 Get the mind map for free at the end of the article
Get the mind map for free at the end of the article
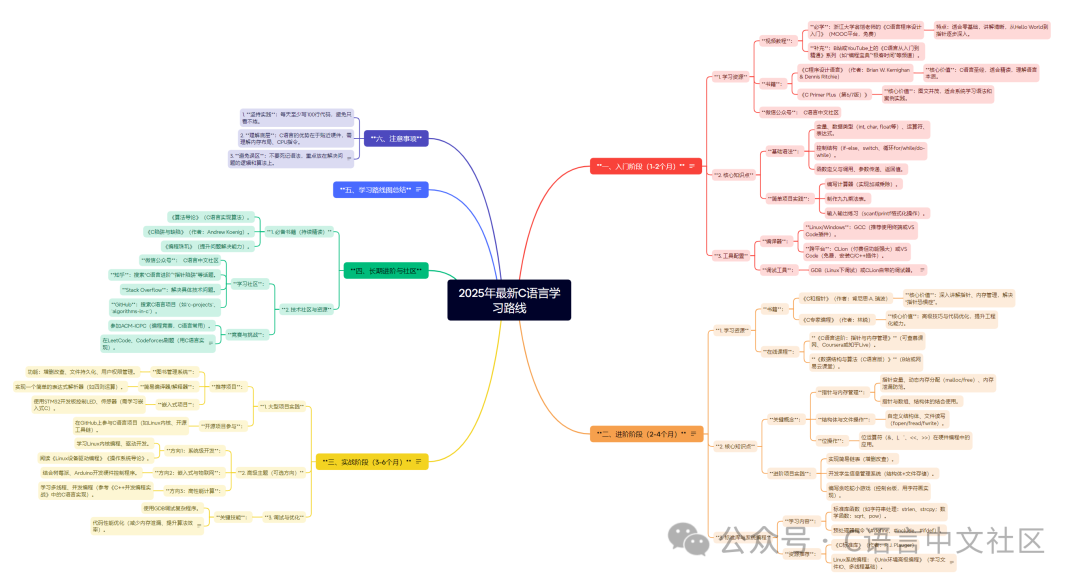
Detailed C Language Learning Path for 2025, divided into Beginner, Intermediate, Practical stages, covering resources, books, projects, and community support to help you systematically master C language:
1. Beginner Stage (1-2 months)
Goal: Master the basic syntax of C language, be able to write simple programs, and understand core concepts.
1. Learning Resources
- Video Tutorials:
- Features: Suitable for beginners, clear explanations, gradually deepening from Hello World to pointers.
- Must Learn: “Introduction to C Programming” by Professor Weng Kai from Zhejiang University (MOOC platform, free)
- Supplementary: Series “From Beginner to Proficient in C Language” on Bilibili or YouTube (channels like “Programming Treasure” and “Geek Time”).
- Books:
- Core Value: Rich in illustrations, suitable for systematic learning of syntax and practical cases.
- Core Value: The C Programming Language, suitable for in-depth reading to understand the essence of the language.
- “The C Programming Language” (Authors: Brian W. Kernighan & Dennis Ritchie)
- “C Primer Plus (6th/7th Edition)”
- WeChat Official Account: C Language Chinese Community
2. Core Knowledge Points
- Basic Syntax:
- Variables, data types (int, char, float, etc.), operators, expressions.
- Control structures (if-else, switch, loops for/while/do-while).
- Function definitions and calls, parameter passing, return values.
- Simple Project Practice:
- Write a calculator (implement addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division).
- Create a multiplication table.
- Input and output exercises (scanf/printf formatted operations).
3. Tool Configuration
- Compiler:
- Linux/Windows: GCC (recommended to use terminal or VS Code plugin).
- Cross-platform: CLion (paid but powerful) or VS Code (free, install C/C++ plugin).
- Debugging Tools:
- GDB (debugging on Linux) or the built-in debugger in CLion.
2. Intermediate Stage (2-4 months)
Goal: Master pointers, memory management, data structures, and understand the underlying principles of C language.
1. Learning Resources
- Books:
- Core Value: Advanced techniques and code optimization, enhancing engineering capabilities.
- Core Value: In-depth explanation of pointers and memory management, addressing “pointer phobia”.
