 Introduction
Introduction
IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) refers to the integration of various sensing and monitoring devices, controllers, mobile communications, intelligent analysis, and other technologies into all stages of industrial production. This significantly enhances manufacturing efficiency, improves product quality, reduces product costs and resource consumption, ultimately elevating traditional industries to a new stage of intelligence.
The data sources at the perception layer of the industrial IoT are very diverse, typically coming from various multi-source heterogeneous devices and systems. Therefore, obtaining data from these devices and systems is the first hurdle faced by industrial IoT.
However, in actual industrial sites, due to certain specific needs or historical reasons, devices from different manufacturers may be used, and these devices may adopt different industrial protocols. Some devices have been in use for several years, and considering system stability and integration time, replacing them is not a viable option. Yet, devices with different protocols usually cannot be directly interconnected, making protocol conversion essential in the aforementioned scenarios.
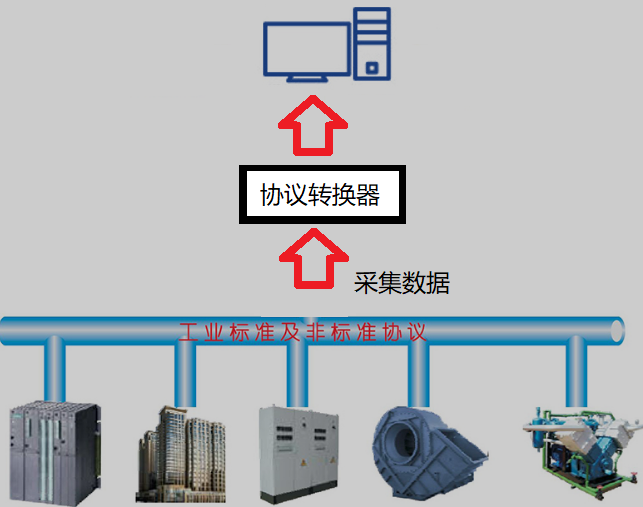
 How to Address the
How to Address the