Toyota C-HR is a global strategic SUV model launched on December 14, 2016. The platform it uses is the new “TNGA” platform (TNGA-C platform) adopted from the 4th generation Prius launched in 2015, which has a shortened wheelbase. In terms of safety configuration, in addition to the standard SRS airbags, SRS side airbags, and SRS curtain airbags across the entire range, it also comes standard with Toyota Safety Sense P, which includes multiple safety features such as a collision mitigation braking system.
This report will mainly analyze the safety performance components of the electronic parts equipped in the C-HR and introduce Toyota’s latest ADAS system. The disassembly research of the Toyota C-HR vehicle was conducted in January 2018 as a benchmark activity of the Hiroshima Industrial Promotion Organization. MarkLines signed a copyright agreement with the Hiroshima Industrial Promotion Organization to sell its benchmark report.
Toyota Safety Sense P (Lexus Safety System+)
The “Toyota Safety Sense P” was developed by Denso and was first adopted in the minor model change of the Land Cruiser in August 2015. The laser radar of “Toyota Safety Sense C” was replaced with millimeter-wave radar, consisting of the following four functions. The C-HR uses devices manufactured by Continental.
Functions of Toyota Safety Sense P
Pre-collision safety system
Radar cruise control
Lane departure warning
Automatic high beam
|
Using millimeter-wave radar and a monocular camera to detect vehicles and pedestrians on the road ahead, if the system predicts a collision, it will issue an alarm to prompt the driver to take evasive action. When driving at speeds between approximately 30 km/h and 80 km/h, if the driver presses the brake pedal, the assistance function will activate; if the brake pedal is not pressed, the automatic brake will activate when the speed is between approximately 10 km/h and 80 km/h, slowing down to about 30 km/h. Additionally, it has a pedestrian detection function, which is not included in Toyota Safety Sense C. |
|
It has full-speed tracking capability, synchronizing with the speed of the vehicle ahead using the millimeter-wave radar and monocular camera system. |
|
The monocular camera recognizes the white lines on the road; if the driver deviates from the lane without signaling, an alarm will be issued through a buzzer and display. It also assists the driver’s steering operation by controlling the electric power steering, making it easier to avoid lane departure. |
|
It recognizes vehicles ahead and vehicles in reverse, automatically switching between high and low beams. |
Front millimeter-wave radar
|
|
|
(Source: Toyota) |
To achieve ADAS functions, the C-HR uses a combination of millimeter-wave radar and a monocular camera. The millimeter-wave radar is installed behind the license plate at the front center of the vehicle, and the monocular camera is mounted on the windshield. Equipped with a 77GHz millimeter-wave radar, it effectively monitors vehicles ahead at a distance and is less affected by rain, fog, snow, and other environmental conditions.
|
|
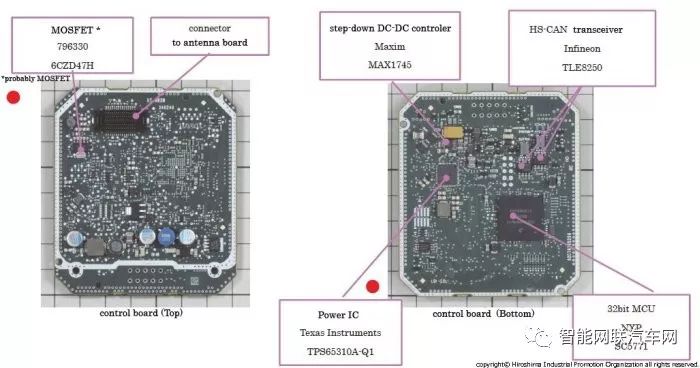
This millimeter-wave radar is a 76-77GHz radar manufactured by Continental, consisting of an antenna mainboard and a control mainboard.
|
|
The RF front end on the antenna mainboard consists of three chip devices manufactured by NXP: transmitter (TX), receiver (RX), and VCO (voltage-controlled oscillator).
|
|
The control mainboard mainly uses the NXP MCU [SC5773] (32bit Power Architecture) for various controls, the internal power block is primarily generated by the Texas Instruments [TPS65310A-Q1] power IC, and the communication block is mainly composed of two Infineon High Speed CAN transceiver ICs [TLE8250], forming two CAN communication systems.
