
Click the above to follow us!
MQTT
MQTT is a Machine-to-Machine (M2M)/ Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity protocol. It is an extremely lightweight publish/subscribe messaging transport protocol. It is well-suited for remote connections that require small code footprint or have very precious network bandwidth, designed specifically for constrained devices and low-bandwidth, high-latency, or unreliable networks. MQTT is widely used in fields such as IoT, mobile internet, smart hardware, vehicle networking, and electric energy.
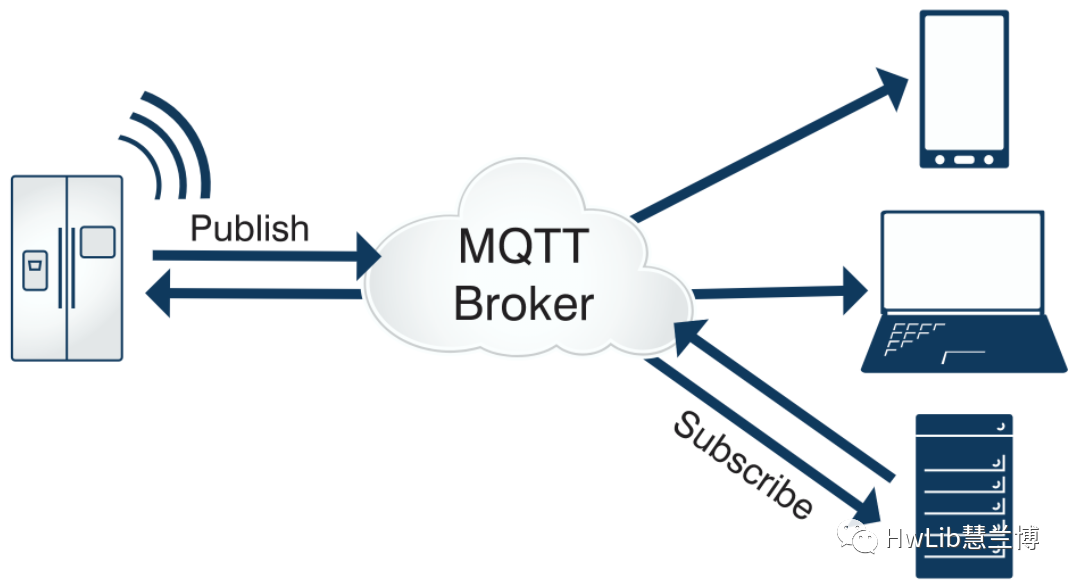
Figure 1: MQTT Publish/Subscribe Model
WINCC and MQTT
WinCC has supported the MQTT protocol since version 7.5. The introduction of the MQTT protocol provides a good interface for remote data collection. However, current support is limited, only allowing for reading, not writing. Through the MQTT protocol, WinCC can send data to public clouds such as SIEMENS MindSphere, Amazon, and Microsoft Azure with just a few simple configuration steps. Additionally, we can also set up our own MQTT Broker to receive and forward data.
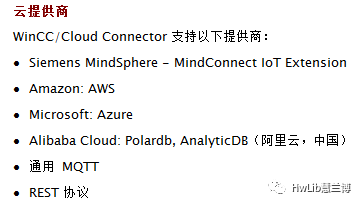
Figure 2: Supported Cloud Service Providers by WinCC
MQTT Broker
The main responsibility of the MQTT Broker is to accept all messages published by publishers and distribute them to different message subscribers after filtering. There are many open-source MQTT Broker products, some of which we have introduced in previous articles (S7PLC sends messages to mobile via MQTT).
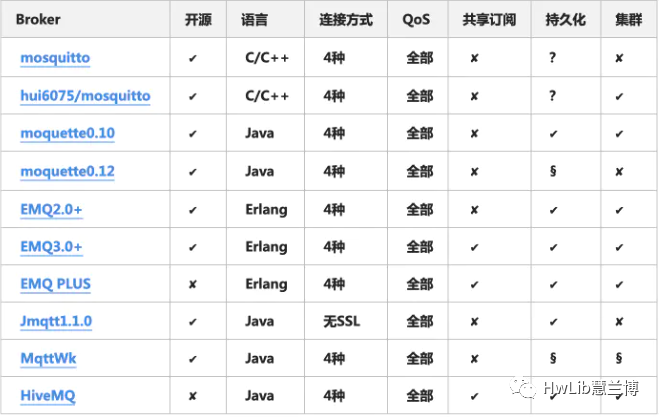
Figure 3: Open-source MQTT Broker
While there are many open-source MQTT Brokers, they all have various limitations, such as some not supporting persistence, and others gradually shifting to a paid model. Therefore, we are using an MQTT Broker we developed ourselves, which currently has simple functionality and can be gradually improved based on demand. For convenience in testing, we have deployed this MQTT Broker on Tencent Cloud server.
