
On the afternoon of April 16, the “5G NB-IoT Billion Journey” online industry summit was officially held, with leaders from numerous NB-IoT industry chain companies such as Huawei, HiSilicon, China Mobile IoT, China Unicom IoT, Tianyi IoT, MediaTek, Unisoc, and Quectel participating in the event and sharing their views on the NB-IoT industry and related cases.
What is NB-IoT, and what advantages does it have compared to other IoT technologies?
NB-IoT (Narrow Band Internet of Things) is an emerging technology in the IoT field based on cellular narrowband IoT, supporting low-power devices in wide-area cellular data connections, also known as Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN).
As early as May 2014, Huawei and Vodafone first proposed NB M2M technology, which later evolved into NB-CIoT in May 2015. In July 2015, Nokia, Ericsson, and Intel proposed NB-LTE technology, and subsequently, 3GPP began to formulate standards, officially establishing the NB-IoT standard in July 2016.
NB-IoT defines the concept of building a dedicated IoT network, with specific application scenarios including public utility applications, industrial fields, agricultural fields, and consumer fields. Among them, public utility application scenarios, such as livelihood projects and smart cities (water meters, smart parking, smart streetlights, gas pipeline systems, monitoring, environmental protection, etc.), can effectively reduce costs through NB-IoT. As the agricultural sector develops towards intensification, high value-added, and scale, NB-IoT can provide low-cost monitoring modes for temperature, humidity, etc. In the consumer field, smart homes, shared bicycles, remote medical care, and smart wearables can be realized through NB-IoT.
In addition to NB-IoT, there are also low-power IoT technologies such as LoRa, SigFox, and eMTC (LTE-M).
Low-power IoT technologies can be divided into two categories: one operates in unlicensed spectrum, such as LoRa and SigFox; the other operates in licensed spectrum, supported by 3GPP’s 2/3/4G cellular communication technologies, such as NB-IoT and eMTC.
Among them, LoRa WAN is a network standard promoted by various industry alliances, providing open technology; Sigfox is a technology developed by the French company of the same name, which controls the construction and operation of the core network and deploys networks globally. Both LoRa and Sigfox feature long-range, low-power characteristics, extending battery life and enabling large-scale information transmission, and both use the unlicensed Sub-1GHz ISM band without additional licensing fees.
Compared to LoRa and SigFox technologies, NB-IoT and eMTC technologies are strongly promoted by operators, using licensed GSM and LTE frequency bands, and do not require redeployment of networks; existing 4G base stations and related equipment can be used with just software updates.
Although NB-IoT and eMTC use licensed spectrum and require licensing fees, they have the core advantages of communication assurance and unlimited data transmission. In terms of advantages, NB-IoT and eMTC have less interference due to the use of licensed bands, ensuring high communication quality and message security. Moreover, compared to LoRa and SigFox, NB-IoT and eMTC do not limit the number of data transmissions, while LoRa and Sigfox have daily transmission limits, making them suitable for fields without real-time communication needs.
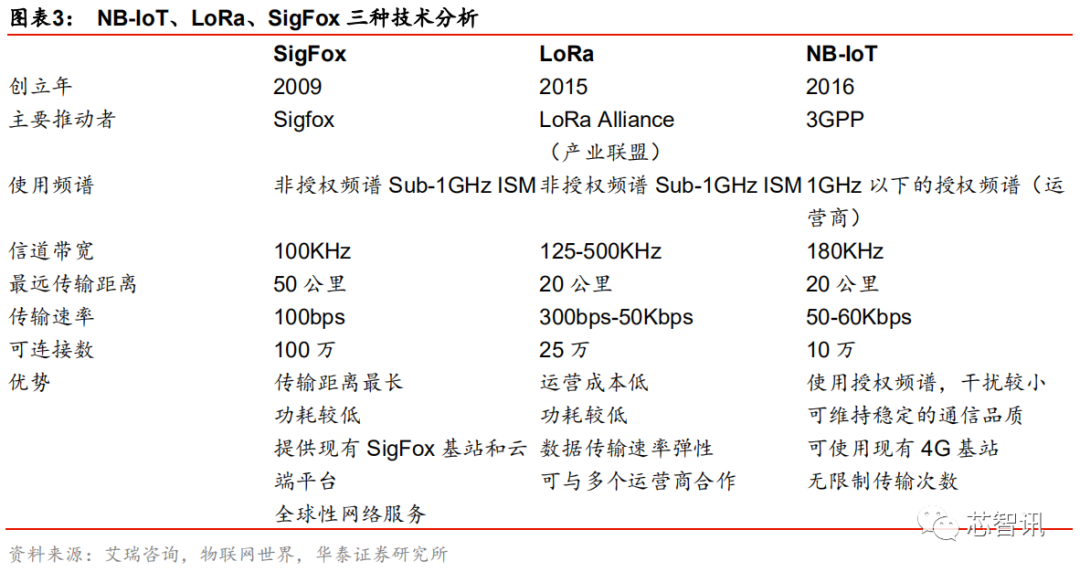
Although NB-IoT and eMTC have many similarities, there are also significant differences between the two.
eMTC is also an IoT access technology based on LTE evolution, using licensed spectrum like NB-IoT, but eMTC has significant advantages in mobility, latency, and throughput: latency is less than 100ms, and the maximum uplink and downlink rate can reach 1Mbps. Although NB-IoT has higher latency, reaching 10s, and a maximum uplink and downlink rate of only 60kbps and 20kbps, it has a larger access capacity. Currently, a single NB-IoT network base station can connect up to about 100,000 terminal devices, while eMTC can only connect tens of thousands of devices. In addition, NB-IoT can achieve lower costs and longer battery life.