Regarding millimeter-wave radar, for the pedestrian detection SRR (Short Range Radar) applications, 24/26GHz frequency (UWB, 4GHz) quasi-millimeter-wave radar is widely used, but to avoid interference with satellite communications, the signal transmission power is kept low, making it unable to detect long-distance signals. Therefore, the high-sensitivity 77GHz radar has started to be applied to high-end vehicles. Compared to the 24GHz frequency millimeter-wave radar, its feature is the detection distance of over 200m, enabling narrow-angle LRR (Long Range Radar). To enhance the performance of ADAS, the C-HR also uses a 77GHz frequency millimeter-wave radar.
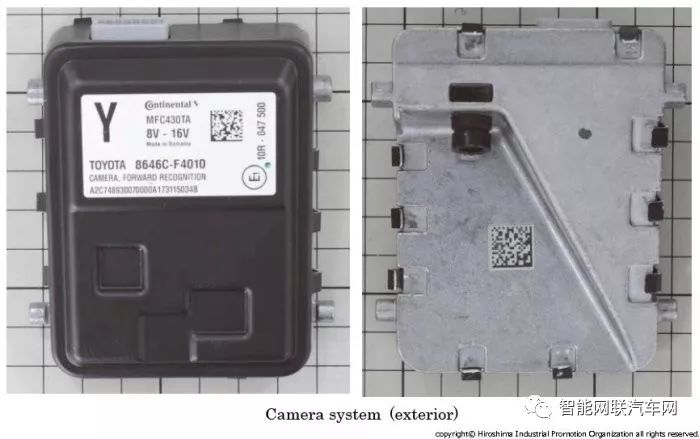
Front Monocular Camera
Another important device in the Toyota Safety Sense P system is the monocular camera. This monocular camera is installed on the inside of the windshield in front of the interior mirror.
|
|
This device is manufactured by Continental and is equipped with a 1.25 million pixel (estimated) camera.
The overall control of the camera system is conducted by a 32-bit microcontroller manufactured by ST Micro, and the image processing technology is developed independently by Continental on a Texas Instruments DSP (digital signal processor).
Most major OEMs are adopting Mobileye’s image processing technology, while Toyota, Mercedes, and Subaru have built their unique technologies with their suppliers.
|
|
Rear Millimeter-Wave Radar
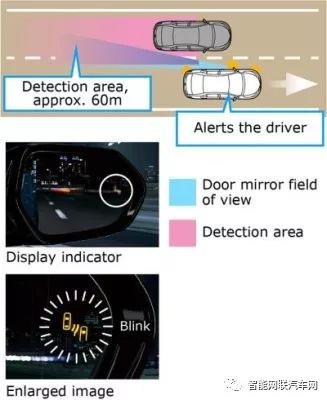
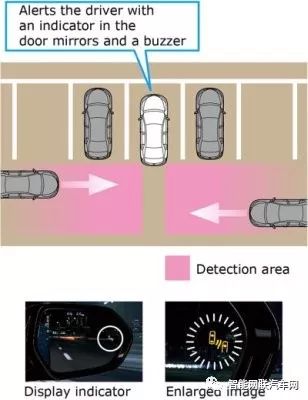
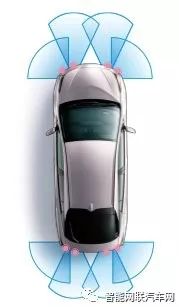
Each side of the rear bumper of the vehicle is equipped with one rear millimeter-wave radar. Using 24GHz frequency radar, it provides blind spot monitoring (BSM) functionality to assist in confirming the situation behind when changing lanes, as well as rear cross traffic alert (RCTA) functionality to detect blind spots when reversing, alerting the driver to traffic at the rear intersection.