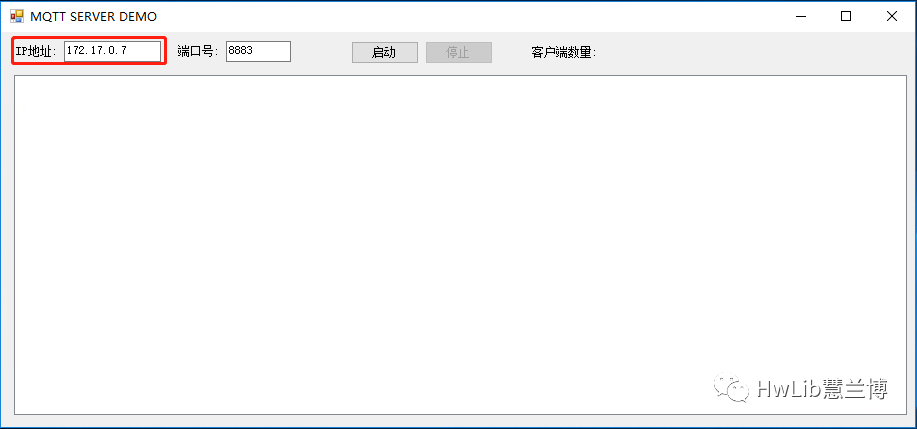
Figure 4: MQTT Broker
One point to note is that the network card address seen on the Tencent Cloud server is not the allocated public address. Therefore, when binding the IP, do not write the public IP, but directly write the internal IP as shown in the figure above.
WINCC Configuration
First, right-click on Cloud Connector in the resource explorer on the left side of WinCC and select “Cloud Connector Settings”.
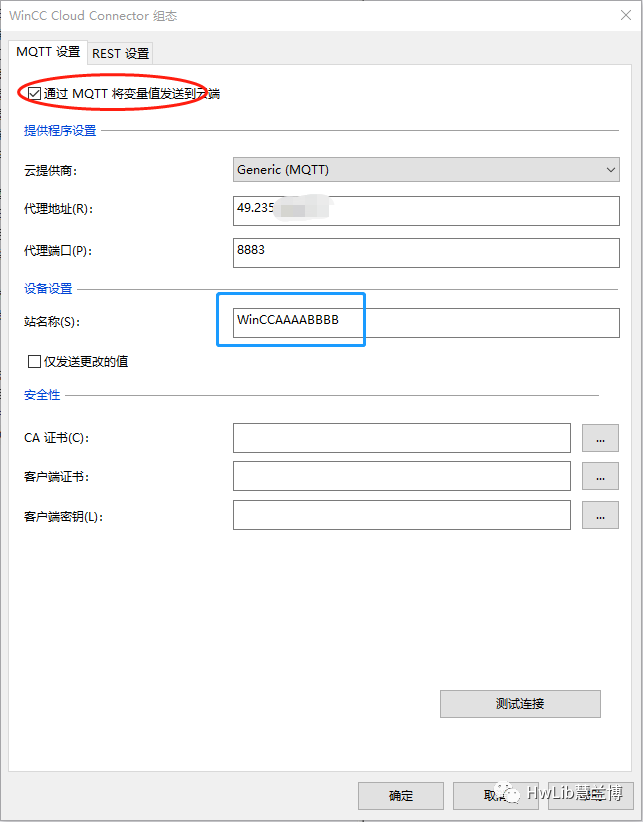
Figure 5: Cloud Connector Configuration
Check the option “Send variable values to the cloud via MQTT” in the above figure. Since we are using our own developed MQTT Broker, select “Generic (MQTT)” for the cloud service provider. The broker address is the server address where our MQTT Broker is located. Start the MQTT Broker and click the “Test Connection” button in the above figure; you should see that WinCC has connected to the MQTT Broker.
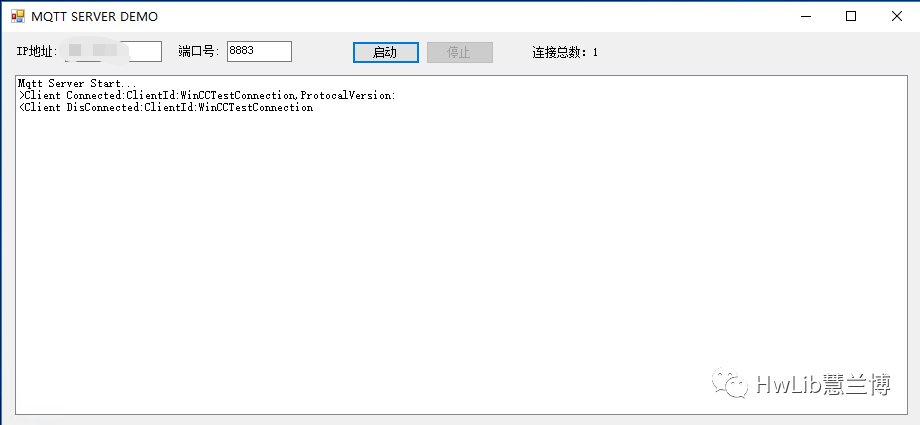
Figure 6: Connecting to MQTT Broker
Next, you need to configure the variables; only the variables checked for “WinCC Cloud” support transmission to the cloud service provider via REST or MQTT.
