Understanding C Language File Operations – An Array in Essence
There are four main components of C language files: Opening (Creating) and Closing Files、Read and Write Operations、Positioning Operations、Error Checking,this article will explain the first two topics. 🌟
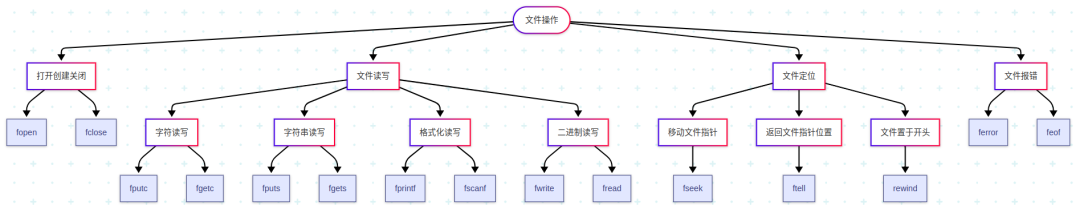
1. Opening and Closing Files
- •
<span>fopen</span> - •Function:Opens a file and returns a pointer to that file.
- •Prototype:
<span>FILE *fopen(const char *filename, const char *mode);</span> - •Parameters:
<span>filename</span>is the name of the file to be opened;<span>mode</span>is the mode in which to open the file, described as follows:
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| r | Opens an<span>existing text file</span>, allowing<span>reading</span>from the file. |
| w | Opens a text file, allowing<span>writes</span>to the file.<span>If the file does not exist, a new file will be created</span>. Here, the program will<span>write content from the beginning of the file</span>. If the file exists, the content of the file<span>will be cleared</span> (i.e., the file length is truncated to 0). |
| a | Opens a text file for<span>appending</span>to the file. If the file does not exist,<span>a new file will be created</span>. Here, the program will append content to the existing file content. |
| r+ | Opens a text file, allowing<span>reading and writing</span>to the file. |
| w+ | Opens a text file, allowing<span>reading and writing</span>to the file. If the file already exists, it will be truncated to zero length; if the file does not exist, a new file will be created. |
| a+ | Opens a text file, allowing<span>reading and writing</span>to the file. If the file does not exist, a new file will be created. Reading starts from the beginning of the file, while writing can only be in append mode. |
The main difference between modes with + and without + is whether<span>read and write permissions are available simultaneously</span>
- •
<span>fclose</span> - •Function:Closes an already opened file.
- •Prototype:
<span>int fclose(FILE *stream);</span> - •Parameters:
<span>stream</span>is a pointer to the file to be closed. - •Return Value:Returns
<span>0</span>if successful; returns<span>EOF</span>if an error occurs.
2. File Read and Write Operations
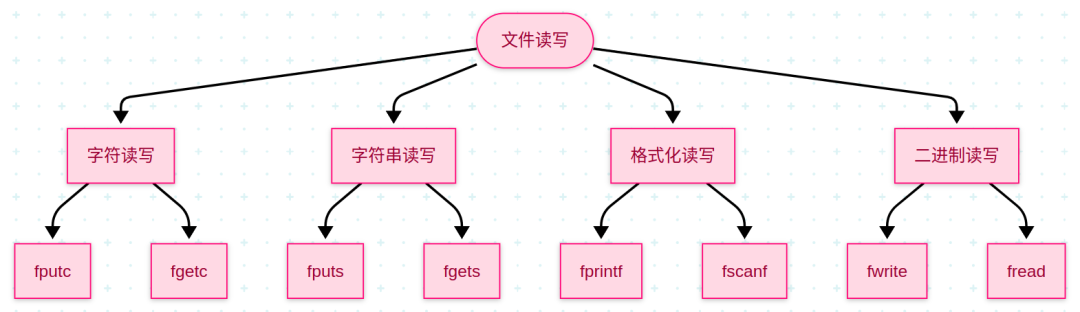
Character Read and Write
- •
<span>fgetc</span> - •Function:Reads a character from the file.
- •Prototype:
<span>int fgetc(FILE *stream);</span> - •Return Value:Returns the character read; returns
<span>EOF</span>if the end of the file is reached or an error occurs. - •
<span>fputc</span> - •Function:Writes a character to the file.
- •Prototype:
<span>int fputc(int c, FILE *stream);</span> - •Parameters:
<span>c</span>is the character to be written;<span>stream</span>is a pointer to the file. - •Return Value:Returns the character written if successful; returns
<span>EOF</span>if an error occurs.
String Read and Write
- •
<span>fgets</span> - •Function:Reads a line of string from the file.
- •Prototype:
<span>char *fgets(char *s, int size, FILE *stream);</span> - •Parameters:
<span>s</span>is the buffer to store the read string;<span>size</span>is the size of the buffer;<span>stream</span>is a pointer to the file. - •Return Value:Returns a pointer to
<span>s</span>if successful; returns<span>NULL</span>if the end of the file is reached or an error occurs. - •
<span>fputs</span> - •Function:Writes a string to the file.
- •Prototype:
<span>int fputs(const char *s, FILE *stream);</span> - •Parameters:
<span>s</span>is the string to be written;<span>stream</span>is a pointer to the file. - •Return Value:Returns a non-negative value if successful; returns
<span>EOF</span>if an error occurs.