|
|
|
|
Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) |
Rear Cross Traffic Alert (RCTA) |
(Source: Toyota)
Through radar detection, it monitors vehicles traveling in adjacent lanes. In addition to vehicles in the rear side area that are difficult to see from the outside rearview mirror, it can also monitor up to about 60m in the rear of the adjacent lane and detect vehicles approaching suddenly. If a vehicle is detected, the LED indicator light installed on the exterior rearview mirror will turn on. If the driver then operates the turn signal, the LED indicator light will flash, further attracting the driver’s attention.
|
|
|
|
Rear Bumper Side Components |
Blind Spot Monitor (BSM) |
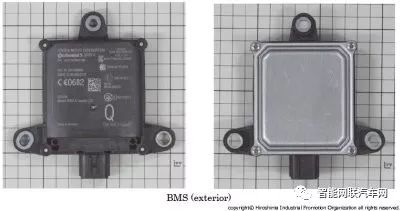
This device is a 24GHz radar manufactured by Continental, consisting of an antenna mainboard and a control mainboard. The back of the BSM device is encapsulated with wave-absorbing materials, and the surface is made of resin molding. The antenna mainboard is mounted on one side of the resin molding.
|
|
|
|
|
Structure of the Blind Spot Monitor (BSM) Device |
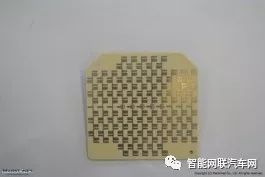
Millimeter-Wave Transceiver Signal Mainboard (Front) |
Millimeter-Wave Transceiver Signal Mainboard (Back) |
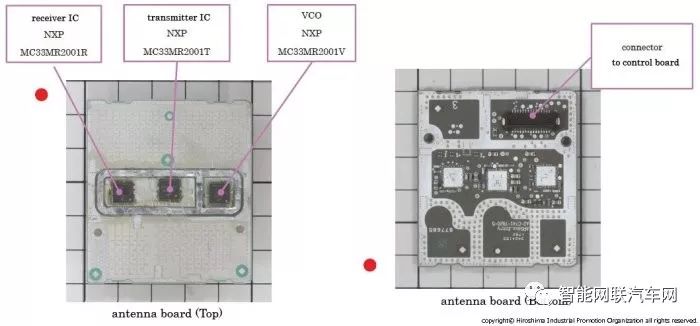
The millimeter-wave receiver IC on the front of the antenna uses Infineon’s BGT24AR4, and the transmitter IC also uses Infineon’s BGT24AT2.
|
|
This radar product consists of four functional blocks.
-
The RF front end for the transmitter (TX) and receiver (RX) semiconductor devices is made using Infineon products. The TX uses BGT24AT2, which integrates the VCO (voltage-controlled oscillator), reducing the number of components.
-
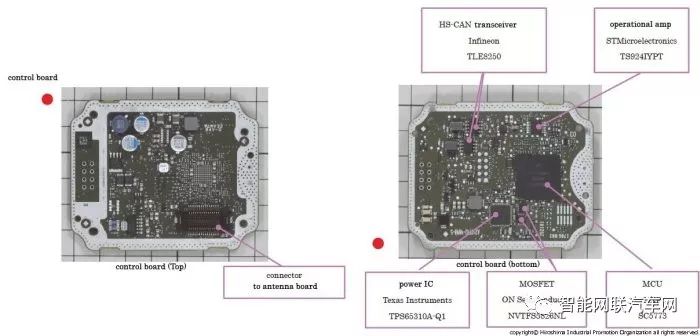
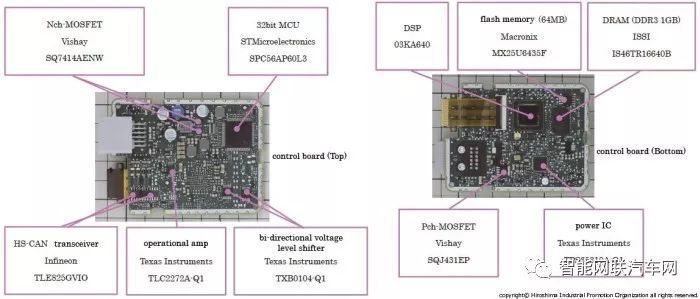
The control block employs a 32-bit microcontroller from NXP for overall system control.
