Author: Zhao Xiaofei
IoT Think Tank Original
Please indicate the source and origin when reprinting
Introduction
The development of technology has made elderly people increasingly isolated, but through some changes in thinking and innovation, we can allow the elderly to enjoy the benefits of technological advancements, making new technologies tools for serving the elderly population.

Last night, the official Weibo account of the People’s Daily published a post titled “Shanghai: Automatic Alerts for Elderly Residents’ Water Meters After 12 Hours of No Usage”. Within 3 hours, over 5 million people viewed this video, garnering more than 150,000 likes. During a visit to the Jiangsu Road Street in Changning District, Shanghai, reporters discovered that the community has installed door magnets, smoke alarms, infrared monitoring systems, and other systems to promote smart elderly care. For example, the smart water meter automatically alerts when the reading is below 0.01 cubic meters within 12 hours, prompting community staff to visit the elderly and report the situation to the responsible department.
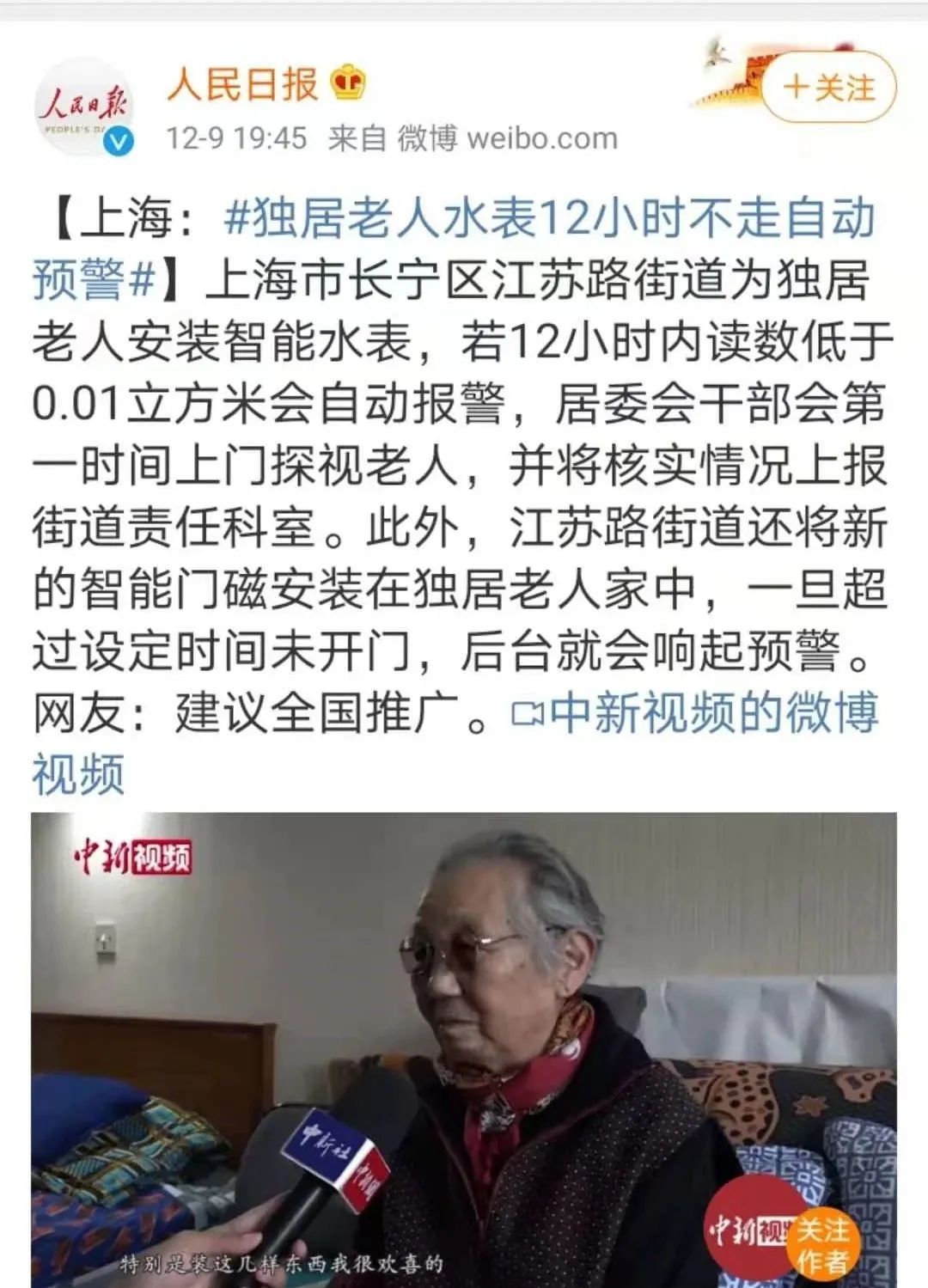
As an IoT practitioner, I firmly believe that similar solutions and scenarios are already quite mature. However, upon seeing this news, I cannot help but feel that despite the increasing isolation of the elderly due to technological advancements, we can still allow them to enjoy the benefits of technology through some changes in thinking and innovation, making new technologies tools for serving the elderly population.
Smart Elderly Care, an Urgent Task
Aging is currently a significant issue in China’s economic and social development. The Fifth Plenary Session of the 19th Central Committee clearly proposed the “implementation of a national strategy to actively respond to population aging,” elevating the response to aging to a national strategic level, highlighting its importance.
In 2017, the State Council published the “13th Five-Year Plan for the Development of the National Aging Undertaking and the Construction of the Pension System,” which stated that by 2020, the elderly population aged 60 and above in China is expected to increase to about 255 million, accounting for approximately 17.8% of the total population; the number of elderly people aged 80 and above will increase to about 29 million, and the number of elderly people living alone and in empty nests will increase to about 118 million.
118 million elderly people living alone and in empty nests is a staggering number, indicating that such a large group of elderly individuals is often left without companionship or care.Due to various reasons, most elderly people living alone and in empty nests cannot access specialized commercial elderly care services, making home and community-based elderly care the core approach. The goal of China’s aging development is also “a pension service system based on home care, supported by the community, supplemented by institutions, and integrated with medical care.” Due to the lack of specialized personnel to provide services, home and community-based elderly care for those living alone and in empty nests may not be guaranteed, and implementing smart elderly care through the latest technological means may be an important way to serve this 118 million elderly population.
