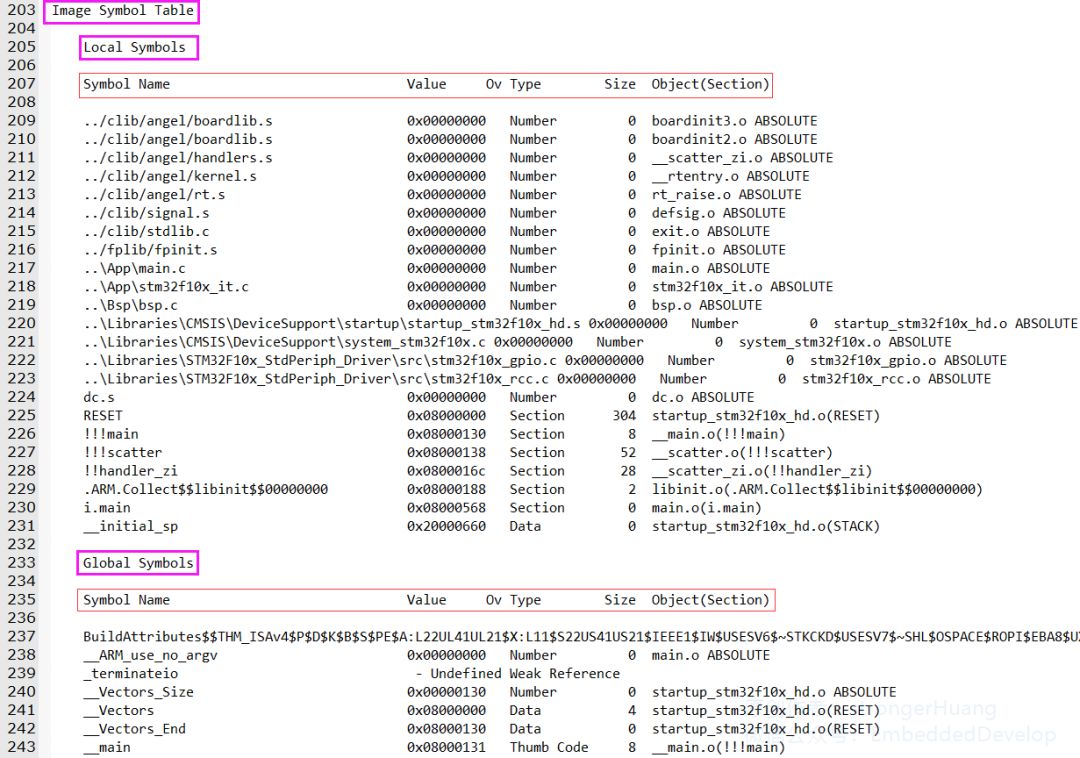
Image Symbol Table:Mapping Symbol Table, which is a table that stores the corresponding addresses of each section (the image has removed part of the content).
Symbols are divided into two main categories
1.Local Symbols:Local
2.Global Symbols:Global
Key Points of Symbol Content
1.Symbol Name:Symbol Name
For naming and classification, please refer to the official reference document provided at the end.
2.Value:Stores the corresponding address
You will find addresses like 0x0800xxxx and 0x2000xxxx.
0x0800xxxx refers to code, variables, etc., stored in FLASH.
0x2000xxxx refers to variables Data, etc., stored in RAM.
3.Ov Type:Type of the symbol
There are several types of symbols: Number, Section, Thumb Code, Data, etc.;
Careful readers will notice that global and static variables are located in the 0x2000xxxx memory RAM.
4.Size:Storage Size
This is easy to understand; it refers to the size occupied by the current row of Symbol.
5.Object(Section):Section Target
This generally refers to the module (source file) in which it is located.
