
So far, protocols such as I2C, SPI, and UART remain the most commonly used communication protocols in electronic embedded devices. In this article, we will analyze these three protocols to provide a clear and intuitive understanding of their functions, advantages, and limitations, supplemented with GIF animations.
I2C Protocol
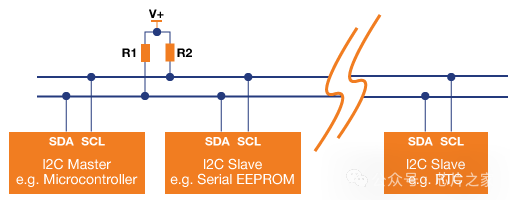
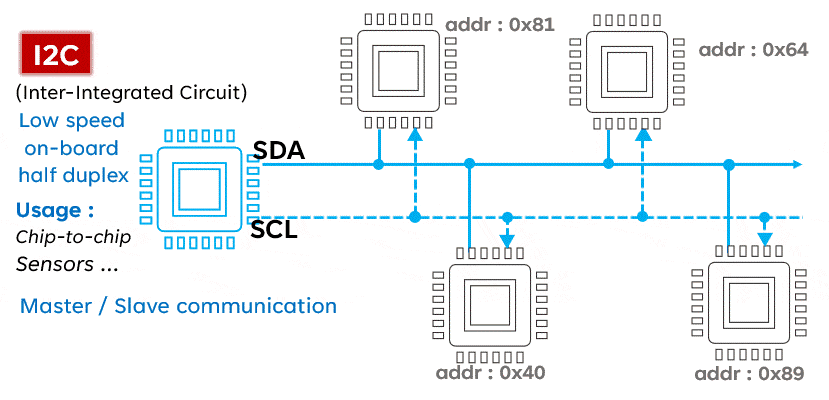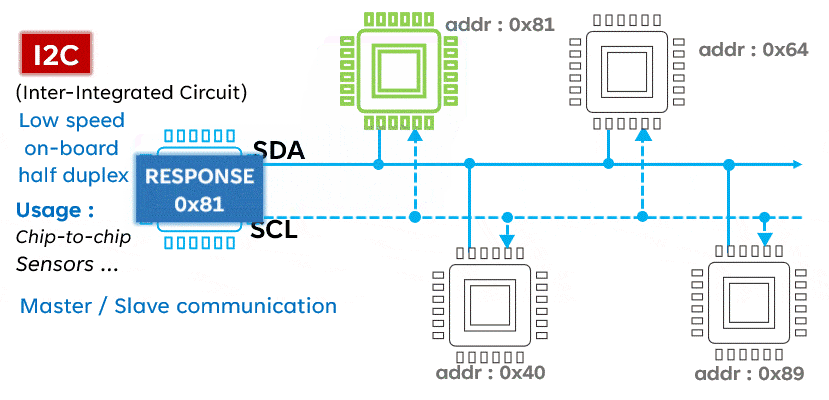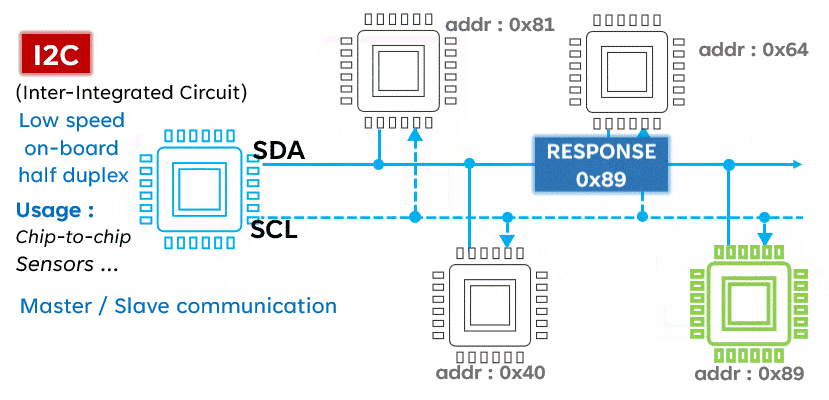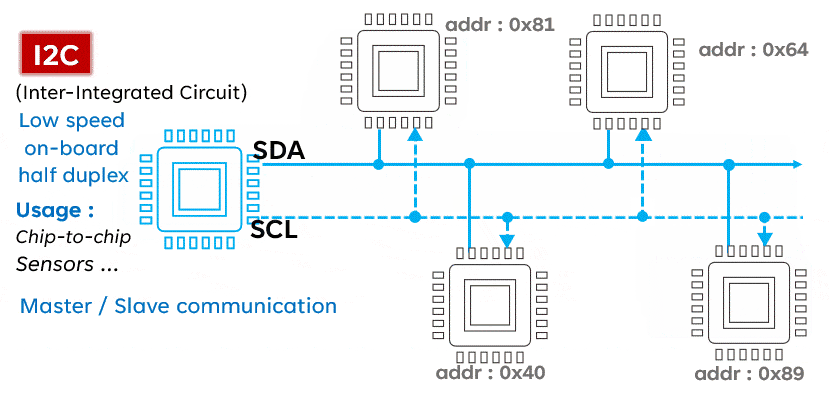 I2C is a serial communication protocol typically used to connect low-speed devices such as sensors, memory, and other peripherals. It uses two lines (SCL and SDA) for bidirectional communication, featuring address orientation and a master-slave mode.Advantages:
I2C is a serial communication protocol typically used to connect low-speed devices such as sensors, memory, and other peripherals. It uses two lines (SCL and SDA) for bidirectional communication, featuring address orientation and a master-slave mode.Advantages:
- Multi-device support: I2C supports multiple devices connected to the same bus, each with a unique address.
