Click the blue text to follow us

1. What is the Rising Star of Network Circles: SD-WAN?
SD (Software Defined) originated from SDN (Software Defined Network). Before the emergence of SDN technology, network device manufacturers operated in a relatively closed ecosystem, pursuing a high degree of coupling between hardware and software, essentially creating a “black box”. The advent of SDN is a step towards “white box” evolution, abstracting the network into data, control, and application layers, separating modules from previously coupled hardware devices. In this new architecture, the data layer is responsible for forwarding, still completed by switches; the control layer manages and configures devices in the data layer, realized by the SDN controller. SDN switches, through network virtualization technology, mask the physical differences of underlying hardware and support standard open interfaces to receive configuration commands from the SDN controller, executing different operations based on the configuration.
In addition to SDN, various concepts such as SDS, SDP, and SDV have emerged in different fields, giving rise to many industries and new opportunities. In our work, these have already become popular terms. The editor has listed some for reference:
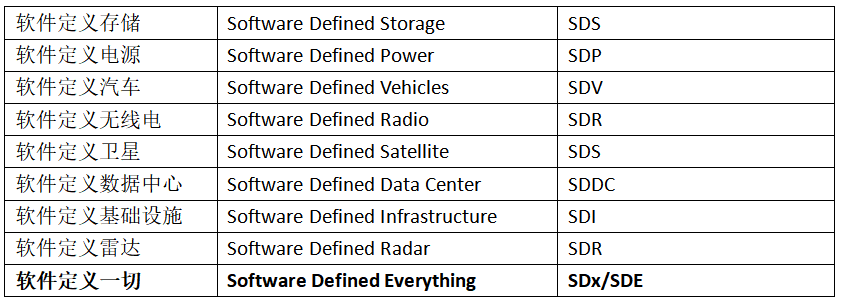
Following similar logic, SD-WAN can be understood as a software technology for WAN, meaning SDx is a technology, and WAN is an application. Introducing SDx technology into WAN applications gives birth to SD-WAN, Software Defined Wide Area Network. Literally, SD-WAN is SD (Software Defined) WAN, so SD-WAN is primarily WAN and secondarily software-defined WAN.
2. Traditional Enterprise Networking vs. SD-WAN
1. Challenges of Traditional Enterprise Networking
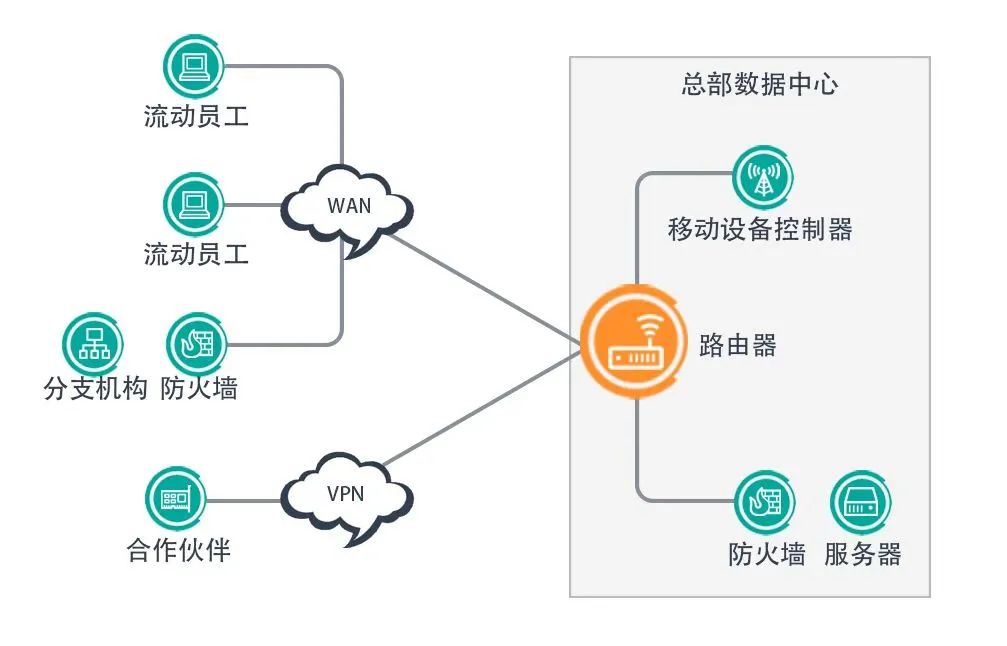
It is well known that networks are crucial for enterprises. Almost all enterprise applications, including email, file sharing, web applications, etc., are typically deployed in the headquarters’ data center and connected to branch offices via leased operator lines. Enterprises often face challenges such as long deployment cycles, vendor lock-in, high costs of dedicated lines, and inflexible control capabilities.
Of course, some enterprise networks establish VPN tunnels manually over the public Internet for connectivity. However, with the development of network-based applications, various VoIP, video conferencing, streaming media, virtual applications, and virtual desktops require low latency and high bandwidth. The transmission quality of VPNs established over the public Internet cannot meet enterprise needs. To ensure application availability, WAN bandwidth must be expanded, directly leading to a significant increase in costs.
2. Advantages of SD-WAN Networks

Flexible Access: SD-WAN retains the flexible access methods of WAN, supporting various access methods such as 4G, 5G, Internet, and MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching) dedicated lines;
Separation of Software and Hardware: Implement CPE (Customer Premise Equipment) in physical or virtual form on general hardware; promote hardware platformization and standardization through the separation of software and hardware;
Traffic Optimization: Improve QoS (Quality of Service, such as speed, latency, packet loss rate, etc.) through load balancing and traffic scheduling, enhancing service quality while reducing overall usage costs;
Security: Integrate security functions such as Firewall, VPN, IPS, and WAF into CPE through virtualization, providing security assurance for business;
Zero-Touch Deployment: No configuration or only minimal configuration is required, enabling remote deployment of branch office devices.
