Download DDNS-go Based on CPU Architecture
I am using the Thunderbolt Treasure 1, which has an arm7 CPU, so I need to download the corresponding arm7 version.
https://github.com/jeessy2/ddns-go/releases
Extract the Files and Copy Them to OpenWrt
Use WinSCP to connect to OpenWRT and copy ddns-go into it.
Download WinSCP
If you are unsure where to place it, use df -h to check the space usage:
root@OpenWrt:~# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Available Use% Mounted on
rootfs 75.7M 3.7M 72.0M 5% /
/dev/ubi0_0 75.7M 3.7M 72.0M 5% /
devtmpfs 512.0K 0 512.0K 0% /dev
tmpfs 113.8M 256.0K 113.6M 0% /tmp
tmpfs 512.0K 0 512.0K 0% /devSSH Client, Terminal Client
Download FinalShell or Download PuTTY
Installation
Navigate to the folder where ddns-go is located via the command line and execute the following command.
Mac/Linux: ./ddns-go -s installAfter installation, the auto-start is already configured. [Optional] Service Uninstallation
Mac/Linux: ./ddns-go -s uninstall[Optional] Supports installation with parameters
-l Listening address-f Synchronization interval (seconds)-cacheTimes Interval N times to compare with the service provider-c Custom configuration file path-noweb Do not start web service-skipVerify Skip certificate verification-dns Custom DNS server-resetPassword Reset password
Troubleshooting
OpenWrt ddns-go query domain information encountered an exception! tls: failed to verify certificate: x509: certificate signed by unknown authority
Reason: Running ddns-go on the router fails due to a lack of certificates, as the /etc/ssl path is mounted as read-only, preventing certificate import.
Solution: 1. Install: ca-certificates, after installation, the corresponding certificate files will be available.
Apply for Cloudflare API KEY
Cloudflare Profile -> Create Token -> Edit Zone DNS (using template)
Configure ddns-go
Configure Cloudflare’s API Key 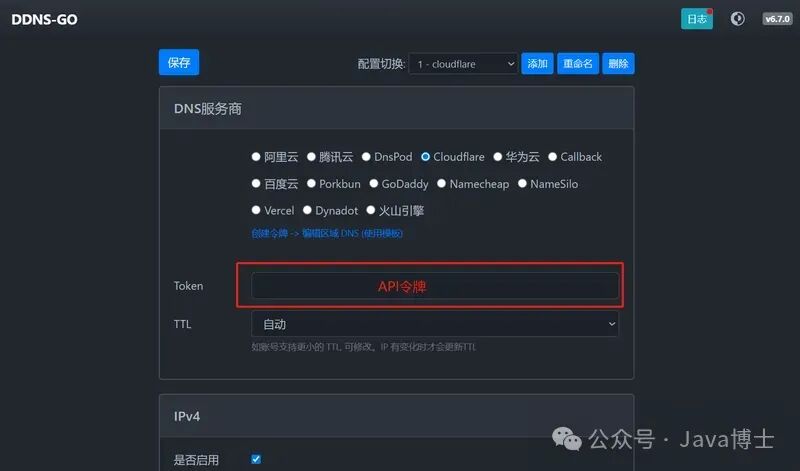 Configure Domain If the secondary domain record you enter does not exist, ddns-go will automatically create it. However, when deleting the ddns-go configuration, it will not be removed.
Configure Domain If the secondary domain record you enter does not exist, ddns-go will automatically create it. However, when deleting the ddns-go configuration, it will not be removed.
For the IPv6 address, it is directly obtained from the network card, as each device has a public IPv6 address. If the main router wants to update ddns ipv6 for other devices in the subnet, you can use commands to obtain it based on the MAC address.
For example:
Get the IPv6 address of the network card eth1 in a Linux system
ip -6 addr show eth1Get the IPv6 addresses of other devices in the local area network. Other devices need to support EUI-64 (the latter part of IPv6 includes ff:fe).
Linux
ip -6 route | awk '{print $1}' | awk '/240:?/' | awk -F::/ '{print $1 ":suffix of other mac"}'Windows
Get-NetRoute -AddressFamily IPv6 | Where-Object { $_.DestinationPrefix.StartsWith("240") -and $_.DestinationPrefix.endsWith("/64") } | ForEach-Object { ($_.DestinationPrefix -split '::/')[0] + ":suffix of other mac" }If the IPv4 address obtained by the device is a private address like 192.168.*.*, choose to obtain it through the interface, as this is the most common situation.
Verify the Effect
ping xl2.500599.xyz