
Source: Yinri Jun
Author: Wang Shuzhen
IoT Think Tank Edited and Published
Please indicate the source and origin for reprinting
—— [Introduction] ——
NB-IoT is indeed designed for device networking; with the advent of NB-IoT, the era of the Internet of Things has arrived.

Shared Bikes as a Mirror of Quality
Some say that entering 2017, the shared bike market is no longer a red ocean but a bloodbath. Consequently, the operational pain points of shared bikes—vehicle parking management—are becoming increasingly prominent.
In response to the chaotic parking of shared bikes, some claim that shared bikes have become a “mirror” reflecting the quality of citizens.
Recently, various regions have introduced new regulations regarding illegal parking and restrictions on shared bike deployment.
Virtual Parking Pilot, Frequent Operational Updates
In light of these reflections, Mr. Deng Yonghao, founder and chairman of Xiaoming Bike, offers a different perspective. He believes that using technology to make bike operations more orderly and environmentally friendly is the fundamental solution to the problem. The “technology” Mr. Deng refers to is virtual parking or electronic fence technology, which allows shared bikes to be parked only within designated areas.
In 2017, various news reports about virtual bike parking continued to emerge: Can virtual parking technology solve the pain points of shared bike development? Virtual bike parking was introduced in Zhengzhou; beware of bikes that cannot be locked if parked chaotically; virtual bike parking officially began operations in Zengcheng…
Can virtual parking really solve the problem of chaotic parking of shared bikes?
Let’s take a closer look at the true nature of virtual parking!
NB-IoT: The Technology Boosted by Shared Bikes
Before examining virtual parking, we need to understand another role boosted by shared bikes: NB-IoT (Narrowband Internet of Things).
NB-IoT was proposed by the 3GPP standards organization in September 2015 and became a highlight at the 2016 Mobile World Congress held in Barcelona, Spain, showcasing advantages such as wide coverage, large connectivity, low power consumption, and low cost.
Thus, some claim that NB-IoT is indeed designed for device networking; only with the arrival of NB-IoT can we say the era of the Internet of Things has truly begun.
NB-IoT + Virtual Parking
Virtual parking can achieve standardized management of shared bikes, and NB-IoT is designed for device networking. So, can these two technologies be combined on a technical level? How can they be combined?
With this in mind, I couldn’t help but dig into the patent information regarding NB-IoT + virtual parking. The search results show that there are currently few publicly available patent applications for NB-IoT + virtual parking, with only three—CN106707871, CN106683483, and CN107040895A—all applied for in 2017, where NB-IoT appears as a wireless communication module or method.
The patent CN106707871 discloses an “intelligent management system for non-motorized vehicles,” which can manage multiple shared bikes from different providers through an intelligent control module. It can also establish communication between the intelligent control module and auxiliary intelligent control modules, thus forming an invisible electronic fence. Additionally, it can achieve compatibility with existing APP systems of various shared bike brands within a large APP system platform, allowing one deposit to be used across multiple shared bike services. The short-range wireless communication module includes one or more of Wi-Fi, LiFi, or NB-IoT modules. The schematic diagram is as follows:
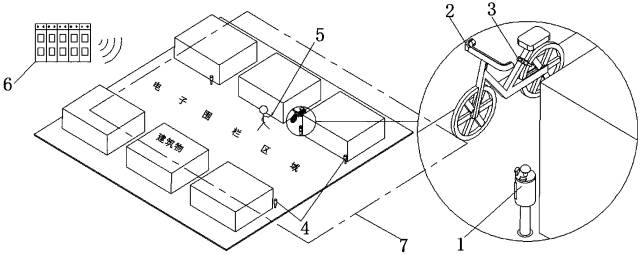
In short, bikes must enter the designated parking area, i.e., within the “electronic fence,” to complete the return process. According to the patent text, existing technology cannot manage shared bikes from different platforms simultaneously at the same virtual parking spot.