4、Memory Map of the image:Memory (Mapping) Distribution
Configuration needs to check: Memory Map
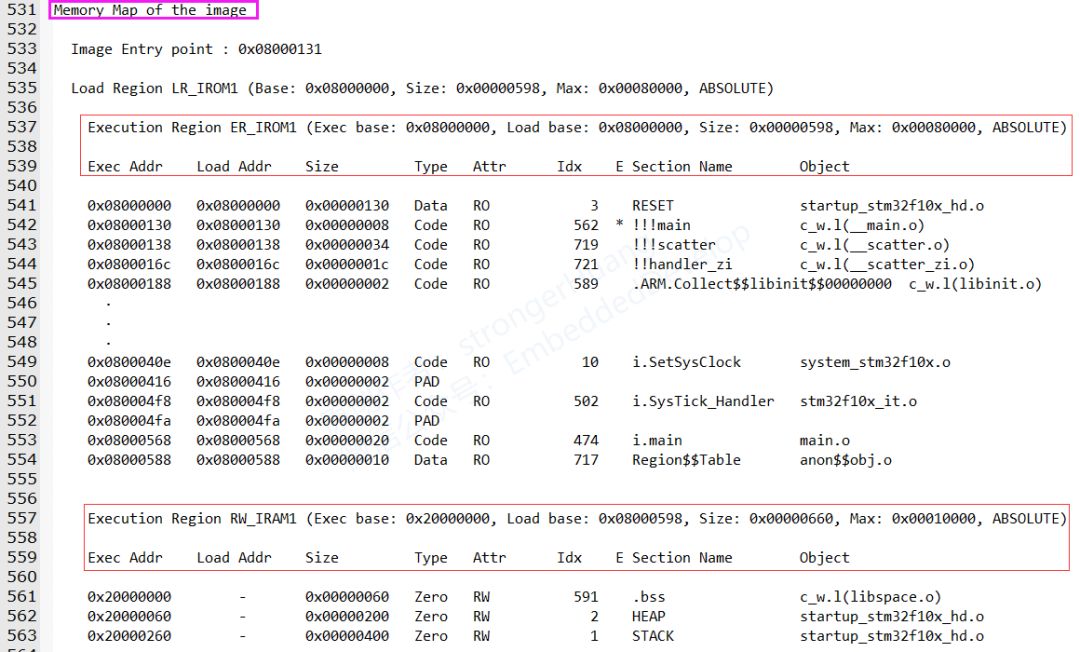
Memory Map of the image:Memory (Mapping) Distribution, the content is relatively more and is quite important.
Main Introduction
Image Entry point : 0x08000131:refers to the mapping entry address.
Load Region LR_IROM1 (Base: 0x08000000, Size: 0x00000598, Max: 0x00080000, ABSOLUTE):
Refers to the loading region starting at LR_IROM1 address 0x08000000, size 0x00000598, with a maximum of 0x00080000.
Execution Regions:
A.Execution Region ER_IROM1
B.Execution Region RW_IRAM1
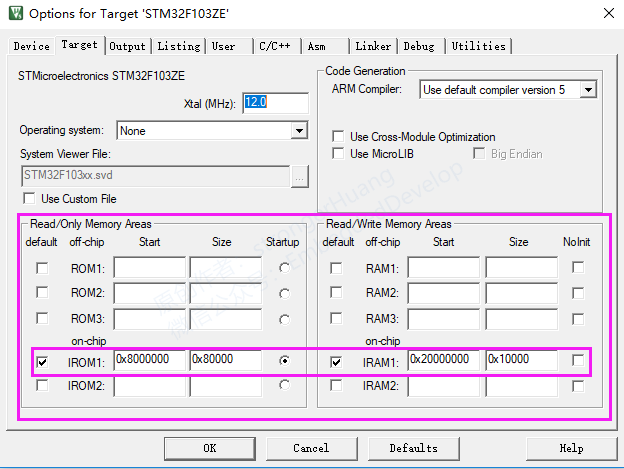
This region corresponds to the regions in our target configuration, as shown below:
Key Points of Content
1.Base Addr:Storage Address
0x0800xxxx FLASH address and 0x2000xxxx memory RAM address.
2.Size:Storage Size
3.Type:Type
Data: Data Type
Code: Code Type
Zero: Uninitialized Variable Type
PAD: This type is placed in this position in the map file; it cannot be counted as a type here. If translated, it can only be described as “padding type”.
ARM processors are 32-bit; if an 8-bit or 16-bit variable is defined, there will be a remainder; this refers to the “padding” part, and you will find that the other options do not have corresponding values.
4.Attr:Attributes
RO: Stored in ROM segments
RW: Stored in RAM segments
5.Section Name:Section Name
This can also be referred to as entry classification name, similar to the modules and sections referred to in the first chapter “Section Cross References”.
It generally includes: RESET, .ARM, .text, i, .data, .bss, HEAP, STACK, etc.
