
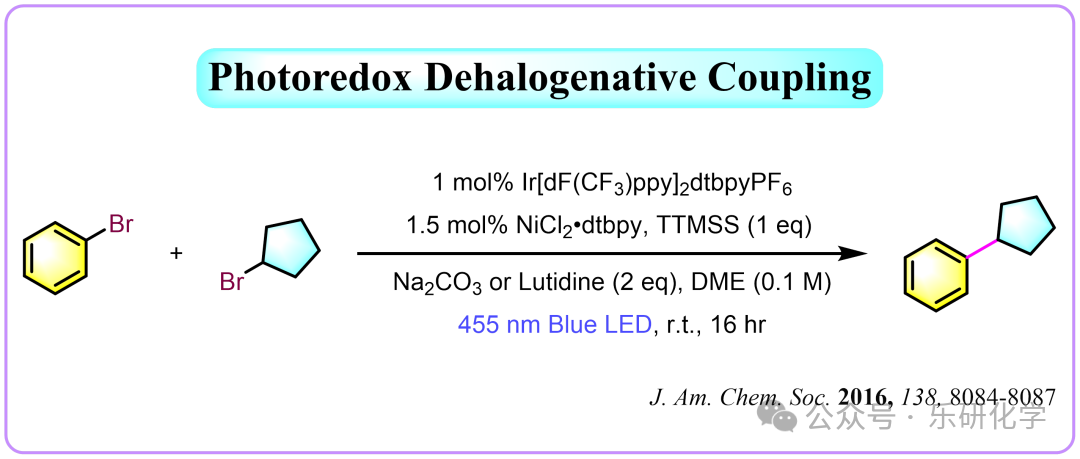
 From J. Am. Chem. Soc.
From J. Am. Chem. Soc.
Hi, everyone! Since 2014, the field of radical chemistry has developed rapidly, establishing various methods for constructing Csp²-Csp³ bonds, achieving remarkable results in practical applications. Among these methods, photocatalytic dehalogenative coupling has remained timeless over the years, becoming a classic method for constructing Csp²-Csp³ bonds in photochemistry:
“Timeless” — Photocatalytic Dehalogenative CouplingMechanism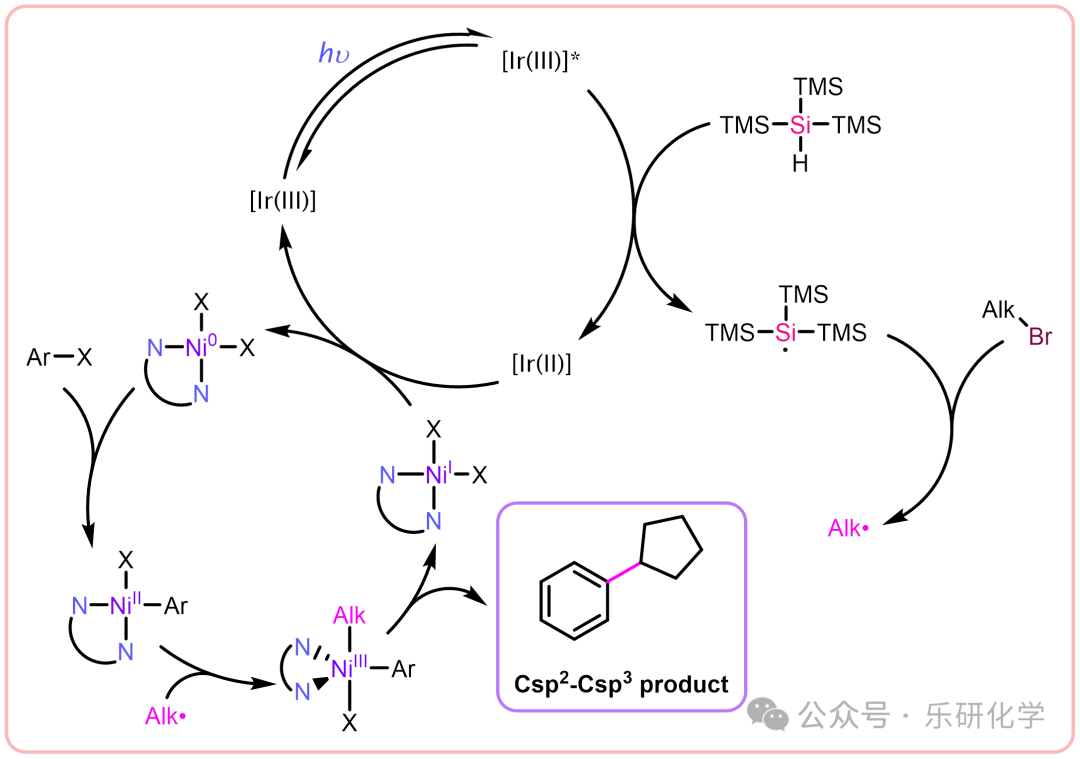 Based on multiple articles and practical illustrationsSubstrate Expansion
Based on multiple articles and practical illustrationsSubstrate Expansion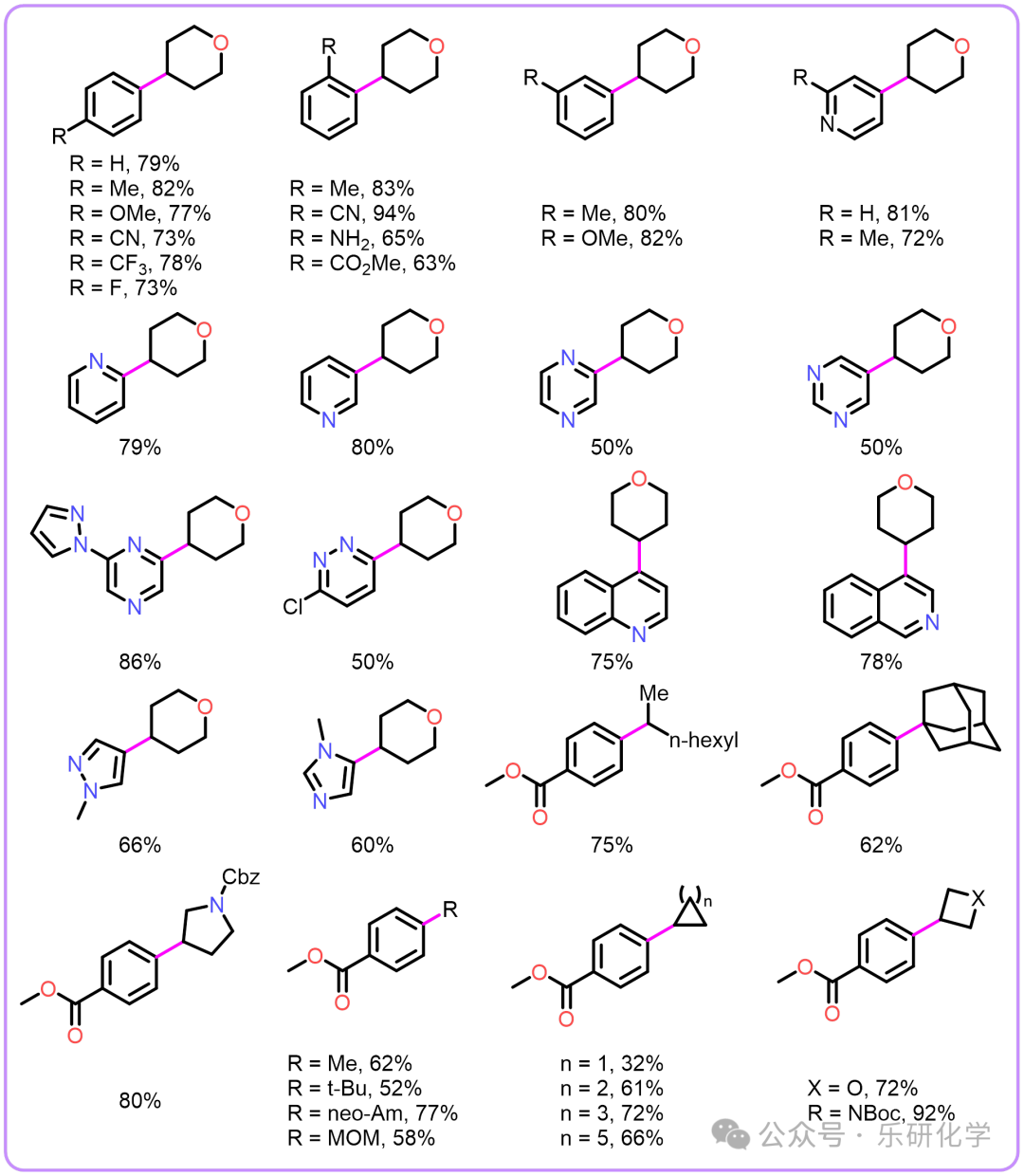 Highlights【1】This method uses readily available and stable aryl bromides and alkyl bromides as starting materials, successfully achieving Csp²-Csp³ coupling under photocatalysis;【2】The