3. How to Solve the Challenges of Enterprise Networking?
The National Supercomputing Center in Jinan (hereinafter referred to as “Jinan Supercomputing”) supports various forms of network access as a public computing power output platform, with the main goal of better serving users. Currently, Jinan Supercomputing supports the following seven methods:
1. Offline access through VPN, suitable for individual user scenarios;
2. Access through network proxy nodes, suitable for computing power agency scenarios;
3. Access through hybrid or distributed cloud, suitable for computing resource sharing scenarios;
4. Direct access through dedicated lines, suitable for users requiring high network security and reliability;
5. Access through supercomputing Internet city-wide dedicated access points, suitable for users in Shandong Province;
6. Access through low-latency optical networks, suitable for access scenarios involving other computing centers and supercomputing sub-centers;
7. Access through the Shanhua Supercomputing Platform’s SD-WAN network service, suitable for users requiring high network security and reliability.
It can be seen that both direct access through dedicated lines and SD-WAN can meet enterprise users’ requirements for network security and reliability, but SD-WAN has stronger universality, allowing for rapid access in minutes online and also supporting individual user application access scenarios. The SD-WAN access service provided by Jinan Supercomputing has several advantages:
1) Comprehensive coverage of enterprise WAN networking needs. Utilize cloud terminals to help enterprise users connect to the “Supercomputing Internet” backbone network with one click, building a hybrid cloud network that achieves rapid interconnection between traditional data centers, supercomputing centers, intelligent computing centers, and branch offices, creating a secure, reliable, controllable, and intelligent exclusive wide area network;
2) Seamless integration with other cloud service products of the Shanhua Supercomputing Cloud Platform. Provide enterprise users with integrated cloud-network solutions, helping users quickly establish network connections to the cloud, while offering solutions covering network, HPC, AI, resources, and applications, including remote disaster recovery and branch cloud desktop services;
3) Reduce access costs for enterprise users. Help users access multiple Internet export connections covering 16 cities in Shandong, providing high-quality network connection services. Provide users with dynamic multi-line Internet export connections, optimizing routing path selection, ensuring high availability of user business access when one export is congested or fails, automatically identifying failures and reselecting exports;
4) Empower enterprise users with intelligent network scheduling capabilities and an extremely simplified management model. Provide an excellent user experience through online usage. Offer self-service to users with flexible billing based on bandwidth demand, allowing dynamic adjustments according to business bandwidth needs and real-time network conditions, achieving load balancing and access path optimization for backbone network traffic, ensuring maximum link utilization; the management platform provides graphical network topology for one-stop design, management, and monitoring of network resources; cloud terminals enable zero-configuration access to the Shanhua backbone network, ready to use, with high usability.
3. Application Scenarios
Scenario 1:
Hybrid Cloud Networking, One-Click Access to Shanhua Public Cloud
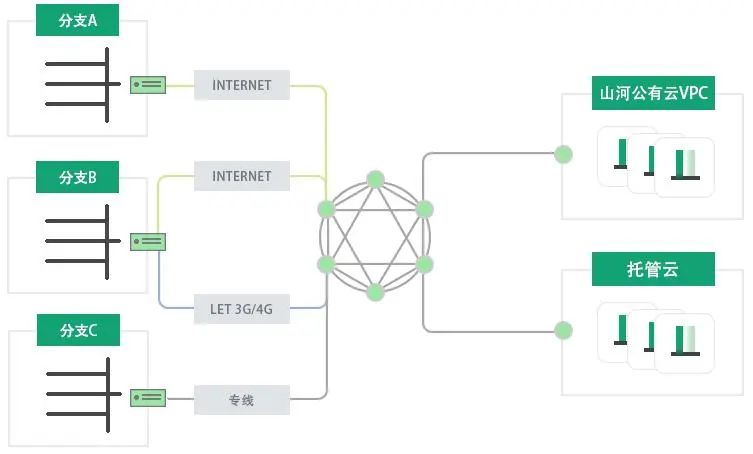
Chain enterprises or group enterprises often face the situation of numerous branch offices and scattered geographical locations. Cross-regional networking often uses MPLS dedicated lines, which are costly and inflexible, with low utilization and complex maintenance, making it difficult to ensure access quality.
By using Shanhua SD-WAN cloud services, enterprises can quickly establish exclusive network connections relying on Shanhua cloud backbone network resources. Branch offices can also quickly connect through cloud terminals, significantly improving networking efficiency and greatly reducing costs. Shanhua SD-WAN cloud services provide high-quality multi-line bandwidth, supporting high concurrency and high throughput application access needs. Cloud terminals support various modes such as dedicated lines, Internet, and 4G/5G, unrestricted by the original network environment, ensuring convenient and quick access for the “last mile”, helping enterprises easily address branch access difficulties.
Scenario 2:
Build a High-Quality Network for Remote Disaster Recovery,Flexible Bandwidth Adjustment
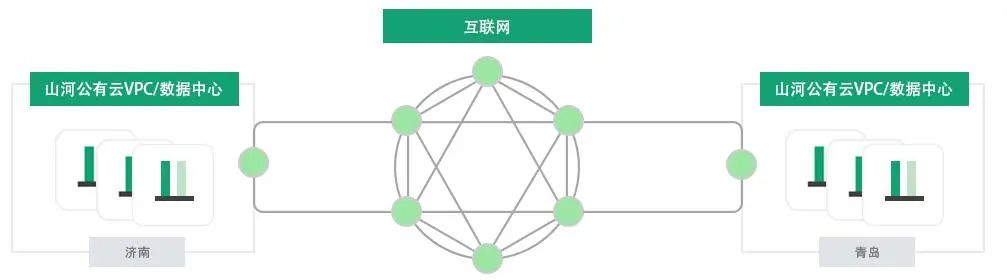
The security of core data and the continuity of business are vital to enterprise operations and development. Data disaster recovery is becoming increasingly important in enterprise information construction. Currently, most enterprises adopt traditional backup methods for data disaster recovery, using a single operator for city-level or remote disaster recovery networking. Since a single operator only provides a single exit, when high concurrent access occurs, access from other operators may cause delays or even network congestion.
With the help of Shanhua SD-WAN cloud services, a multi-line network connection can be established with remote data disaster recovery centers, allowing user access to be direct, without congestion and delay. At the same time, Shanhua SD-WAN users can flexibly adjust network bandwidth, dynamically adjusting bandwidth based on the volume of backup data during non-real-time data backups, making bandwidth usage more flexible, saving bandwidth costs, and ensuring high availability of the disaster recovery network.