6.Object:Target
5、Image component sizes:Storage Composition Sizes
Configuration needs to check: Size Info
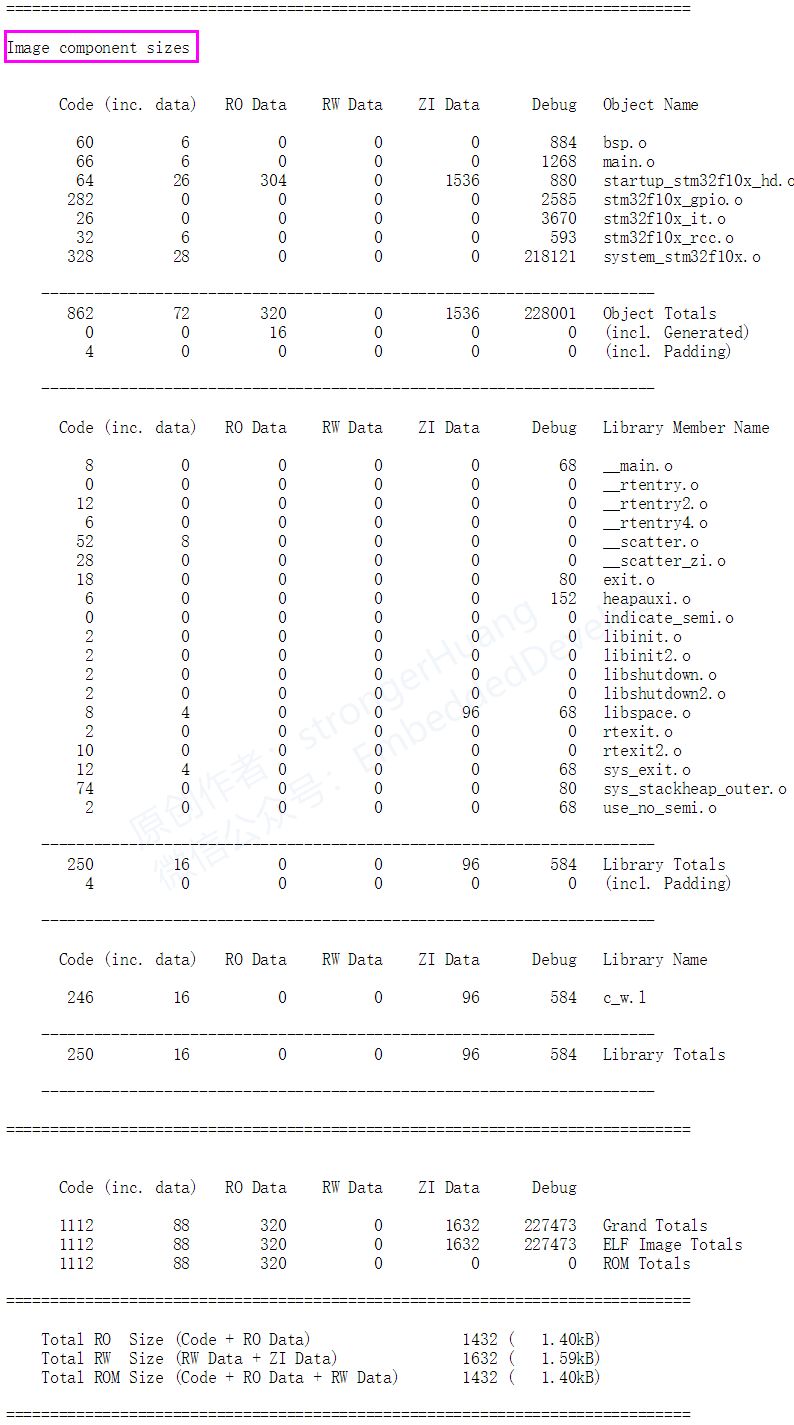
Image component sizes:Storage Composition Sizes, mainly summarizes the storage size information of the modules.
This chapter’s content is believed to be understandable; after compiling the project, we generally see a message similar to the following in the compilation window:
Program Size: Code=1112 RO-data=320 RW-data=0 ZI-data=1632
Code:Refers to the size of the code;
Ro-data:Refers to constant data excluding inline data;
RW-data:Refers to readable and writable (RW), initialized variable data;
ZI-data:Refers to uninitialized (ZI) variable data;
Reminder:
A.Code, Ro-data:Located in FLASH;
B.RW-data, ZI-data:Located in RAM;
C.RW-dataInitialized data will be stored in Flash and moved to RAM on power-up.
The relationships are as follows:
RO Size = Code + RO Data
RW Size = RW Data + ZI Data
ROM Size = Code + RO Data + RW Data