
Author: Ma Zhi
Published by the IoT Think Tank
Please cite the source when reprinting
—— [Introduction] ——
The IoT Think Tank will start publishing a series of articles titled “Exploring Domestic and International IoT Platforms” written by Mr. Ma Zhi every Friday afternoon in the second article of the week.
The IoT Think Tank will start publishing a series of articles titled “Exploring Domestic and International IoT Platforms” written by Mr. Ma Zhi every Friday afternoon in the second article.
—— Domestic ——
(1) Baidu’s Integration with IoT Hub
(2) Alibaba Cloud IoT Suite
(3) QQ IoT · Smart Hardware Open Platform
(4) JD Micro Link
(5) Smart Cloud IoT Cloud Service Platform and Smart Hardware Self-Development Platform
(6) Qingke Cloud FogCloud
(7) Ablecloud IoT Self-Development and Big Data Cloud Platform
—— International ——
(1) Amazon AWS IoT
(2) Microsoft Azure IoT
(3) IBM Watson IoT
Today marks the first part of this series, introducing Baidu’s integration with IoT Hub.


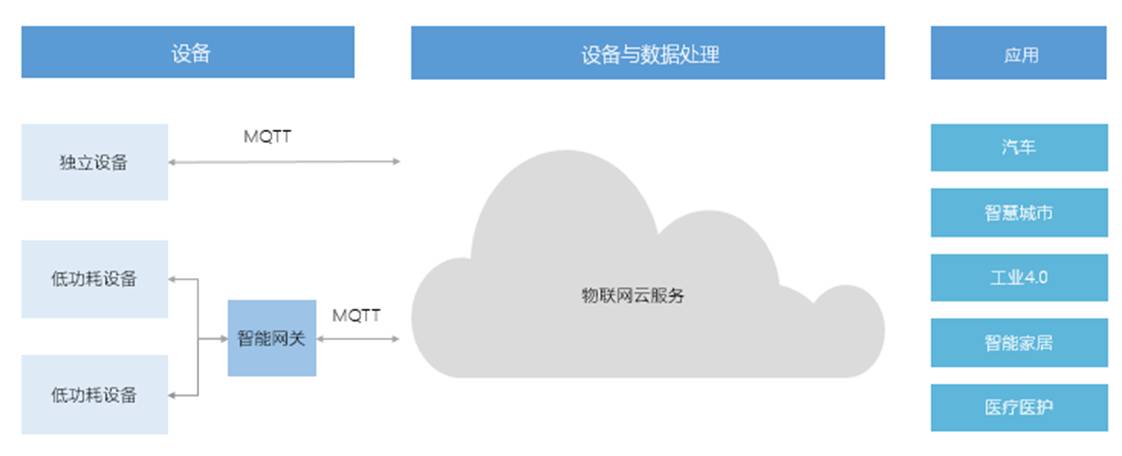
Integration with IoT Hub – Architecture
-
Fully managed cloud service that helps establish a secure and reliable bidirectional connection between devices and the cloud.
-
Supports massive data collection, monitoring, fault prediction, and various IoT scenarios.
Integration with IoT Hub – Features
-
Communication Protocol: Supports MQTT
-
Data Security: Device-level authentication, policy authorization; bidirectional secure connection, SSL transmission
-
Development Languages: Supports multiple programming languages, compatible with mainstream hardware devices
1. Supports C, C#, Python, Java, PHP, etc.
2. Supports CLI command-line tools (Python)
-
Analysis Services: Integrates with Baidu Big Data Services
Integration with IoT Hub – Concepts
|
Concept |
Description |
|
MQTT |
MQTT is a protocol based on a binary message publish/subscribe model, originally proposed by IBM, and has now become an OASIS standard, more suitable for large-scale M2M communication. |
|
endpoint |
Service instance of IoT Hub, representing a complete IoT Hub service. |
|
thing |
Represents an IoT Hub device; users can create one or more things within each endpoint. |
|
principal |
A principal is an abstract concept representing the identity of a device (thing). Each thing can be bound to a principal, and each principal has a policy permission. |
|
policy |
Sets the corresponding policy for the identity principal; one principal corresponds to one policy. |
|
permission |
Sets a set of permissions for each policy, including topics and operation permissions for that topic. |
|
topic |
Each policy needs to specify a topic item; before using the IoT Hub service, a topic name must be created for the subscription and publication of information, which applies to the MQTT client. The topic rules allow strings to contain a wildcard ‘#’; for example, ‘temperature/#’ matches all topics with the prefix temperature; a standalone ‘#’ matches all topics. |
|
operation |
Operation permissions for the topic. Currently, based on the MQTT protocol, IoT Hub supports creating publish (PUBLISH) and subscribe (SUBSCRIBE) permissions. |
MQTT Protocol