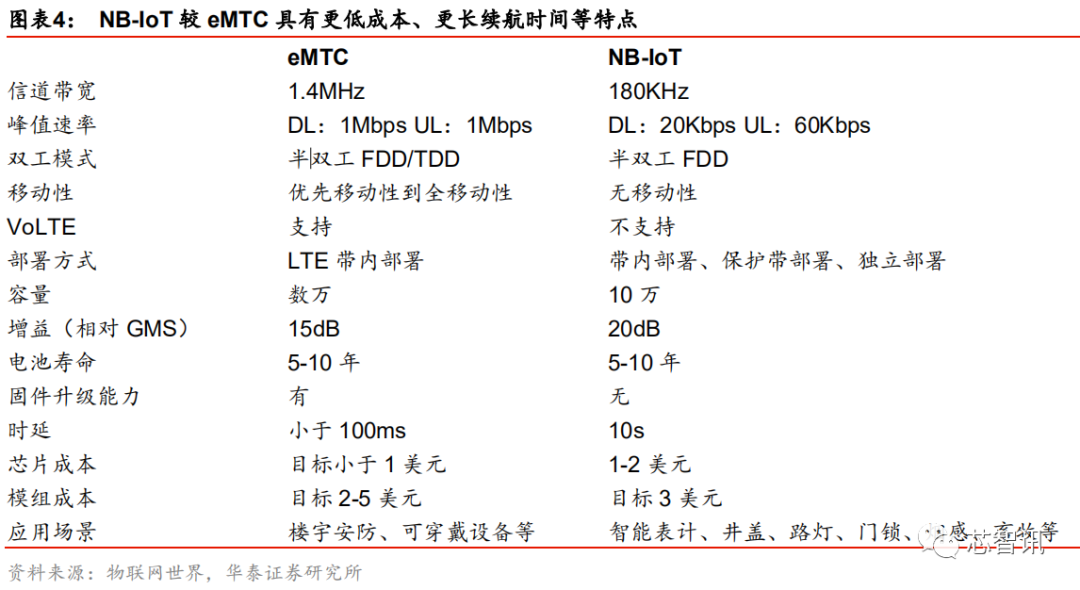
In summary, in IoT application scenarios with low data transmission rates and low latency requirements but high cost and power consumption requirements, NB-IoT has a greater advantage.
Accelerated Retirement of 2/3G Networks Will Accelerate the NB-IoT Market Explosion
In the mobile communication market, with the continuous upgrading of communication technologies, operators’ capital expenditures and operating expenses are also continuously rising, while the available spectrum is becoming increasingly tight, especially in countries and regions where spectrum needs to be auctioned, making spectrum resources increasingly expensive and scarce. The gradual retirement of 2G or 3G networks has become a solution for global operators.
Globally, since 2008, operators in countries such as Japan, New Zealand, Thailand, and Ecuador have begun shutting down 2G networks. Starting in 2017, global operators began intensively shutting down 2G networks: Singapore’s three major operators M1, Singtel, StarHub; US operators AT&T, Verizon; Canadian operators Bell, Telus, and Sask Tel; Australian operators Optus, Vodafone, etc., all successively shut down their 2G networks in 2017.
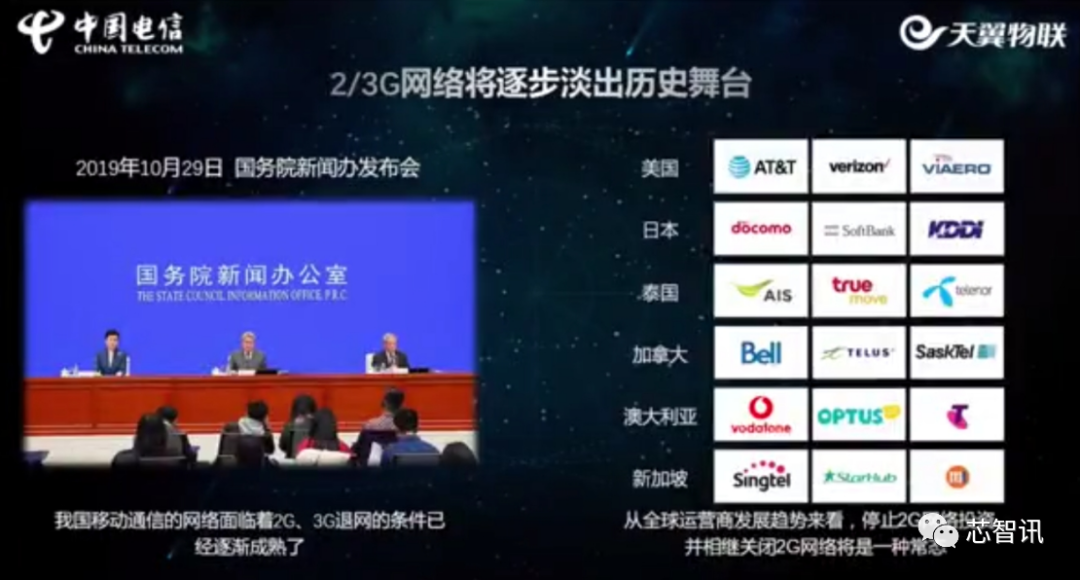
After entering 2018, more operators announced the initiation of 2G/3G spectrum clearing and retirement. Major operators in countries such as China, the United States, Thailand, Mexico, Brazil, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Russia, and Vietnam have successively announced the retirement timelines for 2G/3G networks.
Specifically in China, in recent years, the three major domestic operators have begun the gradual clearing and retirement of 2G/3G networks. Subsequently, in October 2019, the spokesperson for the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, Wen Ku, stated that the conditions for the retirement of 2G/3G networks in China have gradually matured. This clearly indicates that the retirement of 2G/3G networks in China will further accelerate.