- Simple: The I2C protocol is relatively simple, making it easy to implement and debug.
- Low power consumption: Devices on the I2C bus can enter low-power mode when idle, saving energy.
 Disadvantages:
Disadvantages:
- Slower speed: I2C communication speed is lower, suitable for low-speed devices.
- Limited: The bus length and number of devices in I2C are limited; a long bus may lead to communication issues.
- Conflicts: Conflicts may occur when multiple devices attempt to send data simultaneously, requiring additional conflict detection and handling mechanisms.
Application Cases: In terms of applications, I2C excels in environments requiring simple and economical communication. It is particularly adept at being used in small sensors, LCD screens, and RTC (real-time clock) modules. Additionally, due to its efficiency in compact circuits, I2C is useful in temperature control devices, battery management systems, and LED controllers. However, for projects requiring fast or long-distance data transmission, it is better to choose other protocols.
SPI Protocol
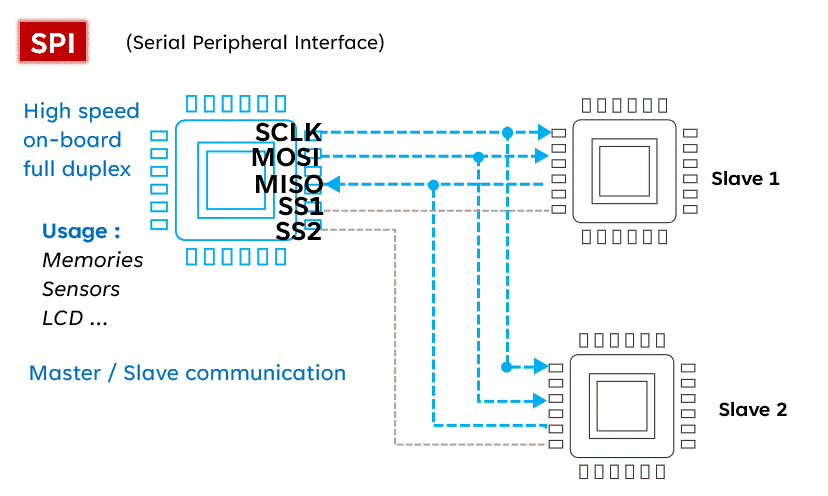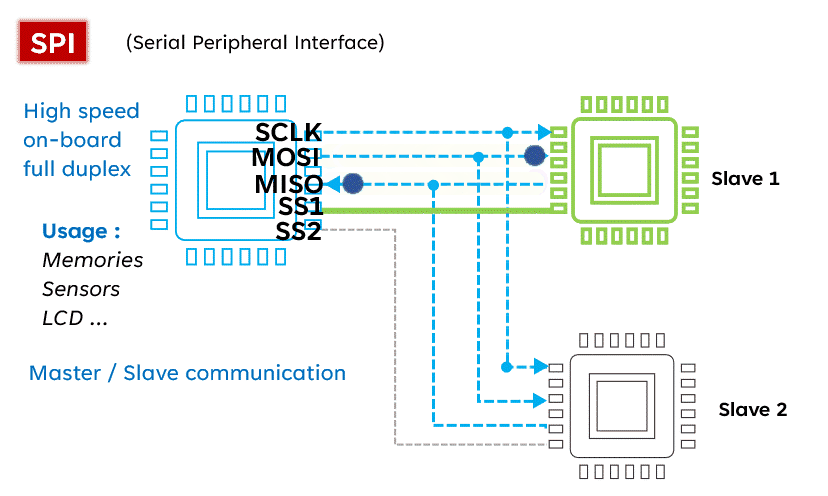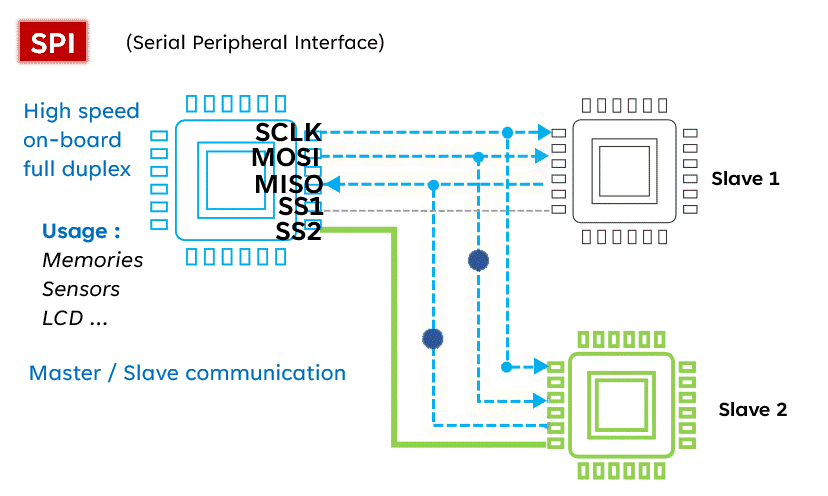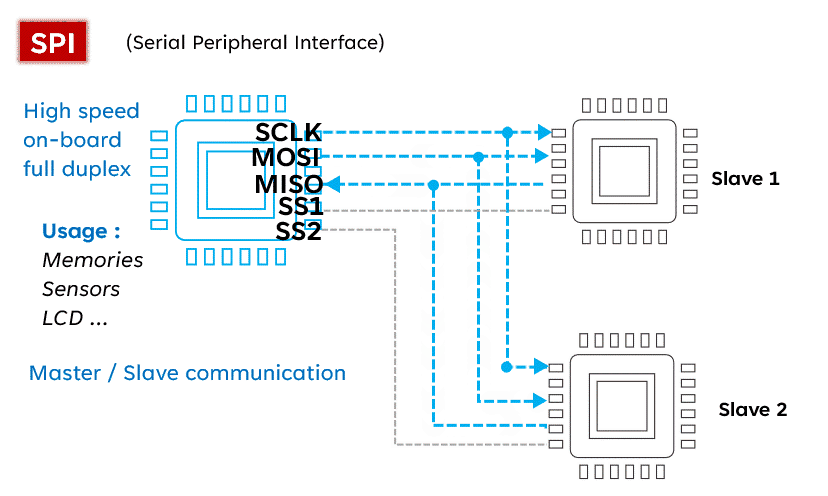 SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) is known for its high speed, making it the preferred choice for fast communication. Unlike I2C, SPI operates with four