As early as 2015, the Ministry of Civil Affairs and ten other ministries jointly issued the “Implementation Opinions on Encouraging Private Capital to Participate in the Development of the Elderly Care Service Industry,” which clearly proposed community home-based elderly care:
Promote the informatization of elderly care services, gradually achieve dynamic management of elderly information. Support private capital to use the Internet, IoT, cloud computing, and other technological means to connect the service needs of the elderly with various social entities, develop remote medical services for elderly care institutions, and provide services such as emergency calls, housekeeping appointments, health consultations, and item purchases for the elderly.
The “Home and Community Elderly Care Project” in the “13th Five-Year Plan for the Development of the National Aging Undertaking and the Construction of the Pension System” also mentioned:
Implement the “Internet+” elderly care project. Support communities, elderly care service institutions, social organizations, and enterprises to utilize IoT, mobile internet, cloud computing, big data, and other information technologies to develop and apply smart terminals and intelligent platforms, information systems, APP applications, WeChat public accounts, etc., focusing on expanding functions such as remote reminders and controls, automatic alarms and responses, dynamic monitoring and recording, standardizing data interfaces, and building virtual nursing homes.
In April 2019, the State Council issued the “Opinions on Promoting the Development of Elderly Care Services,” which also clearly stated: promote IoT and remote intelligent security monitoring technologies to achieve 24-hour automatic safety monitoring, reduce the risk of accidents for the elderly, and improve service experience.
It is evident that IoT is a core technological means in smart elderly care, receiving strong policy support, especially for the elderly living alone and in empty nests, to some extent addressing the shortage of elderly care personnel.
Allowing the Elderly to Dignifiedly Enjoy Basic Elderly Care Services
Although home and community-based elderly care is a top priority in China’s elderly care service system, the business model for home and community-based elderly care is not clear. Last year, renowned demographer Qiao Xiaochun stated at a forum that surveys found that currently, most elderly care institutions in China are still operating at a loss, with only 4% of institutions achieving surplus, and community home-based elderly care service providers are facing even tougher times, with many elderly care stations and care centers in communities struggling to operate, even with strong government support and direct funding, it is difficult to achieve profitability.
