Follow our WeChat public account: Mingge Network, to learn about smart home, smart office, smart monitoring knowledge, data communication products, data communication technology, AI news, AI applications, computing networks, operator information, network fundamentals, and material sharing. Welcome to follow us.

Why Pay Attention to Ethernet Cables in Renovation
In today’s era of smart home popularity, Ethernet cables serve as the “highway” for home digitization. Unlike Wi-Fi, which may experience interruptions, high-quality Ethernet cables can provide stable transmission starting from gigabit for 4K video and NAS storage. Additionally, considering the technological developments over the next decade, the cables embedded in walls should at least meet the upgrade needs of devices for the next 5-8 years while providing interference protection to avoid poor network signal quality caused by microwaves and Bluetooth devices. The 90% of household network interruptions we encounter stem from initially choosing the wrong cables or improper installation.
Classification of Ethernet Cables on the Market
First, we need to understand that the commonly used Ethernet cables are mainly divided into 6 types: Category 5 (CAT-5), Category 5e (CAT5E), Category 6 (CAT6), Category 6a (CAT6A), Category 7 (CAT7), and Category 8 (CAT8). For us, the most intuitive way is to look at the printing on the cable, which indicates the type of cable, so there is no need to worry about buying the wrong one. As for Category 7 cables, the relevant standards have not yet been established, and the Category 7 cables on the market are basically sold as enhanced Category 6 cables.
Category 5 Cable
This type has been phased out in the market, supporting 100 Mbps (Fast Ethernet), with some supporting 1 Gbps but limited by distance (usually not exceeding 100 meters).
Category 5e Cable
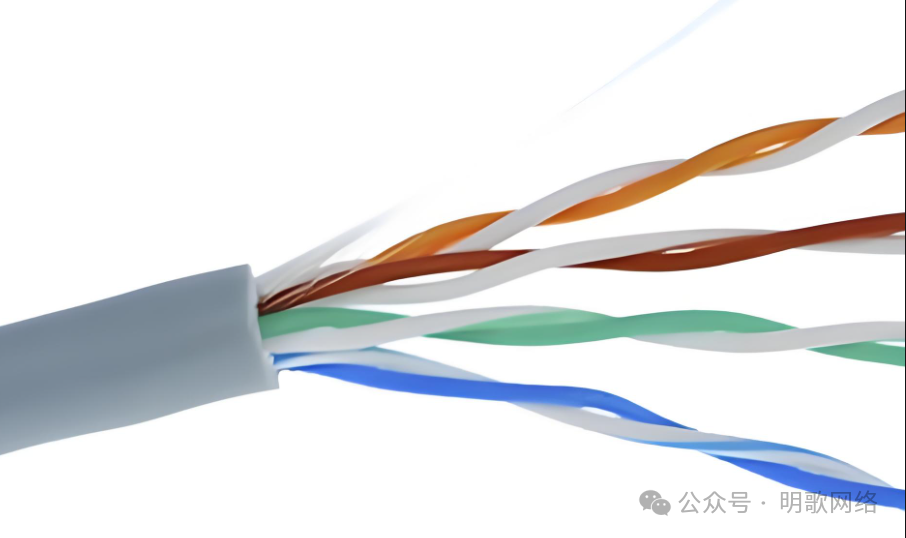
From the label on the cable, we can see the words CAT-5E, indicating that this is an enhanced Category 5 cable. It is also a 4-pair UTP twisted pair cable, with conductors mostly made of pure copper (to enhance performance), and the wire gauge is usually 24 AWG, with stricter twisting to reduce interference. It supports gigabit transmission over a distance of 100 meters.
Category 6 Cable
This type consists of 4 pairs of UTP or STP (shielded twisted pair) cables, with conductors made of pure copper, and the wire gauge is usually 23 AWG or 24 AWG (referring to the thickness of the wire). It includes internal cross-structure separators to reduce crosstalk, supporting 10 Gbps (with a distance limit of 55 meters).
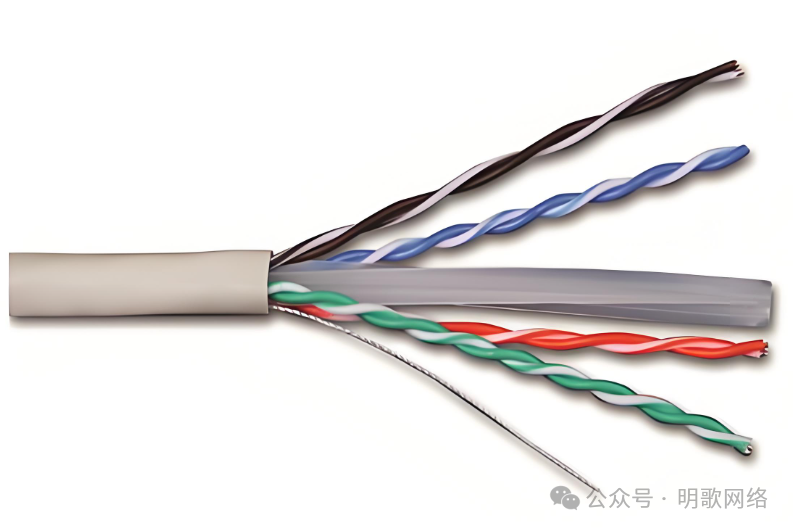
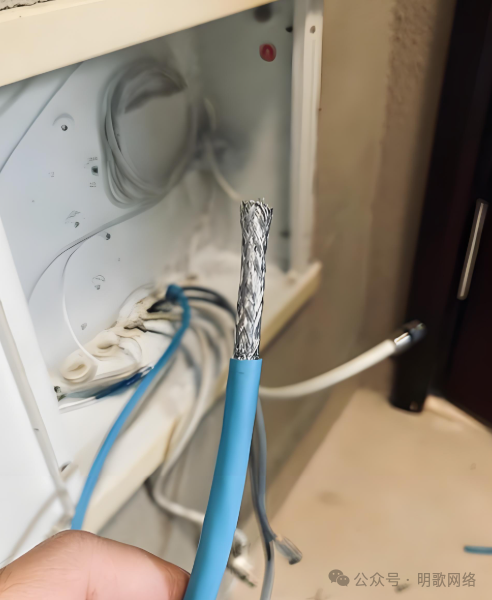
Category 6a Cable
This type consists of 4 pairs of UTP or STP cables, with conductors made of pure copper, and the wire gauge is mostly 23 AWG (referring to the thickness of the wire). The shielding is more comprehensive (such as independent shielding for each pair of wires or overall shielding), as shown in the image below, with more advanced technology. The rate can reach 10 Gbps, supporting a full distance of 100 meters.

