
In the first task of the sixth episode of Funpack Season 2, our requirement was to set up a composite device of a Bluetooth keyboard and mouse, achieving the functionality of mouse clicks and key inputs.
However, the project I want to share today goes beyond just meeting the project requirements. Let’s take a look at what makes the Bluetooth keyboard and mouse project by student Feng Xue Tian special.
The complete project report has been uploaded to the Electronic Forest:
https://www.eetree.cn/project/detail/2100
1
Task Analysis and Implementation
To learn and understand the development of HID devices in low-power Bluetooth, student Feng Xue Tian chose this task. To make the project more interesting, an MPU6050 six-axis sensor was connected to the board, converting the read tilt angles into mouse X and Y coordinate increments, thus creating a gesture-controlled flying mouse.

2
HID Device Descriptor
For common Bluetooth application scenarios like mice and keyboards, there are already corresponding official examples. Therefore, the focus of task one was to modify and merge them to ultimately meet the project requirements. This involves knowledge of HID device report descriptors.
In computer peripherals, a large portion of devices is used for human-computer interaction, such as mice, keyboards, and game controllers, collectively referred to as Human Interface Devices (HID).
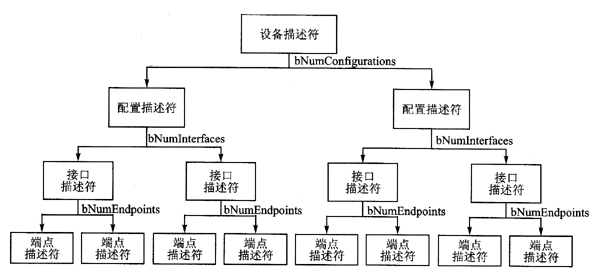
The USB host on the computer needs to determine what kind of device is connected through a series of descriptors, such as device, configuration, interface, endpoint descriptors, and device-specific descriptors. The specific descriptors for HID devices include the HID descriptor and report descriptor.
3
Key Code Design
HID Report Descriptor
The descriptor can be divided into two main parts. The first part is for the mouse, which contains three types of reports: first, the mouse buttons and scroll wheel, represented by three bits for the left, right, and middle buttons, followed by five bits for byte alignment, and then one byte for vertical and horizontal scroll wheels. The second part is for the keyboard, which contains two types of reports. The report ID, length, and callback function are then filled into the configuration structure to complete the final initialization.
Keyboard Input Function
The string to be input is stored in an array, and each time a key is pressed, the corresponding character is sent out, then the pointer is incremented. This achieves the sending function.
Keyboard Caps Lock Indicator
The specific implementation method is to define a callback function that will send data to the development board when the keyboard state on the computer changes, such as the Caps Lock status. In the notification callback function, we read the corresponding status bit for Caps Lock and control the LED’s on/off state based on this status.
Mouse Click Operation
In the key function, construct the corresponding data, set the bit corresponding to the left button to 1, send the data once, then set it to 0 and send the data again to simulate the mouse click operation.
Gesture Control Pointer Movement
In the main loop, read the accelerometer data every 50ms. After obtaining the raw data, first convert it to angles, then convert the angles to X and Y coordinate increments. To make the control less rigid, a nonlinear function is used for this conversion. After obtaining the X and Y coordinate increments, they can be sent to the computer.
For detailed code implementation of each functional part, please refer to the complete project report.
4
Project Effect Demonstration

Although only an additional motion sensor was added to the existing board, this simple addition allows for a lot of creativity and enhances the functionality of gesture-controlled mouse operation, making it a truly fun experience.
Did today’s project sharing inspire you? Don’t hesitate to try boldly; perhaps you can come up with even better ideas!

This concludes today’s project sharing! If you want to know more project details and specific code, remember to click “Read the original” at the end to view the complete project report.

END
Ying He Academy
The Ying He team is dedicated to providing standardized core skill courses for electronic engineers and related students, helping everyone effectively enhance their professional capabilities at various stages of learning and work.

Ying He Academy
Let’s explore and advance together in the field of electronics.
Follow the Ying He public account for direct access to the classroom.

Click to read the original for more.