A chip is a type of integrated circuit that integrates a large number of electronic components and circuits on a piece of semiconductor material (usually silicon), enabling complex functions such as data processing, storage, control, and communication.
Devices such as mobile phones, computers, home appliances, and cars rely on chips to process data, execute algorithms, and run software programs.
Data Processing refers to the process of collecting, manipulating, transforming, calculating, and analyzing data; electronic devices rely on chips for data processing.
Data Storage, memory chips in chips are used to store data and programs, allowing devices to read and write data.
Control and Execution, the circuits and logic components in chips can control and execute various operations, managing device operations.
Communication and Networking, chips are responsible for processing communication protocols and data transmission, supporting communication, calls, and network connections between devices.
There are various types of chips, each with different functions and applications. Here are some common types of chips:
Microprocessor Chips, also known as Central Processing Units (CPUs), primarily execute arithmetic operations, logic operations, data transfers, and control flow instructions.
Memory Chips are used for data storage and retrieval, such as Random Access Memory (RAM) and Read-Only Memory (ROM).
Graphics Processing Chips are specialized for processing graphics and images, used for accelerating graphics rendering, image processing, and computational tasks.
Communication Chips are used to support communication and connectivity between devices, enabling data transmission, network communication, and device interconnection.
Sensor Chips are used to sense and measure physical quantities in the environment, such as temperature, humidity, pressure, light, and acceleration.
Power Management Chips are used to manage and control the power supply and energy consumption of devices, achieving power optimization, power switching, and charging control.
Security Chips provide data security and encryption functions, enabling data encryption, digital signatures, secure storage, and identity verification.
Fingerprint Recognition Chips are used to capture and identify fingerprint information, enabling fingerprint collection, recognition, and biometric identification.
Computers and Servers: Chips are the core components of computers and servers, including microprocessor chips, memory chips, and graphics processing chips.
Mobile Phones and Devices: Mobile phones and devices use processor chips, communication chips, sensor chips, and display control chips.
Automobiles and Transportation: Such as engine management chips, in-car entertainment system chips, safety control chips, and driver assistance system chips.
Communication and Networking Devices: Network routers, switches, modems, and fiber optic devices all use chips for data transmission.
Electronic Products: Such as TVs, audio devices, cameras, and game consoles, all use chips to achieve different functions.
Internet of Things Devices: Such as smart homes, smart cities, and industrial automation, chips are used to achieve sensing, connectivity, and control functions.
Industrial Automation: Industrial control systems use chips to achieve process monitoring, data collection, and automated control functions.
Transistors are one of the most basic components in chips, used for amplifying, switching, and controlling current.
Capacitors are primarily used to store electrical charge, commonly used for filtering, coupling, and energy storage.
Resistors are used to control the flow of current, limiting current, voltage division, and stabilizing circuits.
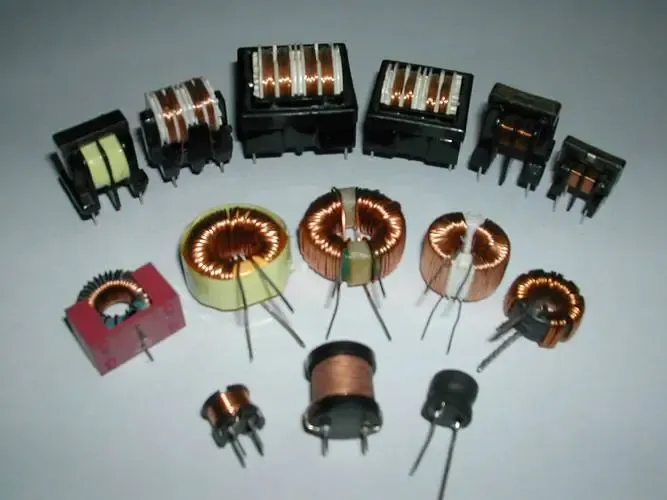
Inductors store electrical energy by generating a magnetic field while resisting sudden changes in current.
Diodes control the direction of current, allowing current to flow in one direction.
Integrated Circuits integrate a large number of transistors, resistors, capacitors, and other components into a single chip.
Functional Components, such as sensor components, memory components, clock components, input-output interface components, transformers, etc.
6. Questions Related to Chips
What Are the Major Manufacturers of Chips? Some well-known chip manufacturers include Intel, AMD, NVIDIA, TSMC, and Samsung Electronics, which play important roles in various fields and markets.
Why Are Smaller Chips Better? Smaller chips have higher integration, lower power consumption, faster speeds, lower costs, and wider applications (especially in fields with high size and weight requirements, such as mobile devices, portable devices, and embedded systems). However, smaller chips require higher manufacturing processes and materials, and managing heat dissipation and signal interference is more complex.
Why Do Chips Need Heat Dissipation? Chips generate heat during operation; if the heat cannot be effectively dissipated, it can lead to increased chip temperature, affecting performance, reliability, and lifespan. For most commercial chips, the common operating temperature range is typically between -40°C and +85°C, which is considered acceptable for general industrial and commercial applications.
What Is the Lifecycle of a Chip? The lifecycle of a chip refers to the entire process from design, manufacturing, and sales to decommissioning, covering all stages and corresponding activities. Generally, the lifecycle of a chip can range from a few years to over a decade, and the chip industry is in a state of rapid change and continuous advancement, with older chips being replaced by more advanced technologies.
Image and text are adapted from Basic Knowledge Encyclopedia
Disclaimer: All reproductions are for sharing purposes only and not for commercial use; copyright belongs to the original author. If there are copyright issues, please contact the editor for removal. Thank you!


#Little Bunny Health Exchange# We look forward to your attention and sharing, so that we can grow together.