The clearing and retirement of 2/3G networks or their reallocation to LTE networks will be very beneficial for operators’ cost control. This also means that a large number of low-speed network applications originally relying on 2G networks will need to switch to NB-IoT networks.
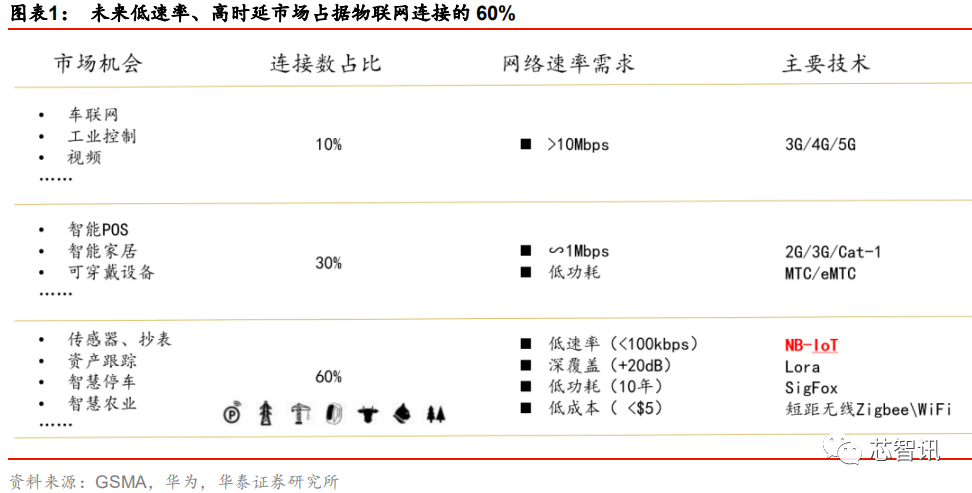
According to industry estimates, based on high, medium, and low network speeds, the distribution of cellular IoT connections is approximately: high-speed 10%, medium-speed 30%, low-speed 60%. NB-IoT primarily targets the 60% low-speed IoT market demand, which undoubtedly represents a huge market opportunity.
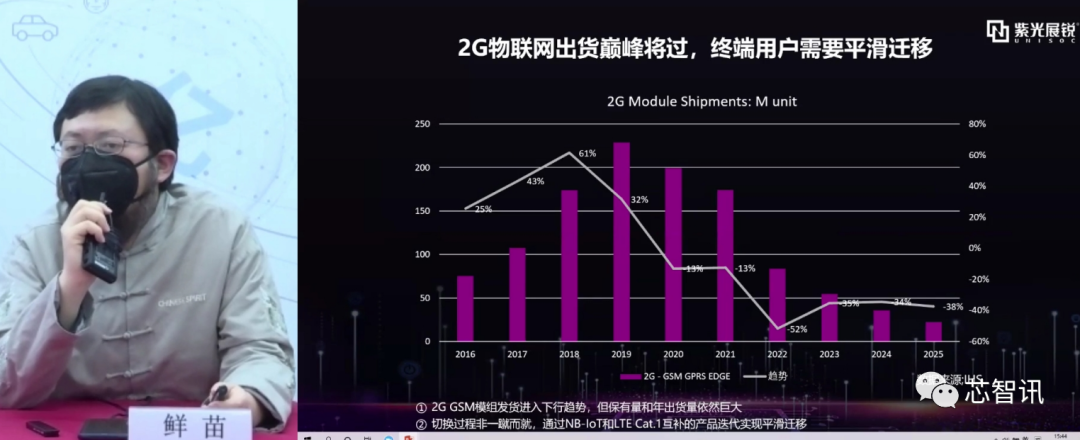
Vice President of Unisoc’s Industrial IoT, Xian Miao, also stated that with the accelerated retirement of 2G networks, the peak shipment of 2G GSM IoT modules will also pass. According to IHS data, shipments of 2G IoT modules reached about 230 million at their peak in 2019, and will begin to decline rapidly in 2020. However, the retained volume and shipment volume in the coming years will still be significant. Clearly, these 2G IoT users need operators to provide a good network for a smooth migration, and NB-IoT will undoubtedly be an excellent choice.
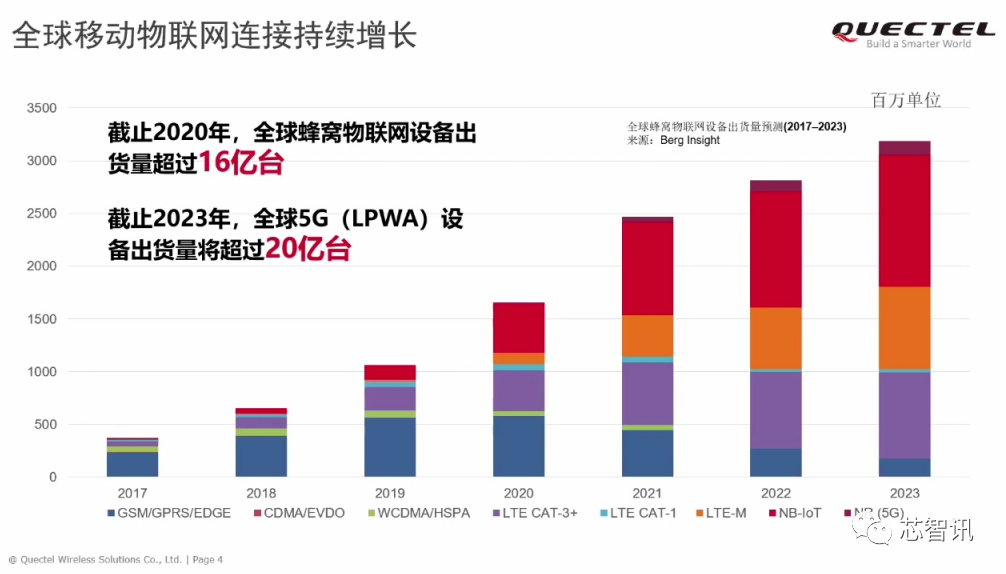
According to Berg Insight’s forecast, global shipments of cellular IoT devices will exceed 1.6 billion in 2020, with NB-IoT devices accounting for nearly 30%. It is expected that by 2023, global LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network) devices will exceed 2 billion, with NB-IoT devices accounting for more than half. This indicates the vast market prospects and rapid development speed of the NB-IoT market in the future.