-
The internal power block is primarily composed of power ICs manufactured by Texas Instruments.
-
The communication block forms two CAN communication systems using two High Speed CAN transceiver ICs from Infineon.
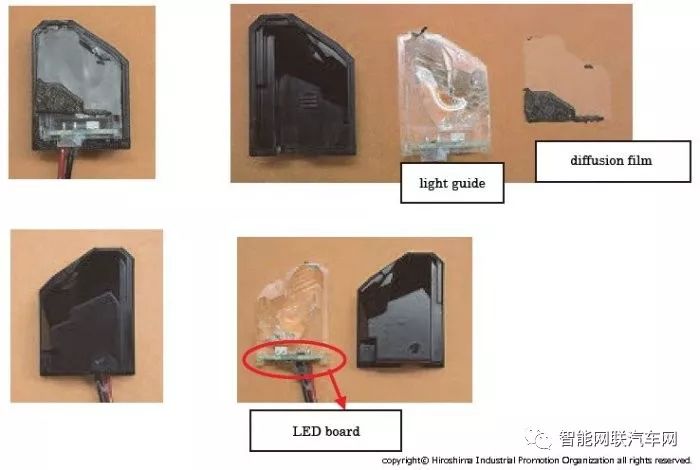
The method used for blind spot display with rear radar involves using one LED to illuminate the display area through a light guide.
|
|
|
Components of the Blind Spot Monitor (BSM) |
Sonar
The C-HR uses four sonar sensors at the front and rear, totaling eight. During low-speed driving (approximately 10 km/h or below) such as parking, the ultrasonic sensors can detect obstacles approaching from the two front corners and the rear of the vehicle. The system displays the distance and position of the obstacles on the multi-information display and notifies the driver through a buzzer.
|
|
|
|
Sonar Sensors in the Front Bumper of C-HR (4 locations in red circles) |
Equipped with 8 sonar sensors (Source: Toyota) |
|
Sonar |
Sonar |
Parking assist module
The ultrasonic sensors used in the C-HR are Valeo’s sensor products. The eight sensors are connected to a device called the “Park Assist Module,” functioning as a gap sonar and reverse sonar alarm for vehicles without parking assist.
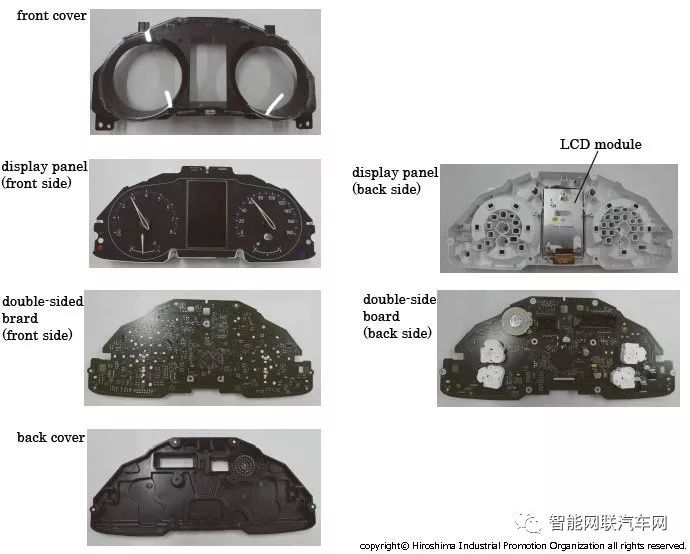
Combination Meter
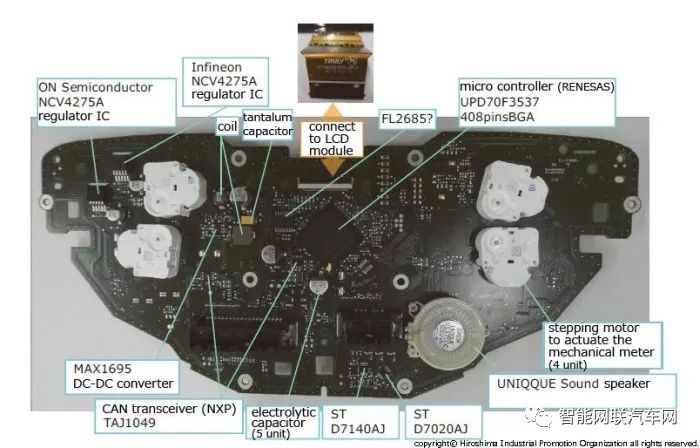
The combination meter of the C-HR mainly consists of mechanical gauges, with a high-precision 4.2-inch TFT color LCD screen in the center. The LCD module is manufactured by Truly from China.