method exhibits good functional group tolerance, accommodating esters, nitriles, alkoxides, ethers, etc., but is intolerant to acyl, isoxazole, aliphatic amines, especially benzyl amines;【3】The method has a wide substrate scope, including but not limited to aromatic rings such as benzene, pyridine, pyrimidine, pyrazine, dazine, quinoline, isoquinoline, etc.;【4】The method uses TTMSS in the reaction, which produces some special MS that need attention;
Highlights【1】This method uses readily available and stable aryl bromides and alkyl bromides as starting materials, successfully achieving Csp²-Csp³ coupling under photocatalysis;【2】The method exhibits good functional group tolerance, accommodating esters, nitriles, alkoxides, ethers, etc., but is intolerant to acyl, isoxazole, aliphatic amines, especially benzyl amines;【3】The method has a wide substrate scope, including but not limited to aromatic rings such as benzene, pyridine, pyrimidine, pyrazine, dazine, quinoline, isoquinoline, etc.;【4】The method uses TTMSS in the reaction, which produces some special MS that need attention;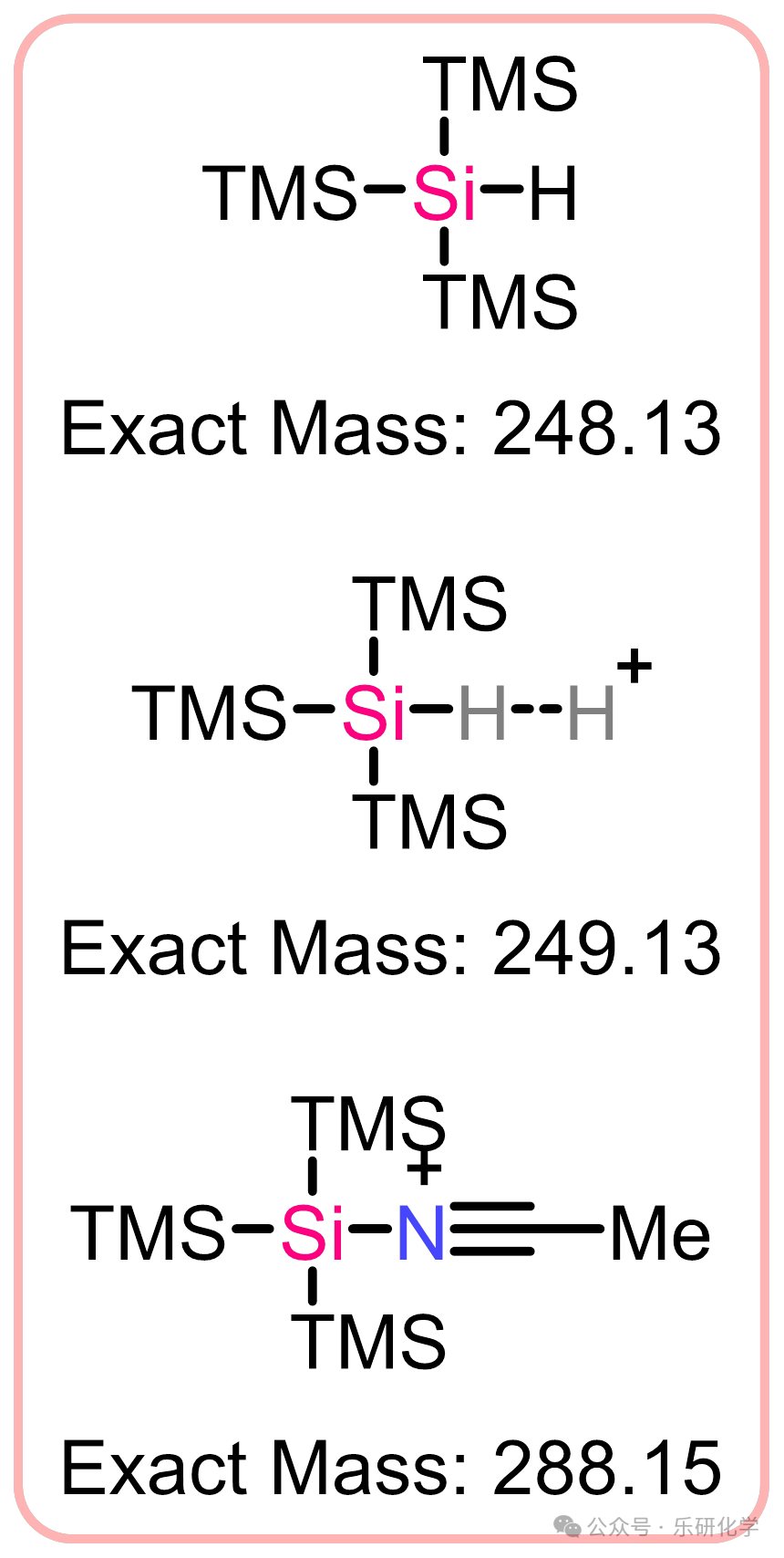
【5】The photocatalyst Ir[dF(CF₃)ppy]₂dtbpyPF₆【CAS#870987-63-6】 is a commercial reagent, readily available from Leyan, and similar iridium photocatalysts are in stock for easy selection..
 ReferencesSilyl Radical Activation of Alkyl Halides in Metallaphotoredox Catalysis: A Unique Pathway for Cross-Electrophile CouplingPatricia Zhang, Chi “Chip” Le, David W. C. MacMillanJ. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 26, 8084–8087.DOI : 10.1021/jacs.6b04818
ReferencesSilyl Radical Activation of Alkyl Halides in Metallaphotoredox Catalysis: A Unique Pathway for Cross-Electrophile CouplingPatricia Zhang, Chi “Chip” Le, David W. C. MacMillanJ. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 26, 8084–8087.DOI : 10.1021/jacs.6b04818