Current Development Status of the NB-IoT Industry
Although eMTC and NB-IoT are both low-power IoT technologies developed around the same time based on cellular networks, and eMTC has advantages such as higher transmission rates, low latency, support for mobility, and VoLTE voice communication, it has not been widely adopted. Additionally, the inherent existence of 3G networks by operators has created a certain degree of substitutability between the two, which has hindered the development of eMTC. In contrast, NB-IoT seems to be more favored by operators and users due to its advantages in low power consumption, low cost, and deep coverage, thus developing faster.
1. The NB-IoT Layout of the Three Major Operators
According to data released by China Telecom, as of 2019, 71 countries worldwide have invested in the construction of 129 mobile IoT networks, of which 93 are NB-IoT networks.

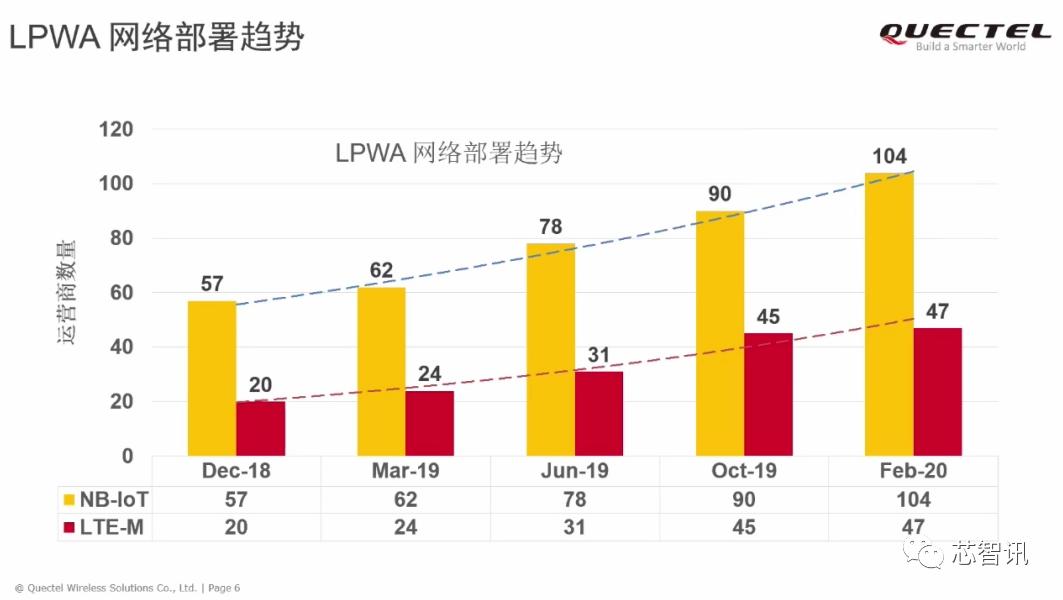
According to data released by Quectel as of February 2020, among the low-power wide area networks deployed by global operators, NB-IoT networks have reached 104, while eMTC networks only have 47.
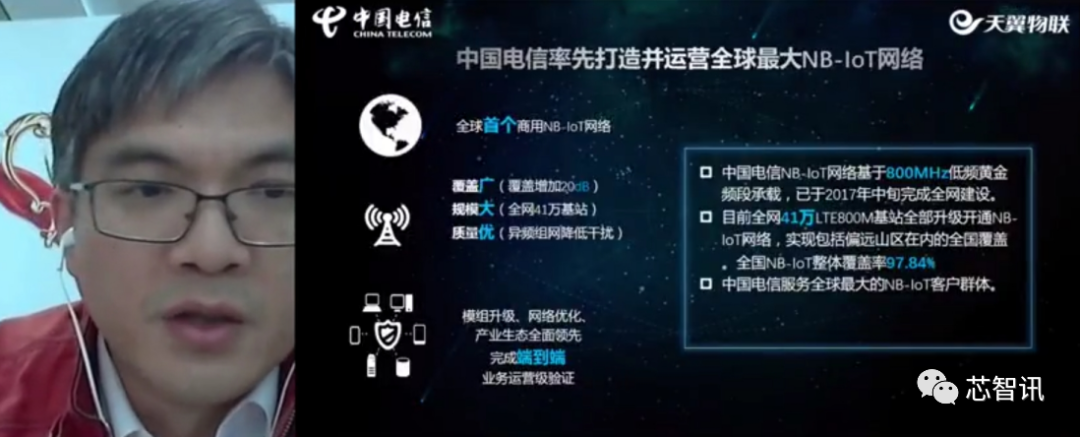
Specifically regarding domestic operators’ deployment of NB-IoT, according to Chen Jianhua, head of the Tianyi IoT Solutions Department, China Telecom has taken the lead in building the world’s largest NB-IoT network, with all 410,000 LTE 800MHz base stations upgraded to open NB-IoT networks, achieving nationwide coverage, including remote mountainous areas, with an overall coverage rate of 97.84%. In September 2019, China Telecom’s smart gas service became the first NB-IoT industry application to exceed 10 million shipments.