Formatted Read and Write
- •
<span>fscanf</span> - •Function:Reads data from the file according to the specified format.
- •Prototype:
<span>int fscanf(FILE *stream, const char *format, ...);</span> - •Parameters:
<span>stream</span>is a pointer to the file;<span>format</span>is the format control string; the following are variable arguments used to store the read data. - •Return Value:Returns the number of input items successfully matched and assigned; returns
<span>EOF</span>if the end of the file is reached or an error occurs. - •
<span>fprintf</span> - •Function:Writes data to the file according to the specified format.
- •Prototype:
<span>int fprintf(FILE *stream, const char *format, ...);</span> - •Parameters:
<span>stream</span>is a pointer to the file;<span>format</span>is the format control string; the following are variable arguments containing the data to be written. - •Return Value:Returns the number of characters actually written; returns a negative value if an error occurs.
Binary Read and Write
- •
<span>fread</span> - •Function:Reads binary data from the file.
- •Prototype:
<span>size_t fread(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream);</span> - •Parameters:
<span>ptr</span>is the buffer to store the read data;<span>size</span>is the size of each data item;<span>nmemb</span>is the number of data items to read;<span>stream</span>is a pointer to the file. - •Return Value:Returns the actual number of data items successfully read.
- •
<span>fwrite</span> - •Function:Writes binary data to the file.
- •Prototype:
<span>size_t fwrite(const void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream);</span> - •Parameters:
<span>ptr</span>is a pointer to the data to be written;<span>size</span>is the size of each data item;<span>nmemb</span>is the number of data items to write;<span>stream</span>is a pointer to the file. - •Return Value:Returns the actual number of data items successfully written.
Test Function
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>typedef const char *string;int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ FILE *fp = fopen("/home/eyk/桌面/MCU/1.C基础/3.Unix系统其他特点/5.文件处理/test/12.读写测试.txt", "w+"); if (fp == NULL) { perror("fopen"); } else { printf("File opened successfully\n"); printf("File descriptor: %d\n\n", fileno(fp)); printf("Testing character read and write:\n\n"); { printf("Writing character:\n"); fputc('a', fp); printf("Wrote 'a', current position: %ld \n", ftell(fp)); fputc('b', fp); printf("Wrote 'b', current position: %ld \n", ftell(fp)); printf("\nReading character:\n"); printf("Current position: %ld \n", ftell(fp)); rewind(fp); printf("Reset file pointer to start, current position: %ld\n", ftell(fp)); char c = fgetc(fp); printf("Read character: %c\n", c); c = fgetc(fp); printf("Read character again: %c\n", c); } printf("\n\nTesting string read and write:\n\n"); { printf("Writing string:\n"); fputs("hello world", fp); printf("Wrote 'hello world', current position: %ld \n", ftell(fp)); printf("\nReading string:\n"); printf("Current position: %ld \n", ftell(fp)); rewind(fp); printf("Reset file pointer to start, current position: %ld\n", ftell(fp)); char str[128]; fgets(str, 128, fp); printf("Read string: %s\n", str); } printf("\n\nTesting formatted read and write:\n\n"); { printf("Writing formatted: %d %s %c\n", 1, "hello", 'a'); fprintf(fp, "%d %s %c", 1, "hello", 'a'); printf("Wrote formatted, current position: %ld \n", ftell(fp)); printf("\nReading formatted:\n"); printf("Current position: %ld \n", ftell(fp)); rewind(fp); printf("Reset file pointer to start, current position: %ld\n", ftell(fp)); char str[128]; while (!feof(fp)) { /** * func descp: You can see that the read and write here are similar to scanf series, using spaces, tabs, and newlines as delimiters. */ fscanf(fp, "%s", str); printf("Read string: %s\n", str); } } printf("\n\nTesting binary read and write:\n\n"); { string str = "hello world"; printf("Writing binary: %s\n", str); /** * func descp: * fwrite reads sizeof(str) characters from str into the file * fread reads sizeof(str) characters from the file into str */ fwrite(str, sizeof(char), strlen(str), fp); printf("Wrote binary, current position: %ld \n", ftell(fp)); printf("\nReading binary:\n"); printf("Current position: %ld \n", ftell(fp)); int len = ftell(fp); rewind(fp); printf("Reset file pointer to start, current position: %ld\n", ftell(fp)); char str2[128]; fread(str2, sizeof(char), len, fp); str2[len] = '\0'; printf("Read binary: %s\n", str2); } fclose(fp); }}Test Results
File opened successfullyFile descriptor: 3Testing character read and write:Writing character:Wrote 'a', current position: 1Wrote 'b', current position: 2Reading character:Current position: 2Reset file pointer to start, current position: 0Read character: aRead character again: bTesting string read and write:Writing string:Wrote 'hello world', current position: 13Reading string:Current position: 13Reset file pointer to start, current position: 0Read string: abhello worldTesting formatted read and write:Writing formatted:1 hello aWrote formatted, current position: 22Reading formatted:Current position: 22Reset file pointer to start, current position: 0Read string: abhelloRead string: world1Read string: helloRead string: aTesting binary read and write:Writing binary: hello worldWrote binary, current position: 33Reading binary:Current position: 33Reset file pointer to start, current position: 0Read binary: abhello world1 hello ahello worldFile After Testing
abhello world1 hello ahello world