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is a message transmission protocol based on a client-server architecture with a publish/subscribe model. Its design philosophy is lightweight, open, simple, and standardized, making it easy to implement. These characteristics make it a great choice for many scenarios, especially for constrained environments such as machine-to-machine (M2M) communication and Internet of Things (IoT) environments.
Client
1. Publishes application messages to other relevant clients.
2. Subscribes to request receiving relevant application messages.
3. Unsubscribes to remove the request for receiving application messages.
4. Disconnects from the server.
Server
1. Accepts network connections from clients.
2. Accepts application messages published by clients.
3. Processes clients’ subscription and unsubscription requests.
4. Forwards application messages to clients that meet the conditions of subscription.
MQTT vs HTTPS:
Throughput: 93 times
Data transmission power consumption: 1/11
Data reception power consumption: 1/170
Connection maintenance power consumption: 1/2
Network overhead: 1/8
Integration with IoT Hub – Operational Process
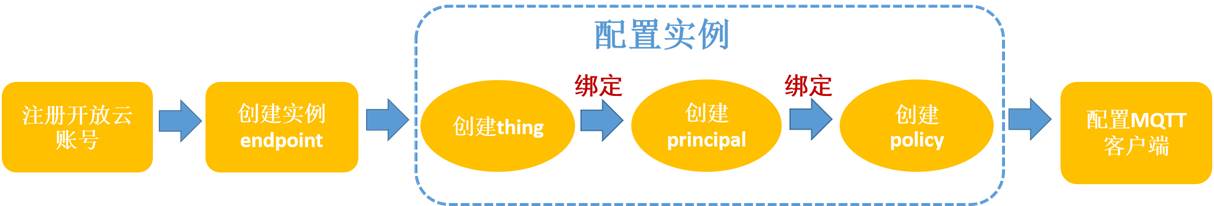
Currently, each account can only create 2 endpoints, 100 things, and 100 principals.
Integration with IoT Hub – Connection Types
IoT Hub provides three default connection methods for each instance
TCP: Port 1883, does not support data encryption, can connect via MQTT.fx client.
SSL: Port 1884, supports SSL/TLS encrypted transmission, connects via MQTT.fx client.
WSS: Port 8884, supports WebSocket browser connection, also includes SSL encryption.
tcp://yourendpoint.mqtt.iot.gz.baiduce.com:1883
ssl://yourendpoint.mqtt.iot.gz.baiduce.com:1884
wss://yourendpoint.mqtt.iot.gz.baidubce.com:8884
Integration with IoT Hub – Operation and Maintenance Interface
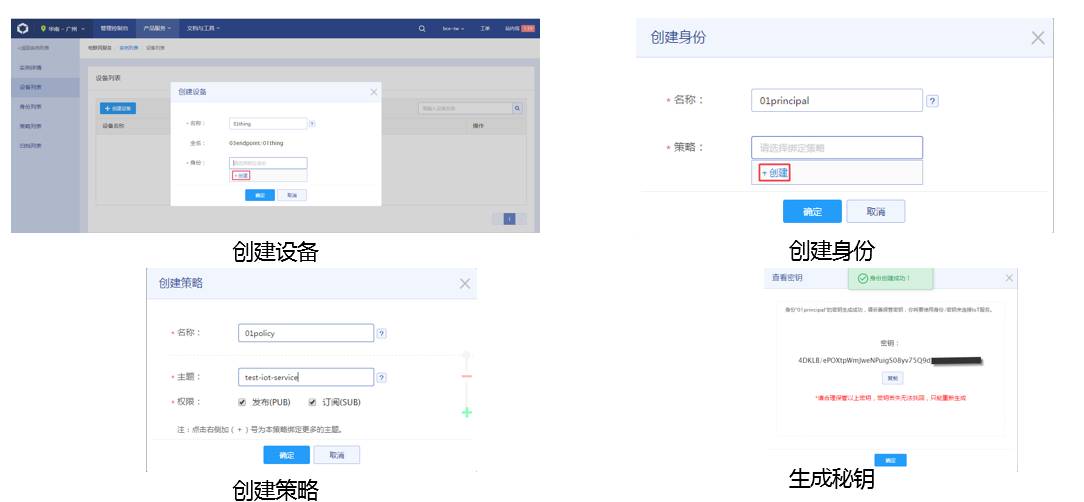
Integration with IoT Hub – MQTT Client Types
-
Websockets Client: An MQTT client developed by Baidu Open Cloud based on the browser.
-
MQTT.fx: A mainstream MQTT client that can quickly verify whether it can communicate with IoT Hub services to publish or subscribe to messages.
-
Paho: An open-source MQTT client implementation provided by the Eclipse Foundation, which supports Baidu Open Cloud’s integration with IoT Hub services for device interconnection and IoT applications.
Integration with IoT Hub – Paho Client Source Code Example

Integration with IoT Hub – Connecting with Big Data Analysis Services

Previous Popular Articles (Click on the title to read directly):
-
“[Heavyweight] IoT Industry Panorama Report, the first domestic IoT industry two-dimensional perspective panorama”
-
“Exclusive Interview with Academician Wu Hequan: Four Good News Indicate That the Development of IoT Has Entered the Right Track”
-
“China’s First Low-Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) Market Report Released: Where is the Next IoT Opportunity? [Text Version]”
-
“A Cartoon Explains: What is LoRa Behind NB-IoT That Everyone is Talking About?”
-
“A Cartoon Explains: Besides WiFi and Bluetooth, What Can the Recently Popular NB-IoT Do?”“
-
“McKinsey’s Heavyweight Report: How Can Enterprises Tap into the Value of ‘Industry 4.0’? (Collection Edition)”