Scenario 3:
Desktop Cloud Networking, Headquarters and Branches Collaborating
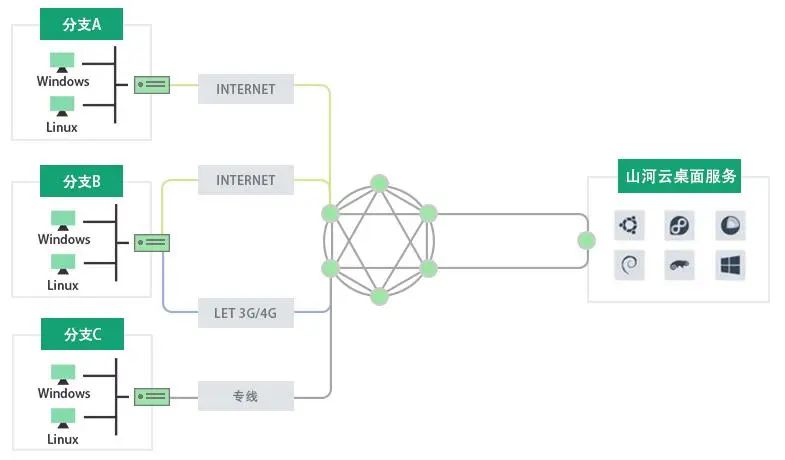
Shanhua Desktop Cloud is a new generation enterprise-level office solution for users, suitable for enterprises, training rooms in universities, and other cloud desktop business scenarios. Traditional remote desktop cloud access has high requirements for network transmission speed and security, facing issues such as long implementation cycles, high maintenance difficulties, and low data security when using dedicated lines, IPSec, or VPN for networking.
Through Shanhua SD-WAN cloud services, enterprises or university users can access the Jinan Supercomputing Cloud Service network, unrestricted by environmental limitations, accessing desktop clouds to meet daily office and teaching training needs. At the same time, Shanhua SD-WAN provides users with a one-stop management platform and graphical network topology interface, allowing users to design and manage networking independently, significantly reducing the difficulty of managing each desktop cloud branch.
◆ ◆ ◆ ◆
4. Practical Networking Scenarios for SD-WAN Applications
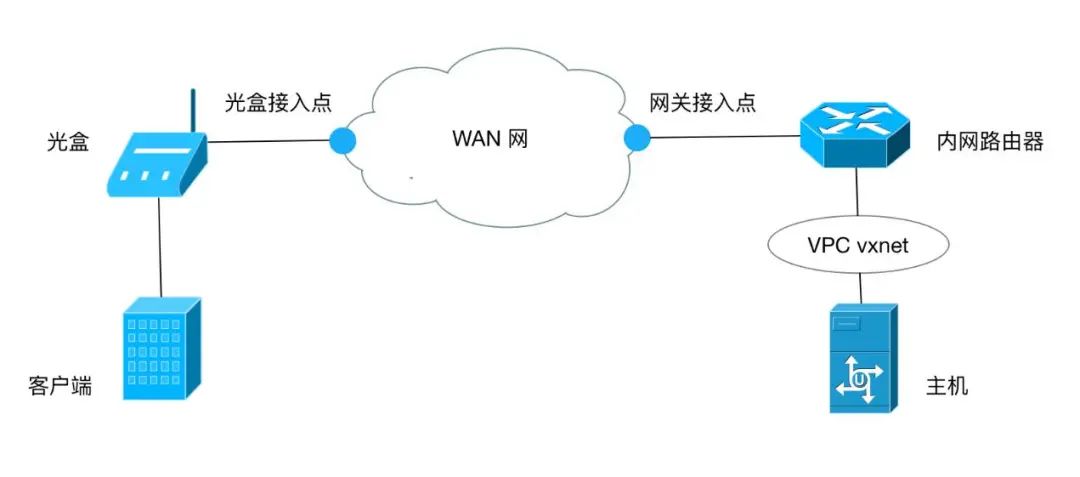
The image above shows the network topology to be constructed for three common application scenarios. The optical box in the image is the network terminal device (CPE) placed in the user-side machine room, training room, or office. User terminals can directly connect to the CPE optical box and perform relevant settings on the Shanhua cloud platform to use Shanhua cloud platform hosts or other resources through the SD-WAN network. Below are the steps to construct the topology shown in the image:
First, log in to the Shanhua platform and register an account, click on the “Products and Services” navigation in the upper left corner to select the SD-WAN service.