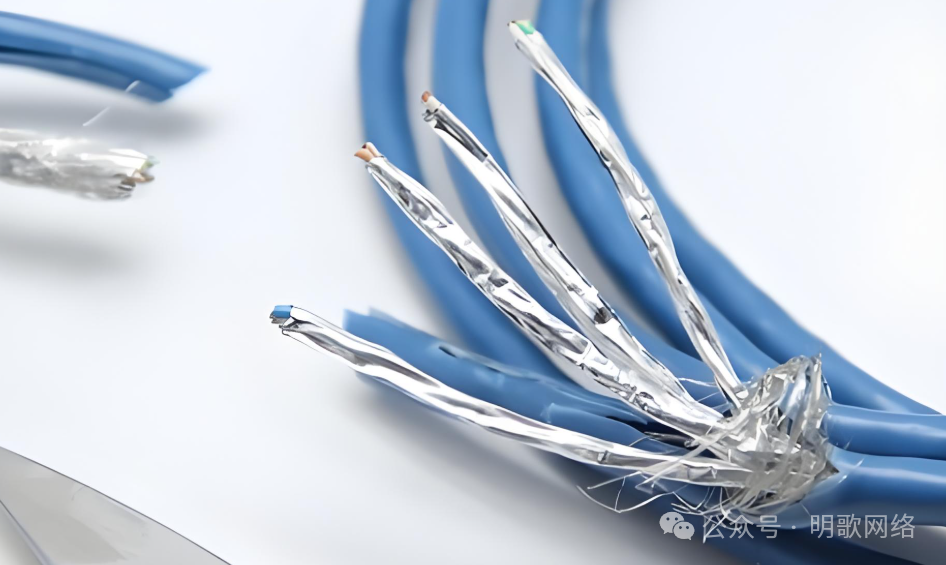
Category 7 Cable
This type supports 10 Gbps transmission (within 100 meters), and some manufacturers’ claims that “Category 7 supports 40 Gbps” are based on extreme short-distance (within 15 meters) non-standard test results in laboratories, which cannot be reliably achieved in actual engineering.

Category 8 Cable supports 25 Gbps (30 meters) or 40 Gbps (24 meters), with a bandwidth of 2000 MHz.
It requires RJ45 45/46 connectors (backward compatible with traditional devices). Of course, if you want to achieve this speed, fiber optics are recommended due to their significantly lower cost.
Differences Among Ethernet Cables on the Market
Category 5 cables are gradually being phased out as they only support 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps networks.
Category 5e cables can reach 1 Gbps over a distance of 100 meters, but do not support 10 Gbps speeds.
Category 6/6a/7 cables: speed increases to 10 Gbps.
Category 8 cables: 25 Gbps/40 Gbps.
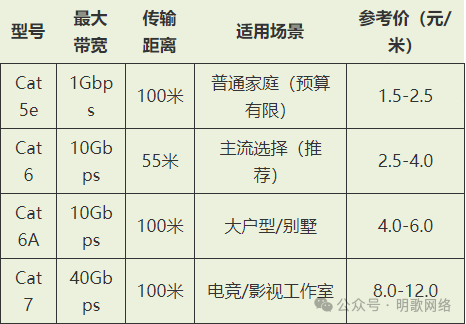
How Should We Choose?
For areas under 100㎡, choose Category 6 unshielded cables (UTP), which offer the best cost-performance ratio. For villas/duplexes, it is recommended to deploy a mix of Category 6A and fiber optics. Ordinary households do not need to pursue Category 7, as 90% of the performance will be wasted by the router.
Remember this phrase: Ethernet cables are the cheapest hidden project in renovation, yet they are the cornerstone of the internet experience for the next decade. Spending an extra 500 yuan to upgrade the cables may save you 5000 yuan in future repair costs.
Please open in the WeChat client