lines: MISO (Master In Slave Out), MOSI (Master Out Slave In), SCK (Serial Clock), and SS (Slave Select), allowing for full-duplex communication (sending and receiving simultaneously). Although simple and fast, SPI requires more pins than I2C, which may be a consideration in circuit design.Advantages:
SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) is known for its high speed, making it the preferred choice for fast communication. Unlike I2C, SPI operates with four lines: MISO (Master In Slave Out), MOSI (Master Out Slave In), SCK (Serial Clock), and SS (Slave Select), allowing for full-duplex communication (sending and receiving simultaneously). Although simple and fast, SPI requires more pins than I2C, which may be a consideration in circuit design.Advantages:
- High speed: SPI communication is fast, suitable for applications requiring high speed.
- Full-duplex: SPI supports full-duplex communication, allowing simultaneous data sending and receiving.
-
Simple: The SPI communication protocol is relatively simple, suitable for rapid development and implementation.
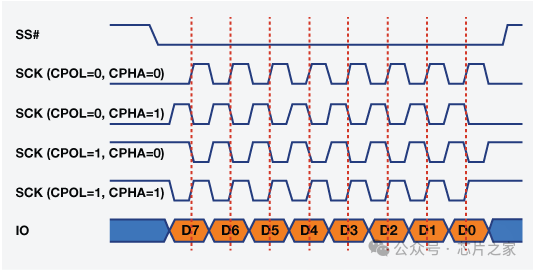 Disadvantages:
Disadvantages:
- Complex wiring: SPI requires multiple wires for connection, which may increase the complexity of hardware design.
- Distance limitations: The transmission distance of SPI is limited; long lines may lead to signal attenuation and interference.