Step 1: Apply for a Physical Optical Box
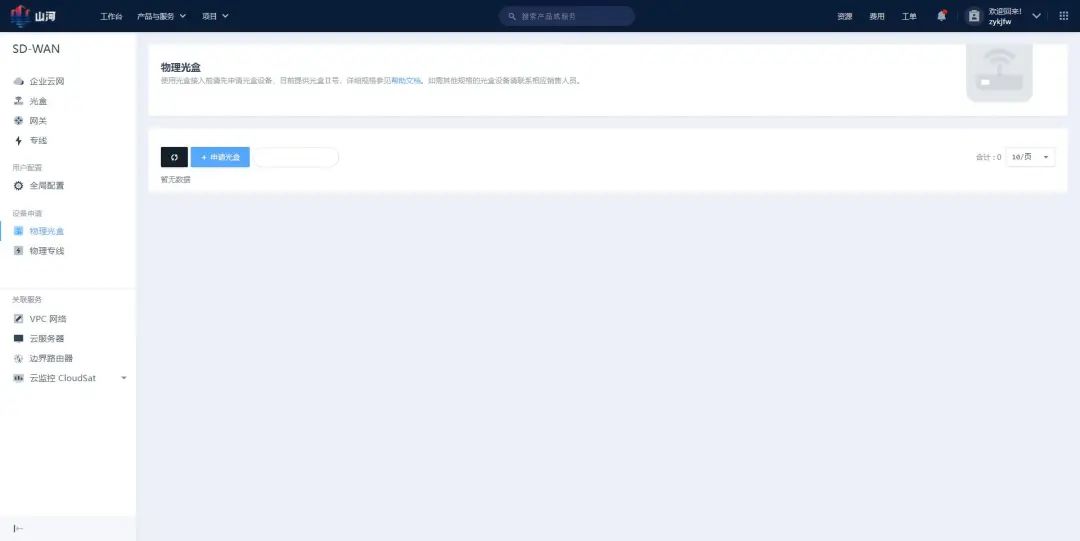
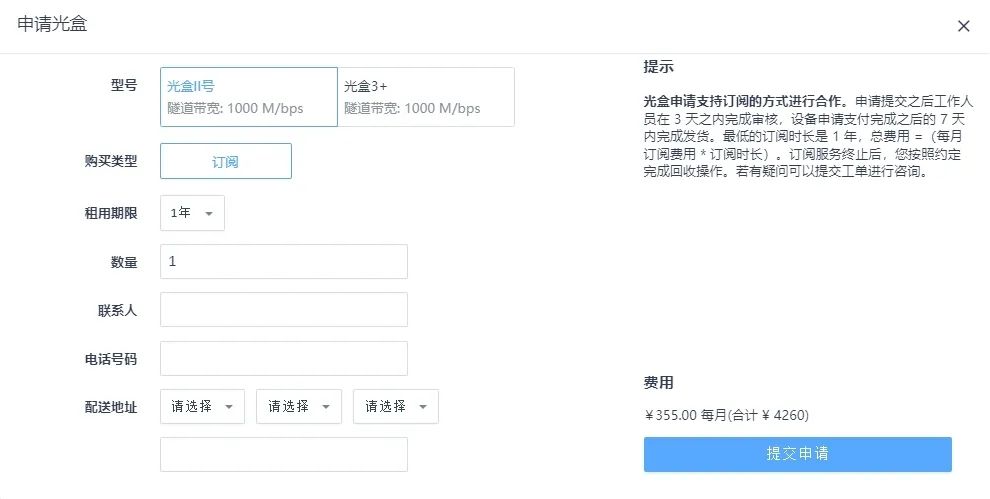
Fill in the optical box application information and submit it. Two types of optical boxes are supported, with slightly different corresponding port numbers and bandwidth. The device will be mailed to the specified address.
Step 2: Create a WAN Network
Enter the Web console, click the “Create Enterprise Cloud Network” button in the right area, and enter a name to create a dedicated WAN network.
Step 3: Create Optical Box Access Point
The user plugs the received optical box device into power and connects the external network link to the optical box WAN port. Then log in to the WEB console, click on “Optical Box” in the left navigation bar, and then click “Create Access Point” in the right area, select the optical box type and fill in the corresponding information. The serial number can be found on the back of the optical box.
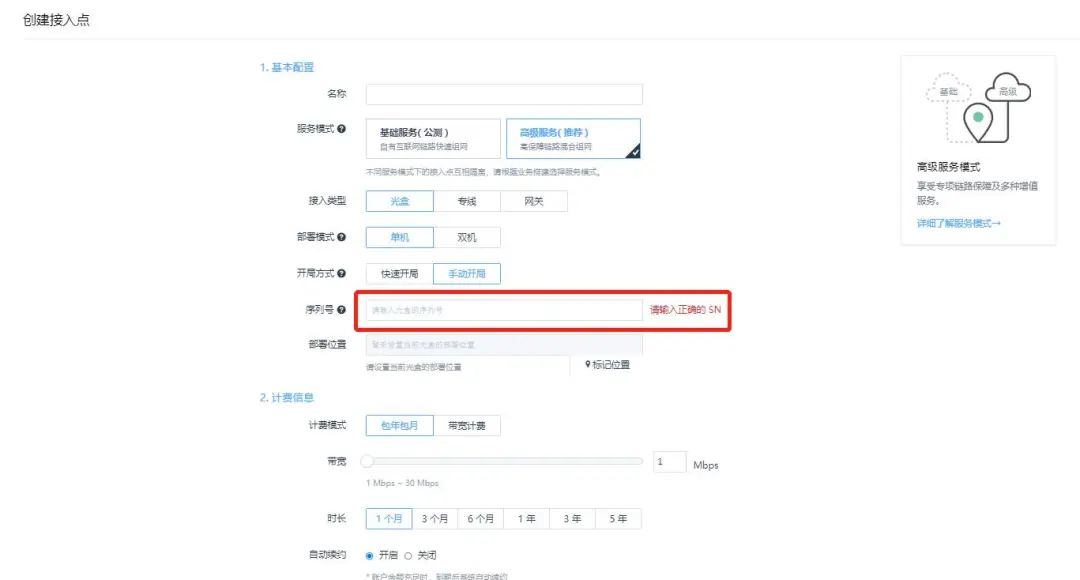
Step 4: Configure the Optical Box
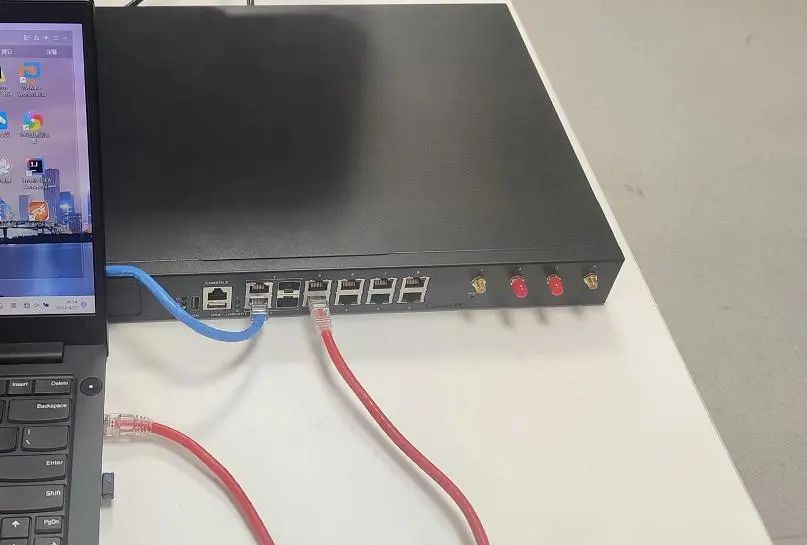
The image below shows the SD-WAN box provided to customers.

In the actual environment, the following connections are made, demonstrating the environment through a user’s laptop connecting to the CPE optical box:
One end of the blue line connects to the LAN port of the office or home network, and the other end connects to port 0 of the box;
One end of the red line connects to the LAN port of the computer, and the other end connects to port 2 of the box.