△ Chen Jianhua, head of the Tianyi IoT Solutions Department
General Manager of China Mobile IoT Integrated Circuit Innovation Center, Xiao Qing, stated that China Mobile IoT has gathered 1,500 partners in the NB-IoT field, covering 27 industry sectors and 8 major industrial fields, forming over 340 industry solutions. They have assisted 693 customers in 12 industries to access the NB-IoT network, with self-developed NB-IoT modules exceeding 12 million shipments.

△ Xiao Qing, General Manager of China Mobile IoT Integrated Circuit Innovation Center
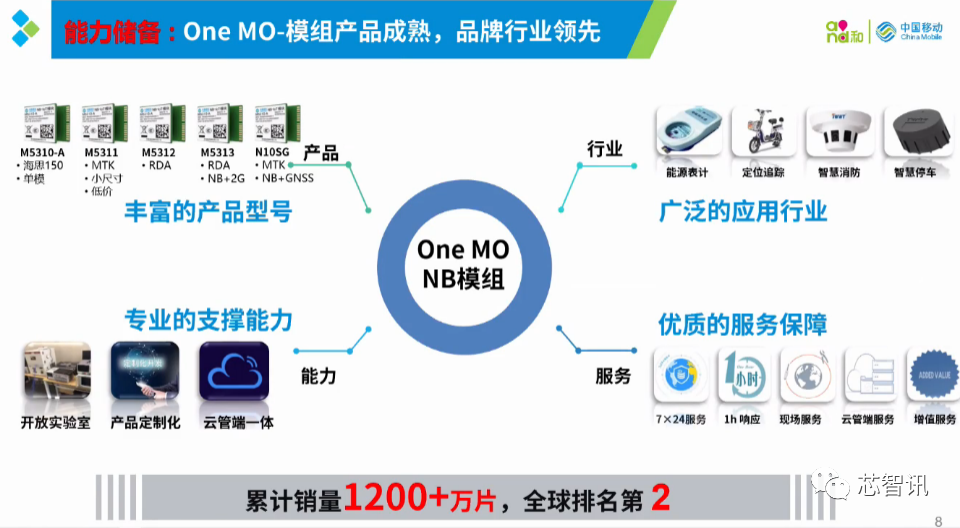
△ China Mobile’s One MO NB-IoT module has shipped over 12 million units
In comparison to the vigorous deployment and promotion of NB-IoT by China Telecom and China Mobile, China Unicom appears less proactive. According to Li Kai, Chief Product Officer of China Unicom IoT Company, the NB-IoT network of China Unicom mainly relies on 8 core city nodes to achieve nationwide network coverage.

△ Li Kai, Chief Product Officer of China Unicom IoT Company
Regarding the pricing of NB-IoT network services, the standard pricing for NB-IoT services among the three domestic operators is generally similar, with prices around 20 yuan per household per year, and discounts are given based on the user’s duration of service and project scale.
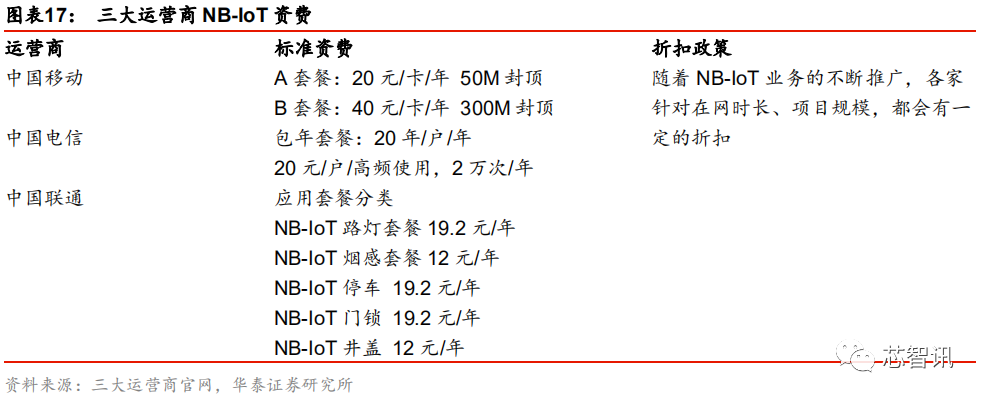
Due to the low investment and maintenance costs of NB-IoT at the network layer, it can be upgraded and transformed based on the existing LTE network, and the high coverage rate of domestic 4G base stations means that for operators, the profit margin of NB-IoT will be higher than that of 4G.
2. Chip Manufacturers Entering the Market
For the development of the NB-IoT industry, the performance and cost of chips and modules are crucial factors. Currently, major NB-IoT suppliers include Huawei HiSilicon, Qualcomm, Unisoc, and ZTE Microelectronics. At this conference, Huawei HiSilicon and Unisoc also introduced their upcoming latest NB-IoT chips.
As a participant in the formulation of the NB-IoT standard, Huawei HiSilicon has been tirelessly promoting NB-IoT chips. In June 2017, Huawei’s first NB-IoT chip based on the 3GPP R13 standard, the Boudica 120 chip, achieved mass production and shipment, with commercial modules provided by ublox and Quectel. Subsequently, in 2018, Huawei launched the Boudica 150 chip based on the 3GPP R14 standard, which has stronger functionality and lower power consumption compared to the previous Boudica 120.
At this conference, Yang Guoxing, head of smart IoT chips at Shanghai HiSilicon Technology Co., Ltd., revealed that as of now, the HiSilicon Boudica 120/150 series NB SoC chips have shipped over 50 million units, serving more than 70 operators in over 50 countries and regions.