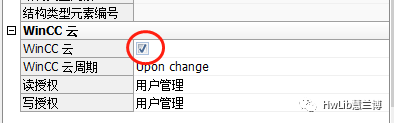
Figure 7: Configuring Variables
After configuration, activate WINCC, change the variable values, and then we can see the transmitted variable information on the MQTT Broker.
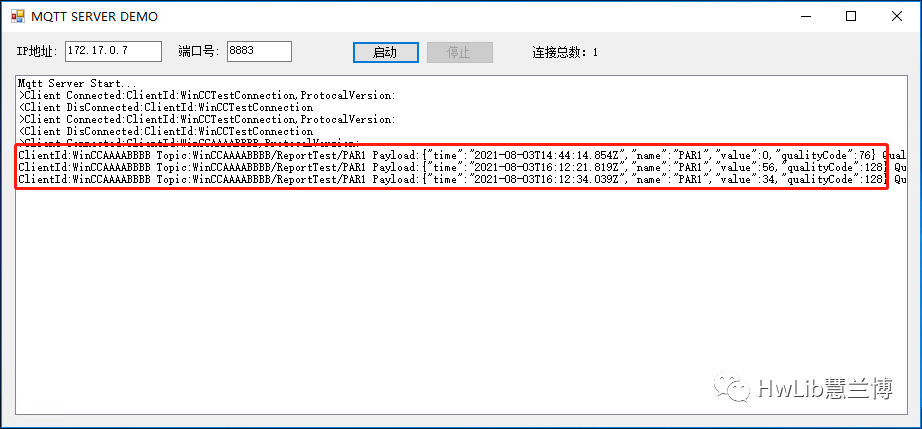
Figure 8: Variable Information
The benefit of setting up your own MQTT Broker is that you are not restricted by other vendors, and it is also more flexible in data processing, such as integrating with WeChat mini-programs or sending messages to mobile phones via SMS, etc.

More information about the HwLib (慧兰博) technical team: www.hwlib.com.cn
HwLib (慧兰博) technical materials:
https://www.jianguoyun.com/p/DR20ZAEQq_K3CBivk5kD
or
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1NzDd4nWeH7qDtzJghbe-oQ
Extraction code: 1234
END
Previous Readings
New Generation HwLib Technical Tutorials and Others
Introduction to WinCC Control Development
Http Communication of S7-1200/1500
TIA Portal Advanced Programming & Object-Oriented Programming Video Tutorial
Free “TIA SCL Core Programming” (Updated)
TIA Portal V17 New Feature VOT Trial Experience
TIA Portal V17.0 Installation Tutorial
TIA Portal Object-Oriented Programming Video Tutorial
TIA Portal Object-Oriented Programming
How We Program (2) – Discussing HMI Configuration Patterns
How We Program (1) – Discussing PLC Programming Patterns
Free “TIA SCL Core Programming”
Automatic Program Generation Based on TIA Openness + HwLib.GCF
SCL Using Ref and Variant to Implement Dictionary
TIA Openness Development Introduction
WinCC WeChat Control Testing
What Kind of Program is Considered a Good Program?
Application of Design Patterns in PLC Programming
TIA Portal V17.0 New Feature Preview
Using HwSheetAdv to Create WinCC Reports
HwLib.IAUA (Industrial Automation Unified Architecture)
Beginner C# Tutorial [Topic 1 – S7 Communication] (1)
SIMATIC Open Controller Evaluation (1)
Two Methods for Recording Data Using S7-1200/1500 (1)
Several Controls for WinCC Reports
Accessing WinCC Screen Objects Using C#
TIA Portal Program Generator (HwLib.TiaPortalTool)
Controls in TIA Portal Unified – Symbol IO Field
S7-1200 Connecting to Beckhoff Absolute Encoder via PROFINET
TIA Portal Object-Oriented Programming Introduction
Using PLCSIM Advanced Simulation Communication
Industrial Automation Unified Architecture
S7PLC Sending Messages to Mobile via MQTT
TIA WinCC Unified Classic Introduction
TIA Portal Top Programming Techniques – Preface (The Significance of Framework)
Write Once, Run Anywhere (Component Cross-Platform Programming)
TIA WinCC Unified Technical Speculations
TIA WinCC Unified First Experience
HwLib (慧兰博) Technical Team Product Materials (2020)
TIA Portal V16.0 (WinCC Unified) Installation Tutorial
TIA WinCC Adv How to Automatically Archive Variables to Database
Why Automation Engineers Should Learn Advanced Programming Languages
Skin Control Suitable for C#
Variant & REF Dual Sword Combination
WinCC Voice Alarm Implementation Method
How to Dynamically Switch Images in WinCC
Discussing the Difference Between Return and Output in FC
HwLib (慧兰博) WeChat Public Account
Focusing on High-End Programming Applications in Industrial Automation

HwLib (慧兰博) WeChat ID