- Master-slave mode limitations: SPI typically uses a master-slave mode, limiting the number of master devices, making it unsuitable for multi-master scenarios.
Application Cases: SPI is very suitable for situations requiring fast and reliable data transmission, such as TFT displays, SD storage cards, and wireless communication modules. However, its effectiveness decreases in complex systems with many slaves.
UART Protocol
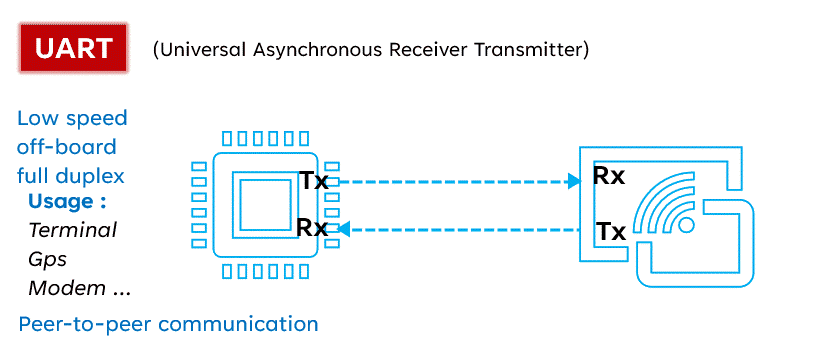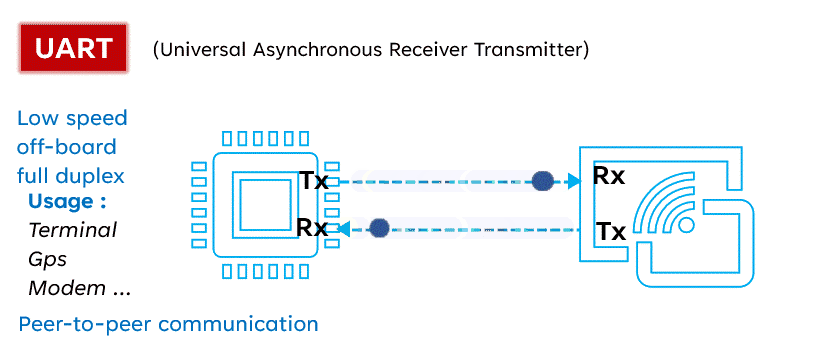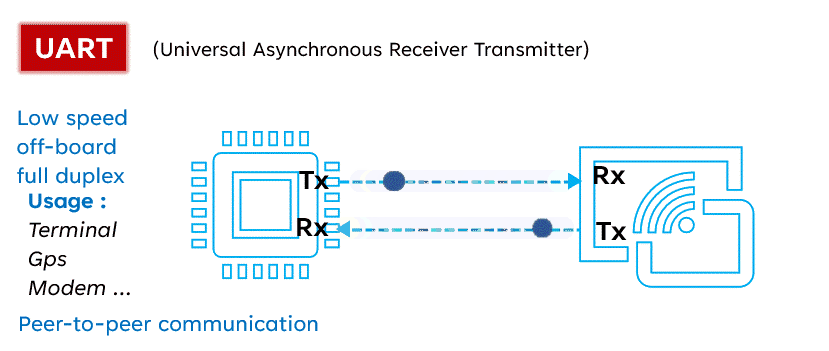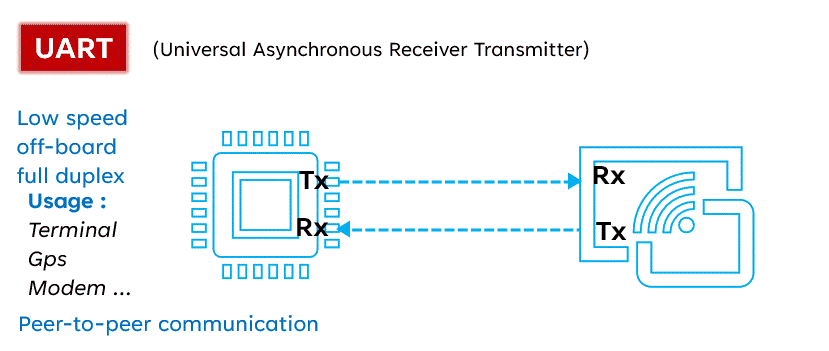 UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) is a serial communication protocol widely used for its versatility and simplicity. Unlike I2C and SPI, UART operates with only two lines: TX (Transmit) and RX (Receive). This protocol allows for asynchronous communication, meaning the transmitter and receiver do not need to share a clock. Data is organized into packets, each containing a start bit, 5 to 9 data bits, an optional parity bit, and one or two stop bits.
UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) is a serial communication protocol widely used for its versatility and simplicity. Unlike I2C and SPI, UART operates with only two lines: TX (Transmit) and RX (Receive). This protocol allows for asynchronous communication, meaning the transmitter and receiver do not need to share a clock. Data is organized into packets, each containing a start bit, 5 to 9 data bits, an optional parity bit, and one or two stop bits.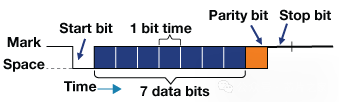 Advantages:
Advantages:
- Simple: The UART communication protocol is relatively simple, easy to implement and debug.
- Wide applicability: UART is widely used for communication between various devices, offering good compatibility.
- Distance: UART communication can cover long distances, suitable for scenarios requiring long-distance transmission.
Disadvantages:
- Lower speed: UART communication speed is relatively low, unsuitable for applications requiring high speed.
- Duplex: UART communication is duplex, allowing for low-speed duplex data transmission, enabling both sending and receiving of data.
- Unreliable: Due to UART being asynchronous communication, it may be affected by noise and interference, leading to unreliable data transmission.
Application Cases:
- Connection between microcontrollers and peripherals: Used for simple direct data exchange.
- GPS modules and serial interfaces with computers: Used for reliable, low-complexity communication.
- Industrial machines: UART is commonly used in industrial equipment for stable communication.
- Using RS standards (e.g., RS-232, RS-485): These standards support longer-distance UART communication and provide the possibility of creating multi-slave networks using appropriate transceivers, thus increasing the flexibility and breadth of UART applications.
Selecting the Right Protocol for Our Project:
- Communication speed: SPI offers high speed, UART provides high flexibility, and I2C is suitable for configurations requiring lower speed and simpler wiring.