Click on the created access point to enter the details page for optical box configuration.
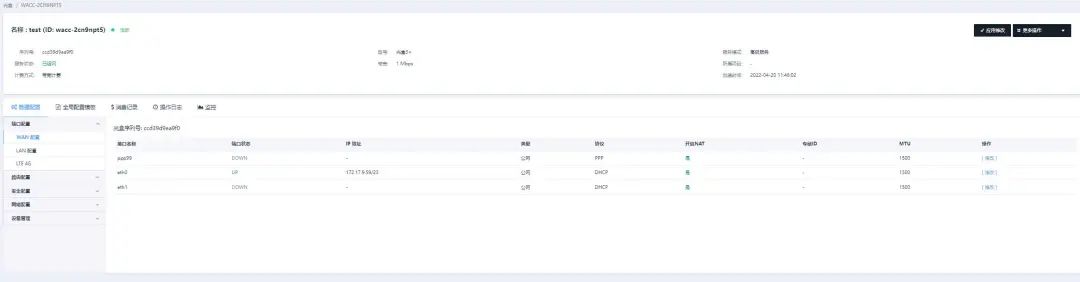
Typically, configure the LAN port, set the LAN segment and gateway address for the optical box, and start the DHCP service.
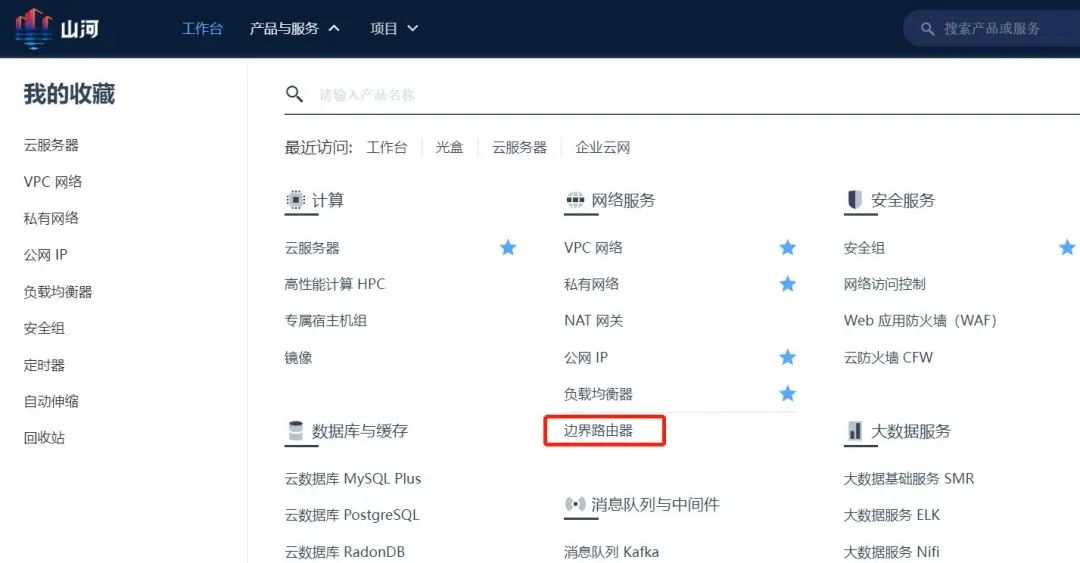
Step 5: Create a Border Router
Log in to the WEB console, search for “Border Router” in the top navigation bar, enter the details page, and click “Create” to create the Border Router.
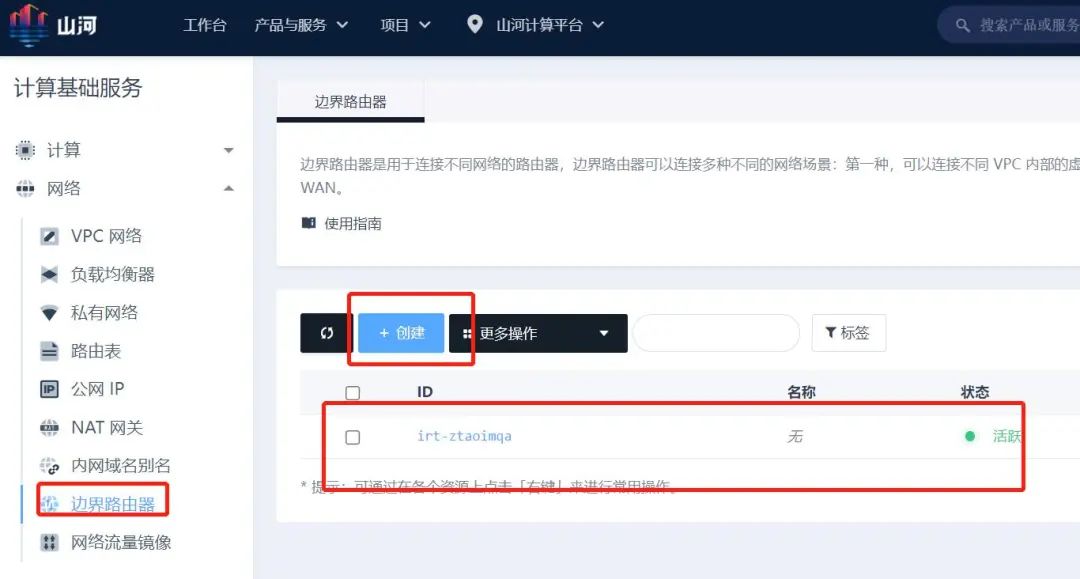
Step 6: Associate the VPC Private Network
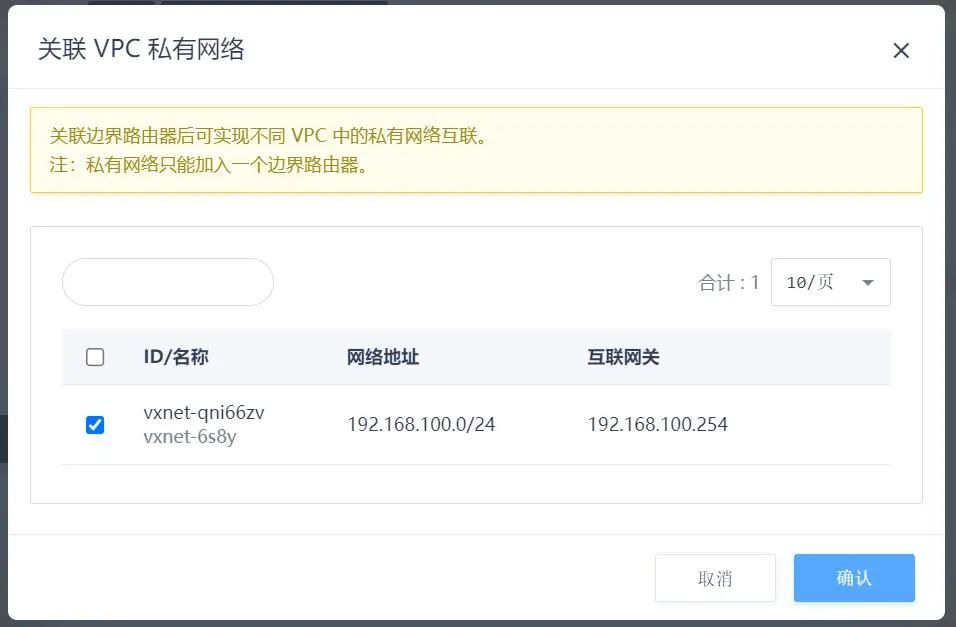
with the Border Router
Click on the created Border Router to enter its details page, then click “Associate VPC Private Network,” select the private network where the cloud server is located to associate with the border router.