In addition, Yang Guoxing also introduced the more advanced NB-IoT chip Boudica 200, which will be launched soon based on the 3GPP R15/16 standards.

It is reported that the Boudica 200 has six major highlights and advantages: 1. Lower power consumption, with sleep and RX state power consumption reduced by 50%; 2. Higher integration, with the BoM count reduced by 50%; 3. HiSilicon’s data from tens of millions of terminal industries allows for better optimization of solutions, improving performance and reducing power consumption; 4. An independent security subsystem that comprehensively enhances security capabilities while integrating SIM functionality, reducing overall costs; 5. Integration of BLE5.0 for easier near-end maintenance and testing, and integration of GNSS for low-cost positioning applications; 6. Support for 5G 3GPP R15/16 standards, with superior performance in latency, power consumption, and coverage.
Yang Guoxing stated that the Boudica 200 chip will start supporting alpha customers for Design-In in June this year and will be commercially shipped in the fourth quarter, enabling 1 billion LPWAN connections.
Qualcomm, also a participant in the NB-IoT standard formulation, has a different strategy from Huawei HiSilicon. Qualcomm believes that in the face of significant uncertainty in IoT development at the time, launching multi-mode chips compatible with various IoT technologies is undoubtedly a more stable approach. Therefore, in 2016, Qualcomm launched the MDM9206 multi-mode IoT chip supporting eMTC/NB-IoT/GSM, with integrated RF supporting 15 LTE frequency bands, covering most regions of the world. However, this also makes its cost relatively high.
Additionally, Unisoc’s RDA8908 (Spring Ivy 8908) dual-mode IoT chip supporting 2G and NB-IoT was launched in 2017, followed by the Spring Ivy 8908 in 2018. At this conference, Unisoc’s Vice President of Industrial IoT, Xian Miao, also introduced the latest NB-IoT chip Spring Ivy 8811, which will be launched in August this year.
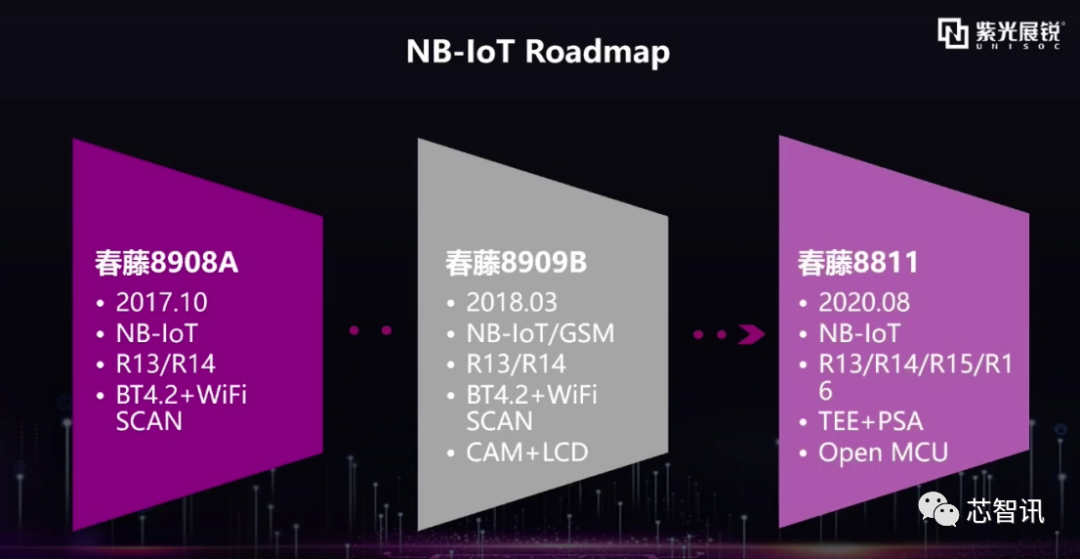
It is reported that the Spring Ivy 8811 will support the latest 3GPP R15/16 standards, as well as TEE+PSA security specifications, and support Open MCU design. However, more detailed information has not been disclosed by Unisoc.
In addition to the NB-IoT chips mentioned above from Qualcomm, Huawei HiSilicon, and Unisoc, there are also ZTE Microelectronics’ Wisefone7100 and MediaTek’s MT2625/2621.
It is worth mentioning that at this summit, Su Weikun, Senior NB Chip Planner at MediaTek, revealed that MediaTek’s R13 standard NB IoT chip achieved very good results in real-world testing in vehicle tracking scenarios in conjunction with Huawei base stations.