- Circuit design: I2C allows for efficient space management of multiple devices, SPI enables performance in large designs, while UART offers simplicity and versatility.
- Distance and communication environment: UART is stable over long distances, while I2C is better suited for short distances.
- Duplex requirements: SPI and UART provide full-duplex capabilities, while I2C is limited to half-duplex.
Conclusion
I2C stands out for its simplicity and ability to manage multiple slave devices with minimal pins, making it an ideal choice for short-distance configurations.SPI, with its high speed and full-duplex mode, is very suitable for fast and efficient data transmission in systems where space is not a major concern.UART is powerful and robust, excelling in long-distance communication and configurations with lower speed requirements.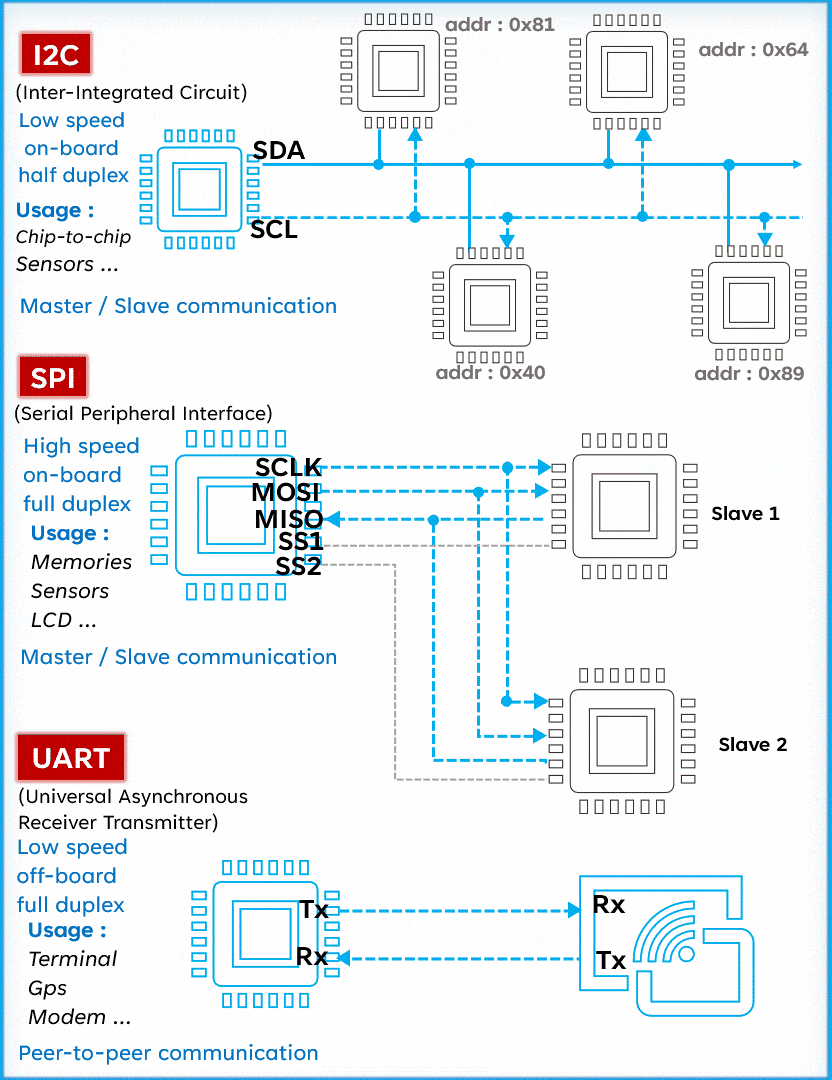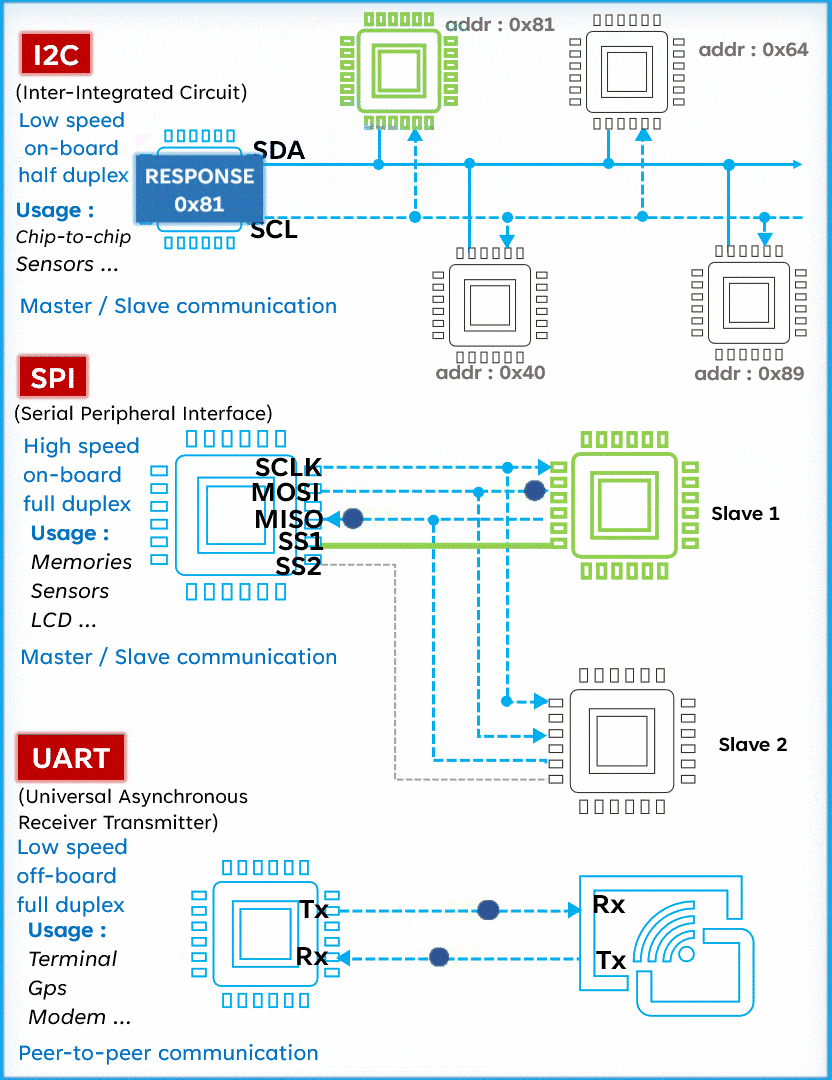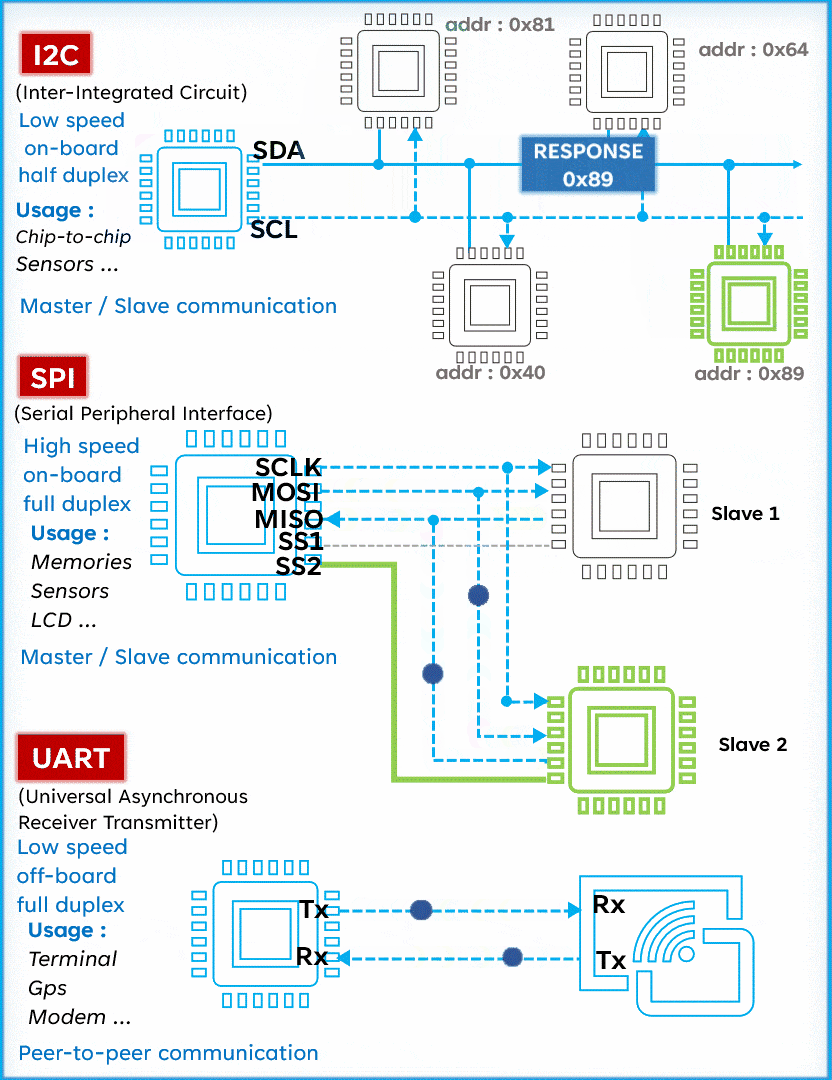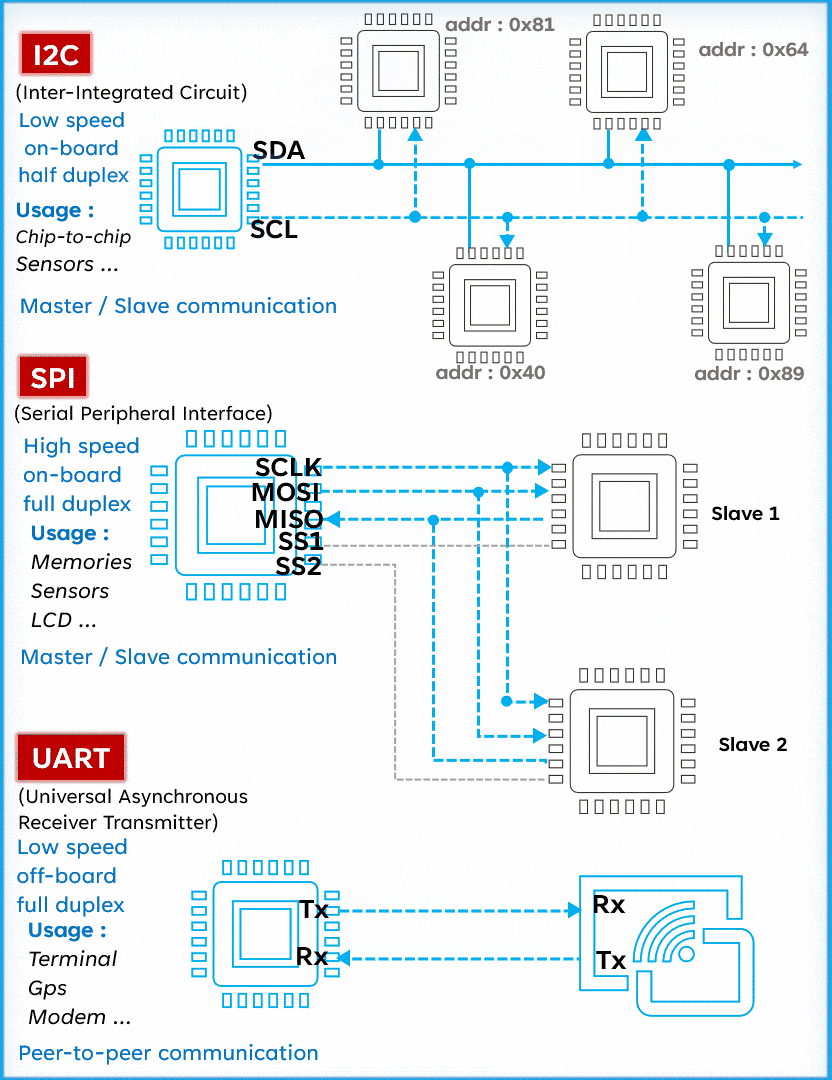 GIF source: www.parlezvoustech.com
GIF source: www.parlezvoustech.com
Hot Articles
2025 China Fabless100 3+10 Category Top 10 Rankings
2025-03-27