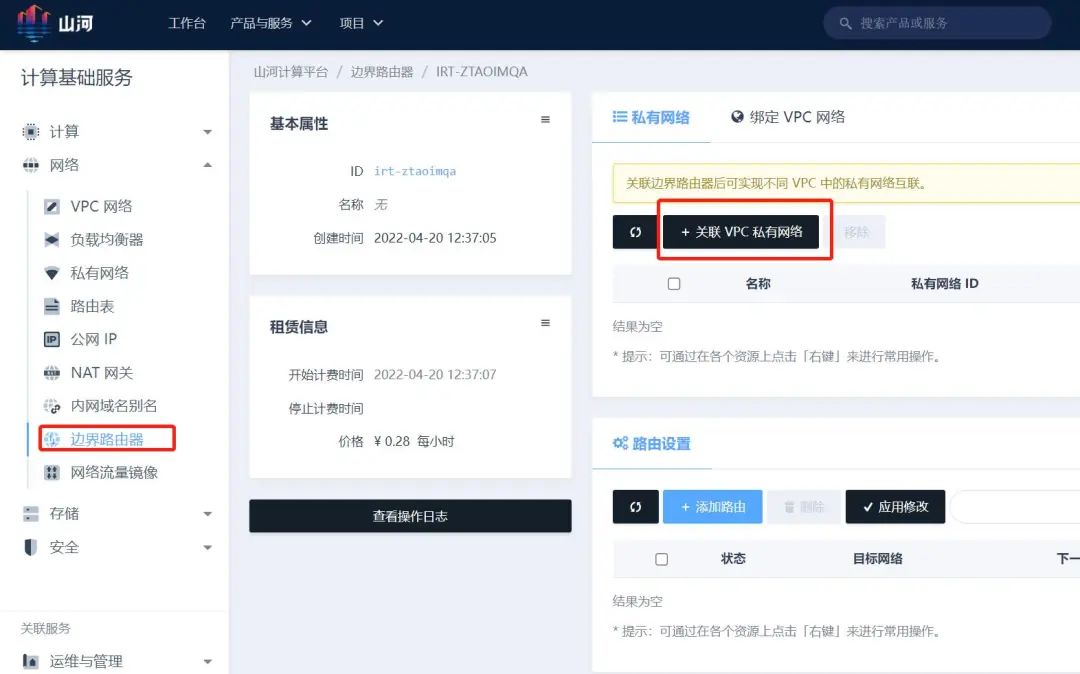
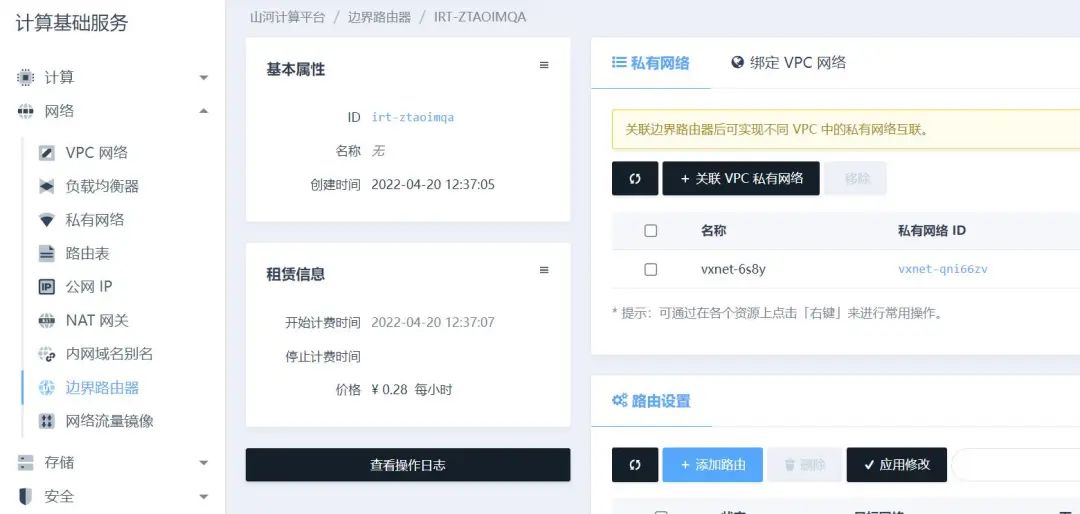
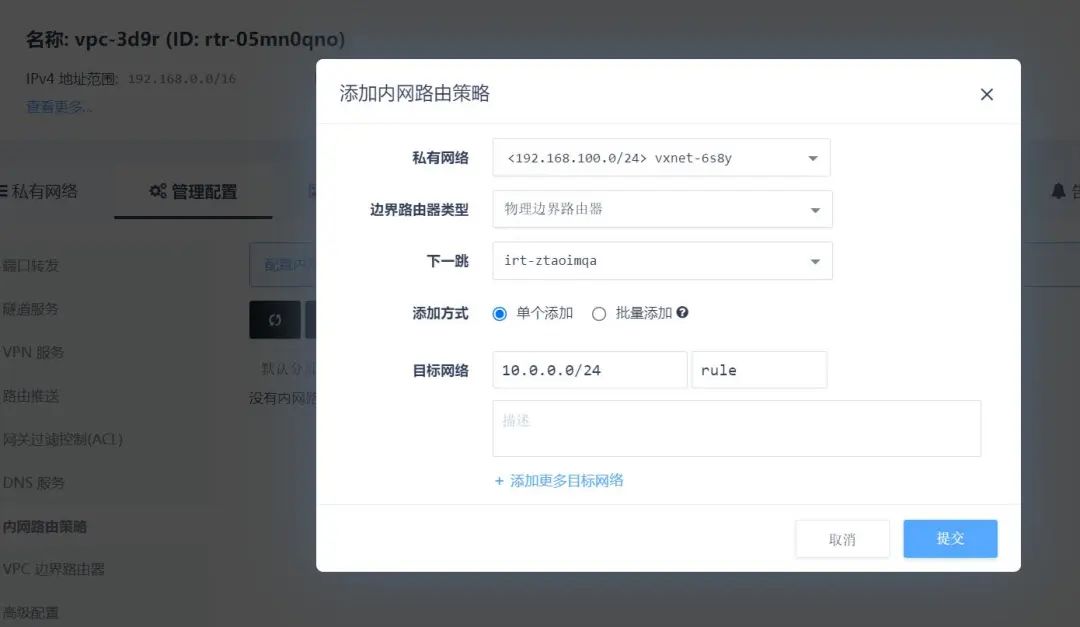
Step 7: Configure Internal Routing Policy for the VPC Private Network
On the border router details page, click on routing settings to enter the internal routing policy configuration page and set the internal routing policy.
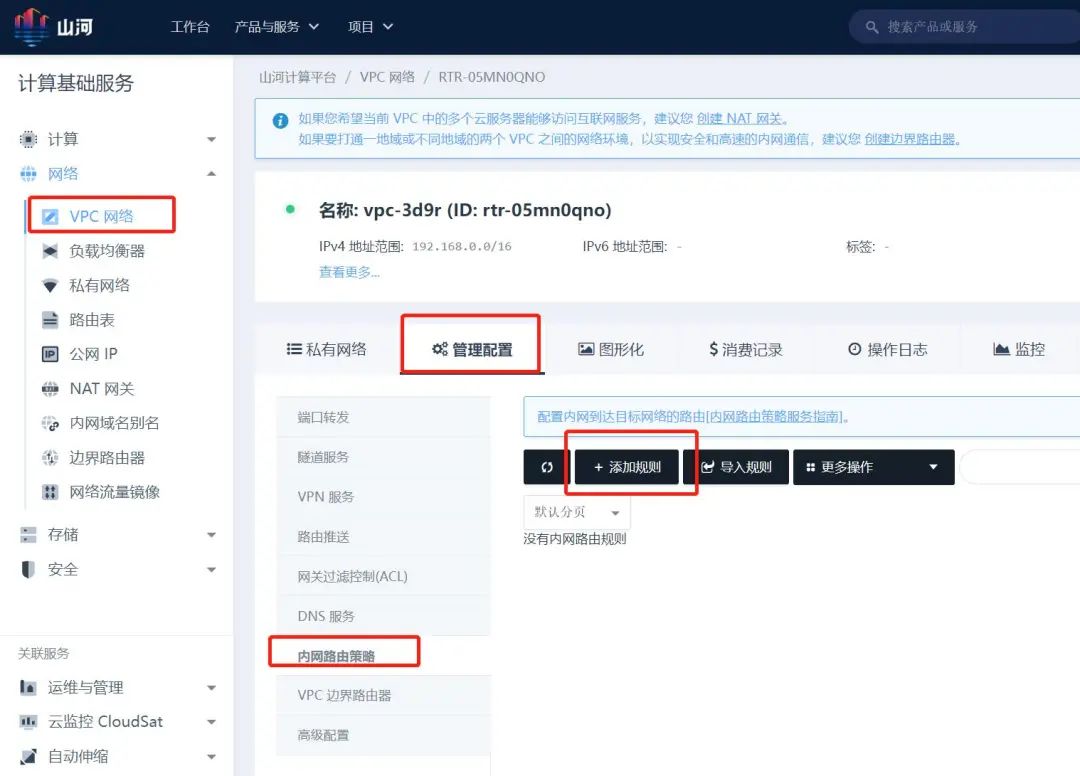
Step 8: Create Gateway Access Point
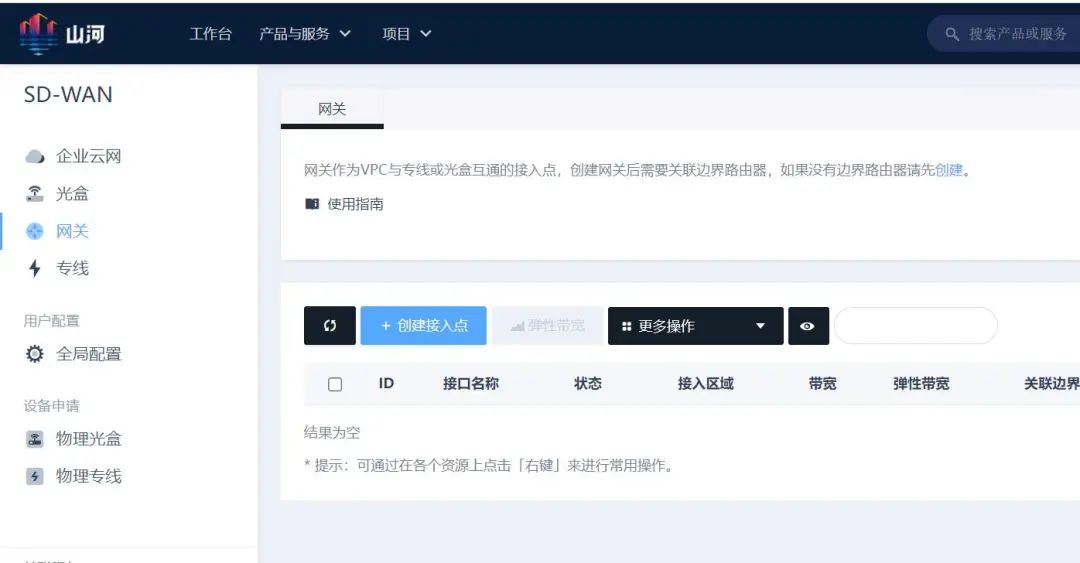
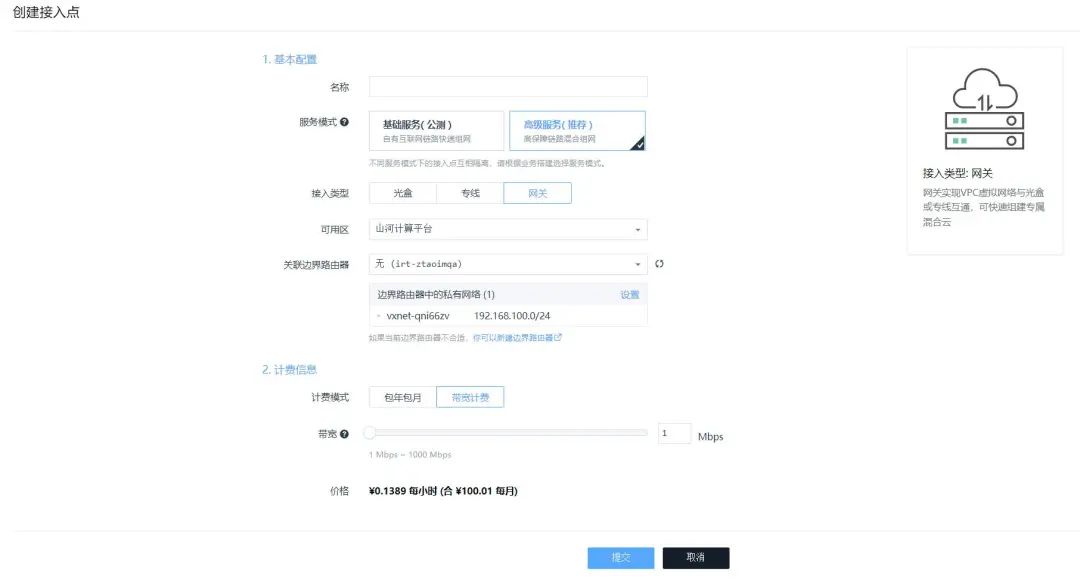
Log in to the WEB console, search for “Enterprise Cloud Network” in the top navigation bar, click on “Gateway” in the left navigation bar, then click “Create Access Point” in the right area, select the “Gateway” type, and configure the associated border router, then fill in the corresponding information to create the gateway access point.
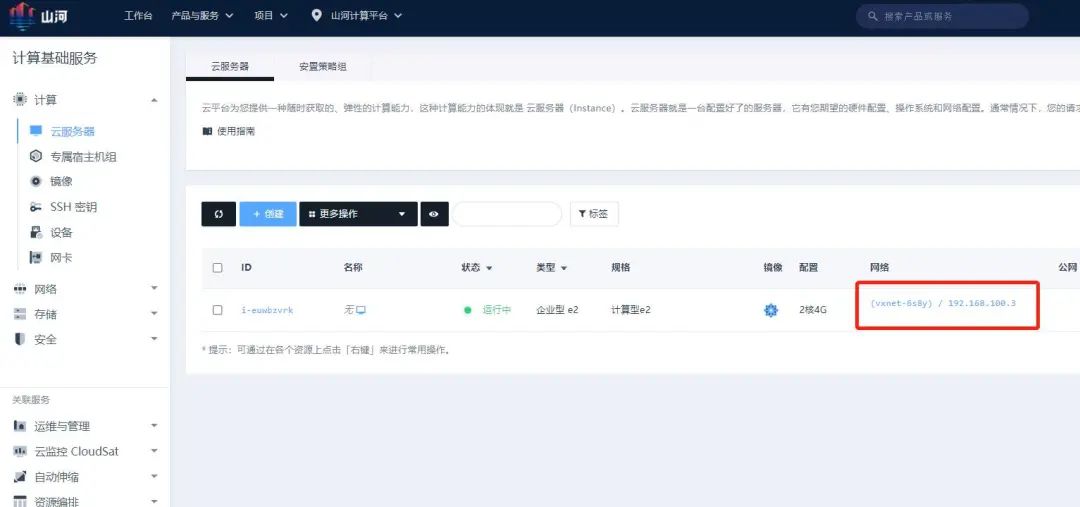