Of course, the one-time investment for specialized home and community-based elderly care service institutions is enormous, while adopting intelligent means to provide the most basic home and community-based elderly care services can explore certain business models. Due to lower costs, it is generally done through government purchasing public services or family purchases, such as the purchase of some smart hardware and wearable devices.
In terms of smart home elderly care, IoT practitioners have never stopped exploring over the years. Smart home elderly care generally involves the use of smart hardware and the collection of related data, but data collection can be divided into two methods: perceptual collection and non-perceptual collection, with different methods determining the ease of implementing IoT solutions.
Perceptual Collection generally involves the elderly wearing monitoring devices, such as bracelets, watches, fall detectors, and canes. The advantage of these devices is that they can accurately understand the elderly’s physiological conditions, but the downside is that they require the elderly to use them daily to obtain data, and many elderly individuals feel they are being monitored constantly, leading to significant resistance and non-cooperation in wearing them, resulting in inaccurate data collection. Moreover, most devices use WiFi, Bluetooth, and other short-range communication methods, leading to low active networking rates among the elderly, and the network configuration can be somewhat complex, making data collection difficult.
Non-Perceptual Collection is similar to the smart water meters and door magnets mentioned at the beginning of this article. Although the data collected is not directly related to the elderly’s physiological conditions, water usage and going out are essential behaviors in the daily life and diet of the elderly, and the data obtained through these devices is objective. Another advantage is that these devices connect through the NB-IoT low-power cellular network, ensuring continuous data collection.
The data from smart water meters provides objective feedback on extreme situations for elderly individuals living alone; for instance, not using water for 12 hours is a significant warning signal. Coupled with cross-validation from data from door magnets, infrared devices, and other smart devices, it can accurately identify extreme situations. It can be said that this allows the elderly to enjoy the most basic elderly care services with dignity in a non-intrusive manner.
AI Recognition, NB-IoT, and the Value of Data as a Production Factor Drive Project Implementation
In my view, while promoting smart elderly care services through smart water meters is not a new concept, its implementation is a product of the combination of various technologies and business models. In the case of Jiangsu Road Street in Changning District, Shanghai, I noticed that these water meters are not truly new smart water meters, but rather a data collection terminal added to traditional mechanical meters, achieving intelligence quickly without altering the original measuring device.
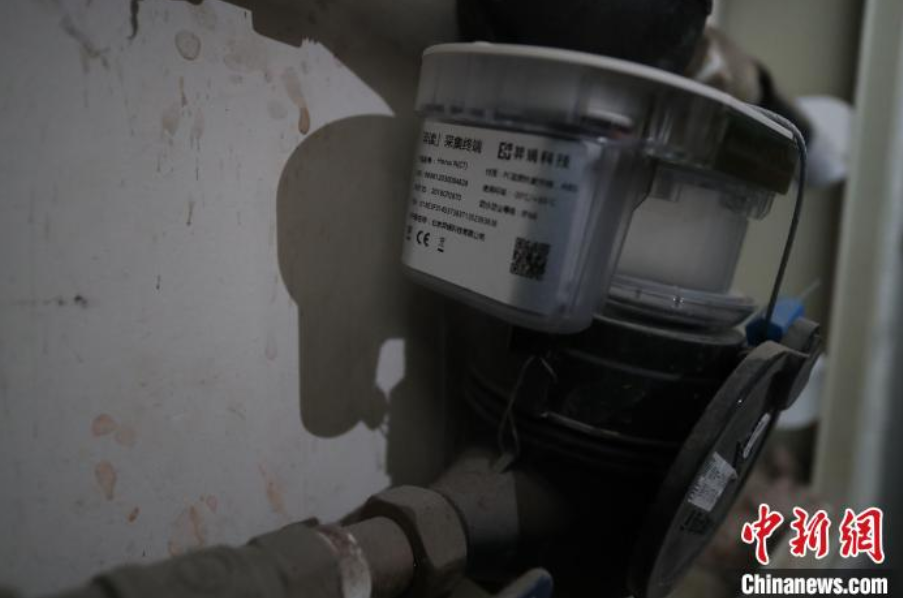