It seems that the competition for parking management of shared bikes is about to begin. Who will unify the market? Let’s wait and see!
The patent CN106683483A discloses “a parking management system and method based on BLE Bluetooth identification” (schematic diagram below), which does not require the setup of parking posts and includes a base station in the parking lot, a server, and a communication terminal. The connection between the three is as shown in the figure: vehicle users obtain geographic location information and monitoring area information from the server via the communication terminal, while prompting the vehicle to travel to the monitoring area. When the communication terminal enters the monitoring area of the base station, it establishes BLE Bluetooth communication with the base station, allowing the return operation to be executed. The main base station device receives auxiliary base station device information and reports messages to the system server as needed. The reporting communication method can be GPRS or protocols of LPWAN IoT such as NB-IoT, prioritizing GPRS.
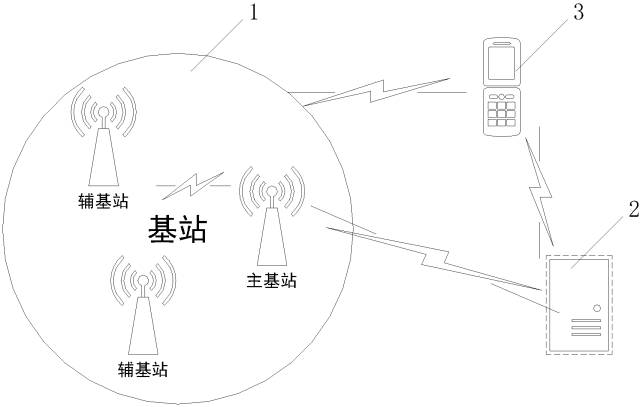
The invisible electronic fence stations created by this invention are easy to deploy, space-saving, and can automatically acquire monitoring areas. This may also be a good parking management solution for the recently popularized shared cars!
The patent CN107040895A discloses “an electronic fence control method for dockless vehicles,” which applies a backend server and a frontend mobile terminal. Through data communication and interaction between the backend server, frontend mobile terminal, and smart hardware on the vehicle, the method defines the dockless electronic fence and determines whether a vehicle is parked illegally. The mobile terminal in this patent can support GSM, WCDMA, CDMA2000, TDSCDMA, NB-IoT, Wi-Fi, WiMAX, and Bluetooth, applicable to various network standards such as 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G, supporting not only voice services but also various wireless data services.
NB-IoT technology fits well with the development opportunity of shared bikes, and virtual parking technology is frequently being implemented. The NB-IoT + virtual parking technical solution has emerged, and we have every reason to believe that the management level of shared bikes will significantly improve!

Infringement Risks
This issue mainly studies infringement risks, so we only focus on patents that are currently valid, particularly authorized invention patents.
Through search and analysis, we find that patent application number CN201210353674.0 is worth attention for shared bike companies. The patent is titled “A Control System and Method for Non-Motorized Vehicle Rental Operations Based on Smart Antennas and Smart Locks,” applied for on September 20, 2012, by Liu Yong’an.
From the patent text, it can be seen that this patent “realizes effective management of rental vehicles to solve the problem of chaotic parking while enabling unobstructed management of fixed parking locations,” which aligns with the issues addressed by virtual parking.
Since this is an infringement analysis, the key lies in the claims. Let’s take a look at the independent claims of the patent. Claim 1 states:
“A control system for non-motorized vehicle rental operations based on smart antennas and smart locks, characterized by including smart lock control devices installed on each rented vehicle, a smart information manager set by the rental management center, and multiple wireless area managers. The wireless area managers are installed at each fixed parking location of the rental vehicles, and the control signals of the wireless area managers cover the respective fixed parking locations, allowing renters to borrow and return vehicles within the coverage area of the wireless area managers.”
This claim is relatively simple and clear.