2025 China Fabless 100 Listed Company Rankings (Beta Version) Released!
2025-03-25
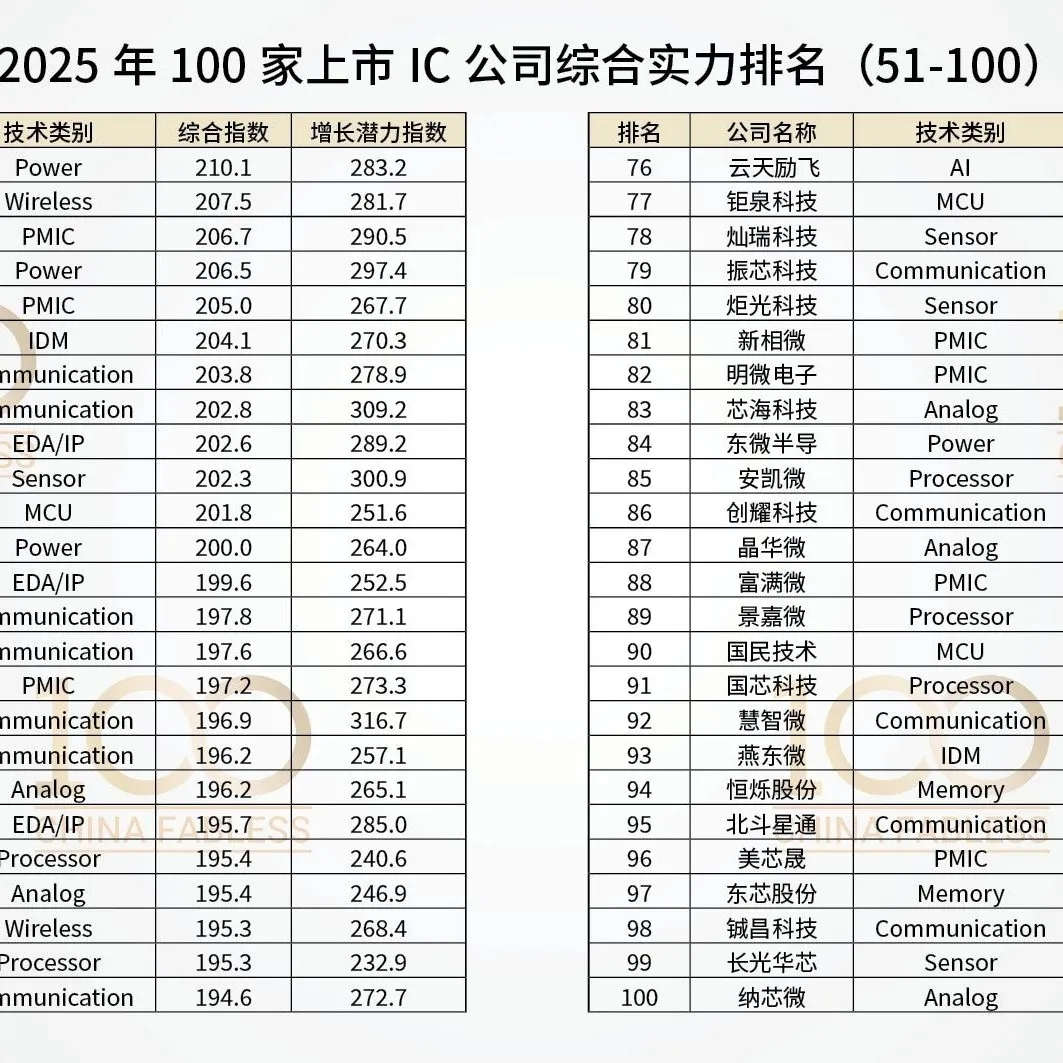
Model Open Source: How is the China Fabless 100 Ranking Calculated?
2025-03-25

Under Trump’s “Reciprocal Tariffs”, automakers accelerate the shipment of core components to the United States
2025-03-26

$390 million smuggling case! The U.S. pressures Singapore and Malaysia to strictly investigate AI chip flow issues
2025-03-25