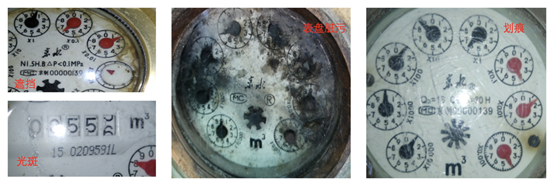
Although smart water meters are developing rapidly, there are still a large number of traditional water meters in the market that are still in their lifecycle. These meters cannot simply be replaced. Many elderly individuals live in old communities where most of their water meters are traditional ones, so implementing elderly care services through smart water meters can only be achieved through innovation based on existing meters. The most critical step is the accurate recognition of meter readings. I also learned about the principles of the solutions provided by the vendor Yiwa Technology, discovering that there is actually strong support from artificial intelligence technology behind this.
The number of existing water meters is enormous and varies widely, with hundreds of different models, specifications, and manufacturers. Additionally, factors such as water droplets, bubbles, and patterns on the meter, as well as dirt, frozen cracks, and reflections on the dial, can lead to reading errors. Achieving accurate recognition at a low cost requires extensive deep learning. Therefore, the algorithm must support hundreds of meter models and different reading rules, possess predictive and self-learning capabilities, and due to cost, power consumption, and transmission bandwidth limitations, the algorithm must also support the formation of low-resolution, low-image quality images based on recognition accuracy. It is evident that the work of recognizing water meter readings is backed by Yiwa Technology’s accumulated AI capabilities.
Of course, the most effective wireless communication technology supporting the meter reading scenario is NB-IoT, which is the communication method adopted in this case, ensuring network coverage and laying the foundation for low-power, maintenance-free smart water meters. In recent years, NB-IoT has made significant progress, and currently, its network coverage, application scenarios, industry ecosystem, and costs can support its large-scale development. The door magnets, infrared devices, and smoke alarms in this case also all use NB-IoT communication methods, becoming the “unsung heroes” behind smart elderly care.
The successful closure of this project also relies on the value extraction of data. In April of this year, the “Opinions of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council on Building a More Perfect Market-Oriented Allocation System for Factors” was released, one highlight of which is the inclusion of data as a new type of production factor alongside traditional factors such as land, labor, capital, and technology. In the case of Jiangsu Road Street in Changning District, Shanghai, the value of data as a production factor is fully reflected. Traditionally, the data generated by smart water meters brings value to water service companies through smart meter reading and smart water management, but this data can now also be used for home elderly care, endowing it with public service value. If further explored, it may also generate new value in other fields. The characteristics of data as a production factor allow the project to be implemented quickly. Of course, the characteristics of data as a production factor are based on data privacy protection, and the meter reading data used for smart elderly care in this case is no exception.
According to staff from Jiangsu Road Street, the elderly population aged 60 and above accounts for about 39% of the total population in the street, indicating a deeply aging community. As a national-level demonstration street for smart health and elderly care applications, the application of these methods provides the public with tangible benefits and a sense of security.
In November of this year, the “Notice on Effectively Solving the Difficulties Faced by the Elderly in Using Smart Technology” was issued by the State Council, proposing that elderly individuals should better share the benefits of information technology development. Although smart water meters, smart door magnets, and smart smoke alarms only partially assist the elderly in achieving the most basic elderly care services, this is a good starting point. Given time, I believe various technological innovations will better serve smart elderly care. The development of technology should not create cold, alienating black technologies that distance the elderly; rather, it should enable the elderly to benefit from technological advancements.
Selected Past Articles
Harbin Institute of Technology is too difficult! Exposed in the National College Student
Mathematical Modeling Competition being banned……

Ultimate move! The US has launched
“Unlimited Traceability” against Huawei, blacklisting 38 more……

Huawei’s high-end Kirin chips may become obsolete,
Yu Chengdong: A countermeasure has been devised!

Just now, the US announced the “Clean Network” action:
Ban Chinese operators, prohibit the use of BAT cloud……

Today will be remembered in the history of technology, as we were robbed by the American empire!
ByteDance agrees to……

Huawei is entering the photolithography machine manufacturing industry, aiming to
mass-produce 5nm photolithography machines within two years?……