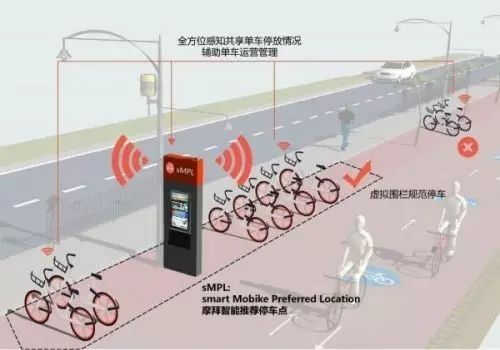
For comparison, let’s look at the schematic diagram of Mobike’s virtual parking technology:
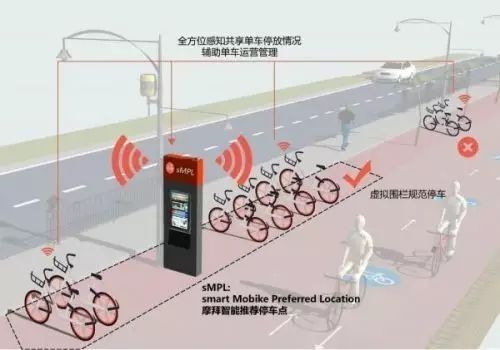
Does it look familiar?
According to the introduction, “Compared to the currently popular GPS electronic fence technology, the wireless signal transmission technology of the smart module used by Mobike’s sMPL is undoubtedly more advanced. With the support of precise positioning algorithms, sMPL can quickly determine the location and status of parked bikes, achieving sub-meter level accuracy.”
The comparison between the patent and the product is as follows:
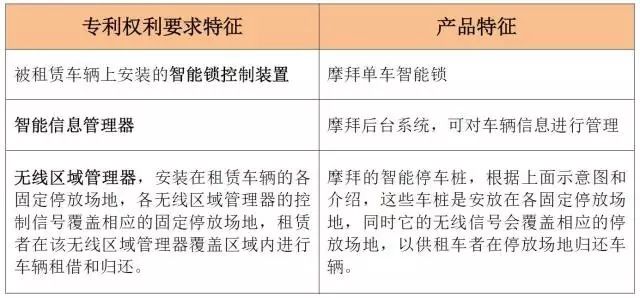
Through comparison, we find that the patent claims and Mobike’s smart parking technology are quite similar.
The patent also mentions smart antennas, which are mainly used to transmit wireless signals to cover parking areas. Smart antennas generally refer to adaptive array antennas, which may not necessarily use array antennas in current technological implementations. However, considering the extensive application of smart antennas in 4G and their adoption in future 5G and millimeter-wave wireless communications, this implementation method is likely to be adopted.
This patent was applied for by Liu Yong’an, who is the legal representative of Nanjing Lvyuan Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd., whose products include management systems for shared bikes and shared cars.

Nanjing Lvyuan Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. Liu Yong’an (image source: internet)
Today’s discussion ends here. Besides the aspects mentioned, there are many other points not discussed or overlooked. We welcome everyone to actively leave comments and discuss with me in the background.
Overall, this patent is worth attention for shared bike companies to mitigate potential infringement risks. Patent disputes in the shared field have been ongoing, and for companies, only by preparing patent layouts and risk avoidance in advance can they gain the upper hand in commercial battles.
Previous Hot Articles (Click the title to read directly):
-
“How Difficult Is It to Create an Intelligent Lock for Shared Bikes?”
-
“Cognitive Computing, Blockchain IoT, IoT Security… Those Who Understand Will Control the Future”
-
“KUKA, ABB, FANUC, Yaskawa, Four Industrial Robot Giants Have Long Been Stationed in the IoT Field”
-
“[Heavyweight] IoT Industry Panorama Report, The First Domestic IoT Industry Two-Dimensional Perspective Panorama”
-
“A Comic Explains: Besides WiFi, Bluetooth, What Can the Recently Popular NB-IoT Do?”
-
“A Comic Explains: Behind NB-IoT, What Is LoRa That Everyone Is Talking About?”