|
|
The mainboard adopts a double-sided packaging mainboard, and the mechanical gauge is also installed on this mainboard, forming a single module.
|
|
The back of the instrument mainboard is equipped with a stepper motor for moving the mechanical gauges, a microcontroller for controlling the LCD module display, other necessary power lines, speakers, etc. The microcontroller for controlling the LCD is a 32-bit microcontroller from Renesas V850 series.
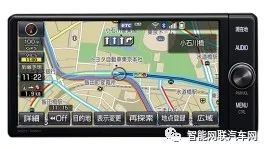
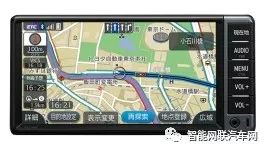
Navigation System
The navigation system of the C-HR now offers three product options, all utilizing Denso’s products (formerly Fujitsu Ten).
|
|
|
|
(Source: Toyota)
The model targeted by this disassembly investigation uses the “Entry-level Navigation 7-inch” product.
|
|
|
|
Navigation Device Appearance |
Navigation Device Internal |
|
|
|
|
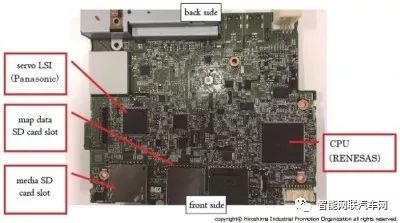
Navigation Control Mainboard (Front) |
Navigation Control Mainboard (Back) |
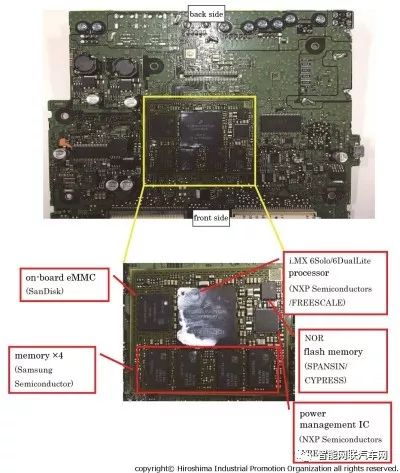
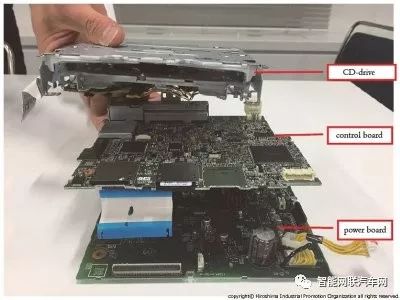
This entry-level navigation product consists of three functional parts: power mainboard, control mainboard, and CD drive. The main difference from the high-end version is that it uses 1Seg playback for Japanese ground digital television and is incompatible with T-Connect.
The main controller for the navigation function uses the NXP iMX6 processor. The iMX6 is mounted on a modular mainboard along with high-speed DDR and flash memory.
Overall
The safety function components of the C-HR are not inferior in functionality compared to the top-end model. Although there is less collaboration with the control system, it includes basic functions such as tracking positioning, lane departure warning, blind spot monitoring, and rear cross traffic alert. Additionally, its functions will expand to other models to reduce costs, and it may become standard equipment for vehicles at the C-HR level in the future.
To join the group, please scan the administrator’s WeChat