Click the blue text to follow us
(1) Sub-industry Situation
1. Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Industry
The Printed Circuit Board (PCB) refers to a board that uses printing technology to form conductive circuit patterns or functional boards with printed components on an insulating substrate according to a predetermined design. It is used to achieve interconnection and relay transmission between electronic components and is an essential basic component of electronic information products. The manufacturing quality of PCB products directly affects the reliability of electronic products and the overall competitiveness of system products, which is why PCBs are referred to as the “mother of electronic system products.” The level of development in the PCB industry reflects, to some extent, the speed and technological level of a country’s or region’s electronic industry.
PCBs are present in almost all electronic devices, and the reliability and competitiveness of electronic products largely depend on the manufacturing quality of PCBs. The PCB industry serves as a foundational industry for the application of electronic information products, covering a wide range of application industries, supporting the development of downstream industries such as industrial control, communication equipment, automotive electronics, consumer electronics, medical health, and semiconductors. Emerging trends such as 5G, integrated circuits, new energy vehicles, and digital economy upgrades and product iterations will continue to drive the development of PCBs.
2. Prototype and Small Batch Board Industry
PCBs come in various models and can typically be classified based on order area, product layers, special processes, or materials. Depending on the focus of PCB companies on the order area market, there are differences in delivery deadlines, product uses, product models, customer structures, production processes, and pricing strategies. The PCB industry is further subdivided into the prototype and small batch board industry and the large batch board industry.
As a basic component of electronic information products, PCBs are experiencing a massive and diverse demand for emerging electronic components in the entire production and manufacturing supply chain, driven by the trend towards intelligence, electrification, and interconnectivity across most industries. From the perspective of PCB order scale and customer demand at different stages, PCBs can be divided into prototypes and batch boards.
The demand for PCB prototypes mainly comes from the research, development, and testing stages of customer electronic products, serving as a precursor to PCB mass production. This stage has certain professional characteristics, as PCBs enter the mass production stage after the successful development and finalization of electronic products. Therefore, prototype orders during the R&D phase exhibit characteristics of multiple varieties, small batches, and quick delivery.
PCB batch boards can be further divided into small batch boards and large batch boards based on order area size. Small batch boards are primarily used for specialized user terminal demands in communication equipment, industrial control, medical health, and automotive electronics, while large batch boards are mainly used for consumer electronics and some automotive electronics for general user terminal demands.
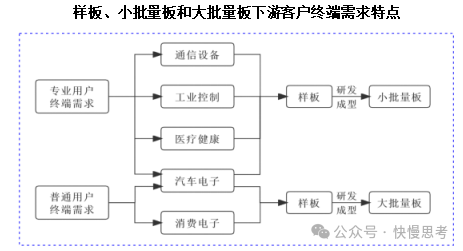
Specialized user PCB downstream application fields mainly cover enterprise-level industries such as communication equipment, industrial control, medical health, and automotive electronics, typically requiring PCB products to have high reliability, long service life, and strong traceability, which places higher demands on PCB manufacturers’ processes and materials. The downstream application fields for general consumer terminal demands mainly include consumer electronics and some automotive electronics, usually requiring PCB products to be lightweight, compact, and flexible. Due to the large demand from ordinary individual consumers and the relatively standardized nature of PCBs, there are higher production scale requirements for PCB manufacturers. Prototype and small batch board products are diverse and relatively less affected by macroeconomic disturbances.
Due to significant differences in R&D, production, management, and sales models between prototypes, small batch boards, and large batch boards, different types of PCB companies have their own characteristics in terms of customers, products, and production. The specific situation is as follows:
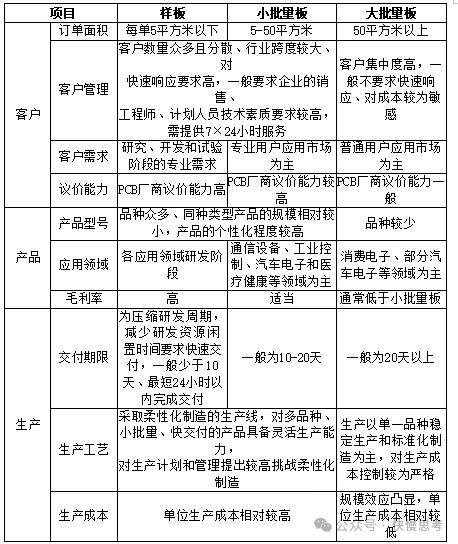
Prototypes are typically in the precursor stage before the mass production of PCB products, with order areas not exceeding 5 square meters, mainly applied in the R&D sampling, testing, and development stages, with many product models. Batch boards are in the mass production stage after the prototype development has been finalized, where small batch boards are customized based on customer needs, with many product models but smaller individual order areas, ranging from 5 to 50 square meters, mainly applied in specialized user application fields after R&D finalization, including communication equipment, industrial control, medical health, and automotive electronics; large batch board products are standardized, with fewer product models and larger individual order areas, exceeding 50 square meters, mainly applied in ordinary user terminal application fields after R&D finalization, including consumer electronics and automotive electronics.
In-Depth Analysis Report on the Printed Circuit Board, Prototype, and Small Batch Board Industry: Policies, Development Status and Trends, Competitive Landscape Full report in WORD format: Please click “Read the original text” to download, or follow our public account and reply “Report 119” to get it for free.