- “C and Pointers” (Author: Kenneth A. Reek)
- “Expert C Programming” (Author: Peter van der Linden)
- Online Courses:
- “C Language Intermediate: Pointers and Memory Management” (available on MOOC platforms, Coursera, or Zhihu Live).
- “Data Structures and Algorithms (C Language Version)” (Bilibili or NetEase Cloud Classroom).
2. Core Knowledge Points
- Key Concepts:
- Bitwise operators (&, |, ^, <<, >>) in hardware programming applications.
- Custom structures, file reading and writing (fopen/fread/fwrite).
- Pointer variables, dynamic memory allocation (malloc/free), prevention of memory leaks.
- Combining pointers with arrays and structures.
- Pointers and Memory Management:
- Structures and File Operations:
- Bit Operations:
- Advanced Project Practice:
- Implement a simple linked list (CRUD operations).
- Develop a student information management system (structure + file storage).
- Write a Snake game (console version, implemented with character graphics).
3. Standard Library and System Programming
- Learning Content:
- Standard library functions (e.g., string handling: strlen, strcpy; math functions: sqrt, pow).
- Preprocessor directives (#define, #include, #ifdef).
- Resource Recommendations:
- “The C Standard Library” (Author: P. J. Plauger)
- Linux System Programming: “Advanced Programming in the UNIX Environment” (learning file I/O, basic multithreading).
3. Practical Stage (3-6 months)
Goal: Enhance comprehensive abilities through project applications and exposure to engineering development.
1. Large Project Practice
- Recommended Projects:
- Use STM32 development board to control LEDs and sensors (need to learn embedded C).
- Implement a simple expression parser (e.g., for arithmetic operations).
- Features: CRUD operations, file persistence, user permission management.
- Library Management System:
- Simple Compiler/Interpreter:
- Embedded Projects:
- Participate in Open Source Projects:
- Contribute to C language projects on GitHub (e.g., Linux kernel, open-source toolchain).
2. Advanced Topics (Optional Directions)
- Direction 1: System-Level Development:
- Learn Linux kernel programming and driver development.
- Read “Linux Device Drivers” and “Operating Systems: Three Easy Pieces”.
- Direction 2: Embedded and IoT:
- Combine Raspberry Pi and Arduino to develop hardware control programs.
- Direction 3: High-Performance Computing:
- Learn multithreading and concurrent programming (refer to C language implementations in “C++ Concurrency in Action”).
3. Debugging and Optimization
- Key Skills:
- Use GDB to debug complex programs.
- Code performance optimization (reduce memory leaks, improve algorithm efficiency).
4. Long-Term Advancement and Community
1. Essential Books (Continuous In-Depth Reading)
- “Introduction to Algorithms” (C language implementation of algorithms).
- “C Traps and Pitfalls” (Author: Andrew Koenig).
- “Programming Pearls” (Enhance problem-solving abilities).
2. Technical Communities and Resources
- Learning Communities:
- WeChat Official Account: C Language Chinese Community
- Zhihu: Search for topics like “C Language Advancement” and “Pointer Pitfalls”.
- Stack Overflow: Solve specific technical problems.
- GitHub: Search for C language projects (e.g.,
<span>c-projects</span>,<span>algorithms-in-c</span>). - Competitions and Challenges:
- Participate in ACM-ICPC (programming competition, commonly using C language).
- Solve problems on LeetCode and Codeforces (implementing in C language).
5. Summary of Learning Path
Beginner Stage → Intermediate Stage → Practical Stage → Long-Term Deepening
Basic Syntax → Pointers/Memory → Data Structures → System Programming/Projects → Open Source/Competitions
Books: The C Programming Language → C and Pointers → Expert C Programming → C Traps and Pitfalls
Tools: GCC/CLion → GDB → Linux Environment
6. Notes
- Practice Consistently: Write at least 100 lines of code every day, avoid just reading without practice.
- Understand the Underlying Principles: The advantage of C language lies in its closeness to hardware, requiring an understanding of memory layout and CPU instructions.
- Avoid Pitfalls: Do not memorize syntax blindly, focus on the logic and algorithms for problem-solving.
If you need specific project code examples or resource links, you can find them in the menu bar below this official account!
Reply in the official account: Mind Map
Get the mind map version of the learning path for free