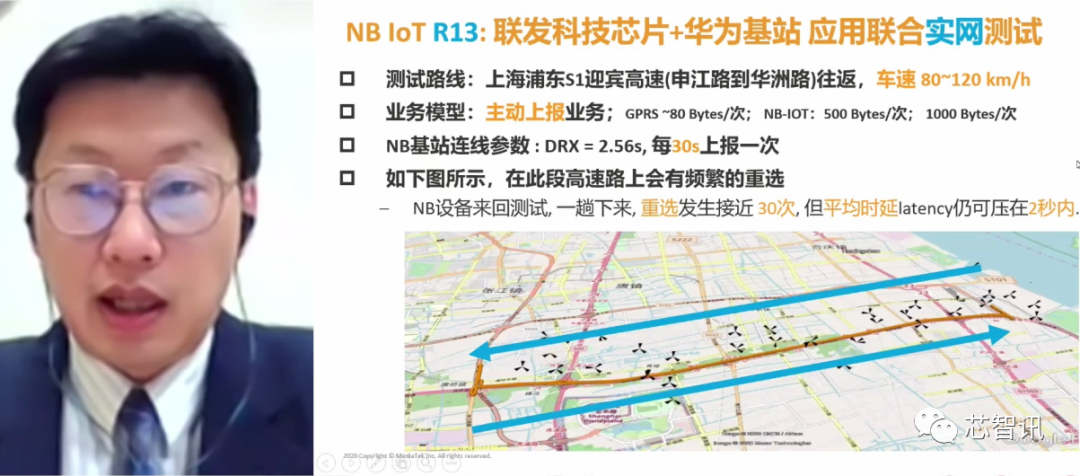
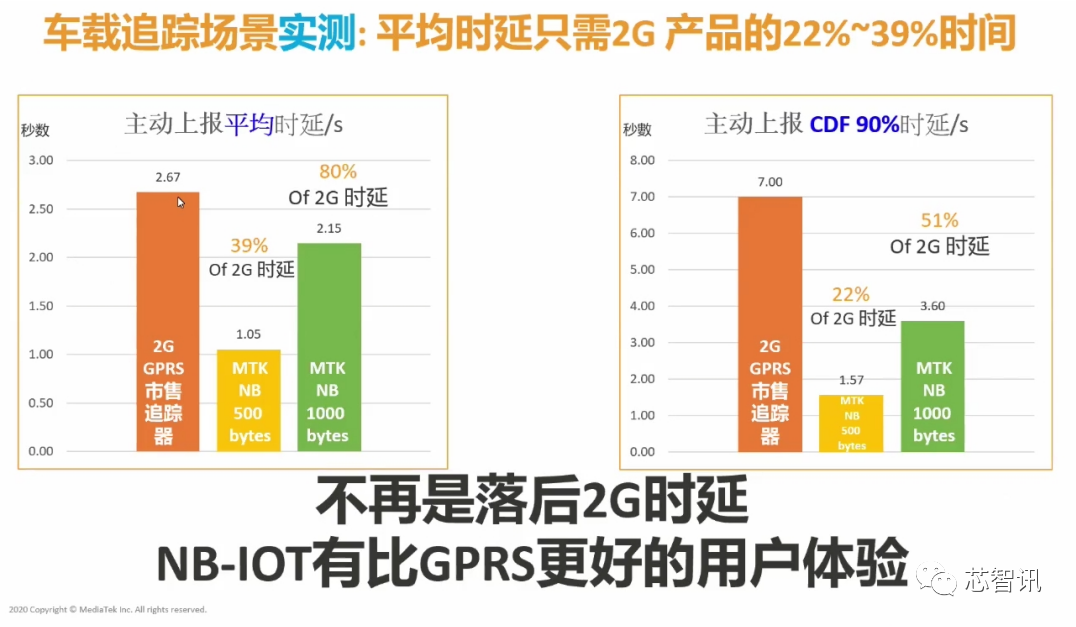
As mentioned earlier, the R13 standard-based NB-IoT is mainly suitable for non-mobile, low-speed, low-power, and low-latency scenarios, and is not suitable for mobile and low-latency scenarios. However, MediaTek has optimized its NB-IoT chip to achieve applications in mobile scenarios such as vehicle tracking, with average latency reduced to only 22%-39% of the time.
3. NB-IoT Module Prices Have Dropped Below 20 Yuan
From the price trend of NB-IoT modules, between 2017 and 2019, module prices dropped from 20 USD to 5 USD. This decline is closely related to the efforts of chip and module manufacturers, as well as the operators’ strong promotion and substantial subsidies.
In the early stages of industry development, operators successively released communication module subsidy policies. In October 2017, China Telecom launched the “Universe’s First Standard,” offering a generous subsidy of 30 yuan per unit, resulting in post-subsidy module prices dropping to 36 yuan per unit. Subsequently, in November 2017, China Mobile announced a 1 billion yuan subsidy plan for NB-IoT modules at the Global Partner Conference, with individual module subsidies ranging from 46 yuan to 29 yuan, directly driving a rapid increase in module shipments.
According to the Secretary-General of the China NB-IoT Industry Alliance, Xie Yunzhao, at the 2019 China NB-IoT Industry Development Conference, it is expected that the price of NB modules will further drop to 3 USD (approximately 21 yuan) in 2020, matching the price of 2G modules. At this industry summit, many guests unanimously stated that the price of NB-IoT modules has been controlled below 20 yuan, with some quotes even as low as over ten yuan. Lower costs can allow the NB-IoT industry applications to enter a rapid development phase.
4. The Number of NB-IoT Users in China Exceeds 100 Million
In terms of the number of NB-IoT users and industry applications, according to data shared by Huawei, as of January 2020, global NB-IoT users exceeded 100 million, and in February 2020, the number of NB-IoT users in China also surpassed 100 million. Clearly, China’s NB-IoT user base occupies a significant proportion globally. Additionally, the number of global NB-IoT users grew from 2 million to the first 30 million in 12 months, then increased to 60 million in just 8 months, and the time taken to reach 90 million was further shortened to 4 months. The development speed of the NB-IoT network far exceeds that of 2/3/4G networks.