Step 9: Test Connection to Cloud Host
On the cloud server page, find the server’s network address and use an SSH connection tool to connect to the cloud server’s IP address.
5. Conclusion
The SD-WAN service provided by the Shanhua Supercomputing Cloud Platform has the capability to connect “cloud, network, and end”. Jinan Supercomputing is continuously enhancing the foundational capabilities of SD-WAN and leveraging this capability to support more services, including building hybrid cloud networks, integrating edge computing business scenarios, WAN access, WAN networking, and supercomputing Internet. In the future, the Shanhua platform of Jinan Supercomputing will present a “full-dimensional” cloud map: full-stack (from IaaS, PaaS to SaaS, meeting customers’ one-stop cloud business needs), full-state (from public cloud, managed cloud to private cloud, meeting different cloud environment needs), full-domain (linking cloud, network, edge, and end, meeting extreme scenario needs in vertical fields).
As an important technology for transforming enterprise networks, SD-WAN involves various technologies and applications, including deployment methods under multi-cloud networks, etc. This article only lists some basic knowledge related to SD-WAN. As networks evolve and SD-WAN is applied on a large scale, new problems and demands will certainly arise, leading to the emergence of new technologies and products. In 2022, Jinan Supercomputing will launch network access services based on the SRv6+EVPN technology stack, stay tuned.
Some images are sourced from the internet, and copyrights belong to the original authors.

Scan the code to follow us
“National Supercomputing Center in Jinan”
WeChat Official Account!