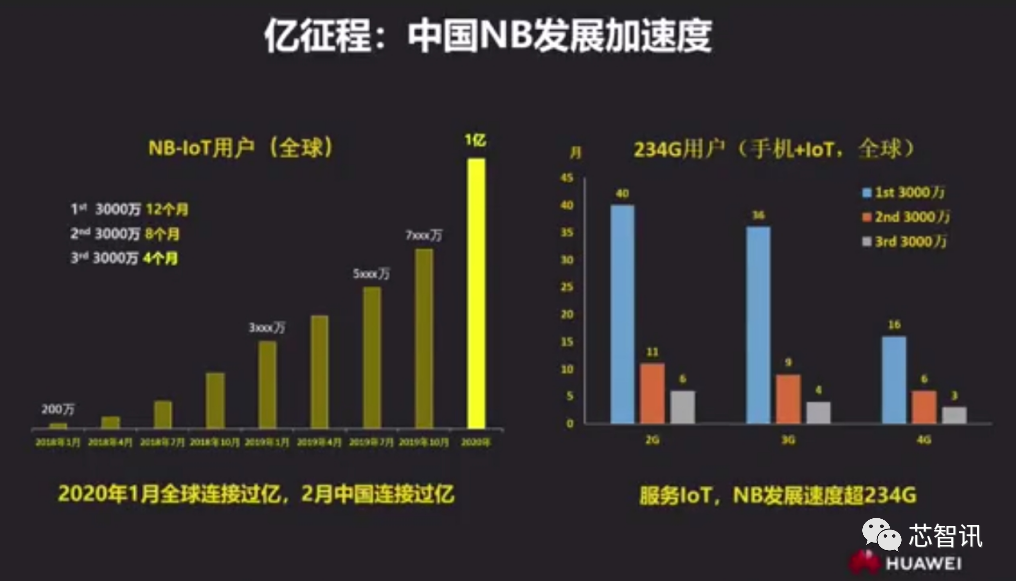

Yang Tao, Vice President of Huawei’s China Operator Business Department, stated, “Yesterday, NB-IoT has entered 40 million industries, especially in the smart gas meter and smart water meter fields, achieving a shipment of 10 million units. In the smart electric vehicle and smart fire protection fields, shipments have also reached 6 million. Additionally, in fields such as door locks, heat meters, and streetlights, shipments have reached the million level. Today, NB-IoT is accelerating intelligence in smart homes, smart factories, consumer electronics, and logistics tracking. Tomorrow, NB-IoT will incubate 100 application scenarios. Through the integration of things, cloud, and applications, operators and industry customers will achieve mutual commercial success.”
According to Sun Yanming, Deputy General Manager of Quectel, the shipment of Quectel’s NB-IoT modules has exceeded 35 million units, with 70% in the domestic market and only 30% in overseas markets.

In the 5G Era, NB-IoT Continues to Evolve
In the IoT era, NB-IoT will be one of the main technical standards for low-power wide-area IoT. Standardization is of great significance for the further popularization of IoT. Currently, the NB-IoT standard is continuously evolving, and with the arrival of the 5G era, the NB-IoT standard will also be incorporated into 5G.
Previously, NB-IoT was mostly based on the 3GPP R13 version, and last year, many have begun upgrading to the R14 version, which not only improved uplink and downlink rates by 5-7 times but also enhanced multi-carrier performance, increasing concurrent capabilities by 2-8 times, with MR measurement reporting and coverage visualization further enhanced, and QoS differentiated services improved.
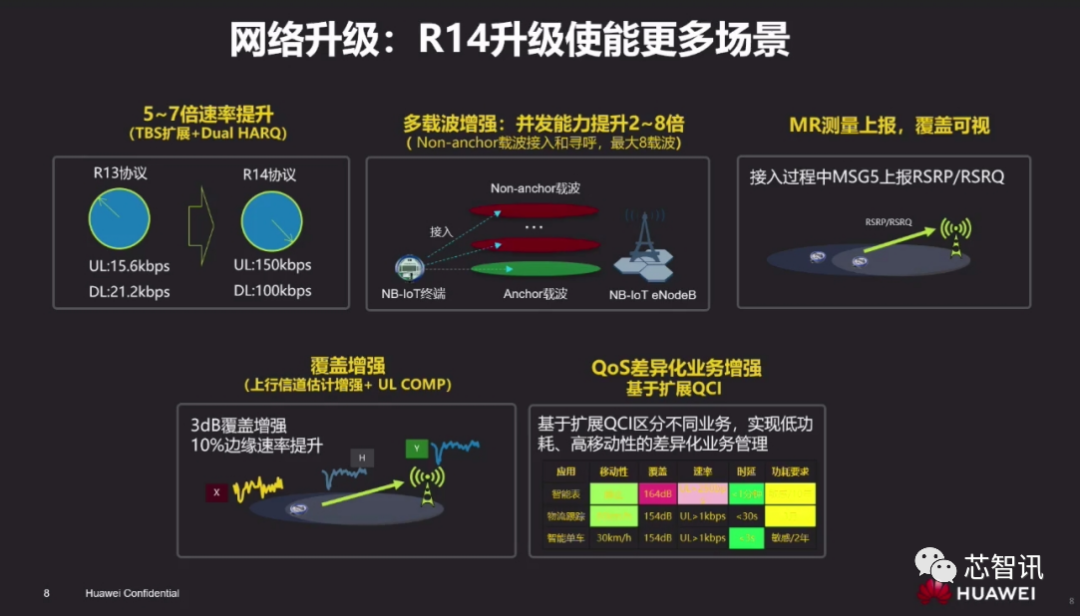
With the large-scale commercial use of 5G this year, the promotion of one of the three major scenarios of 5G business, massive machine-type communications (mMTC), is also accelerating, which is the direction of continuous evolution for NB-IoT technology.


Currently, NB-IoT in the R15 version can support coexistence with NB-IoT and 5G NR air interfaces, and the R16 version will support NB-IoT access to the 5G core network. In July 2019, 3GPP officially submitted a proposal for 5G candidate technology standards to ITU-R (International Telecommunication Union), and NB-IoT technology was officially included in the 5G candidate technology set, submitted jointly with NR to ITU-R. According to the latest information, in June 2020, NB-IoT will officially become an ITU 5G standard, and the continuous evolution of NB-IoT standardization will promote the development of IoT.
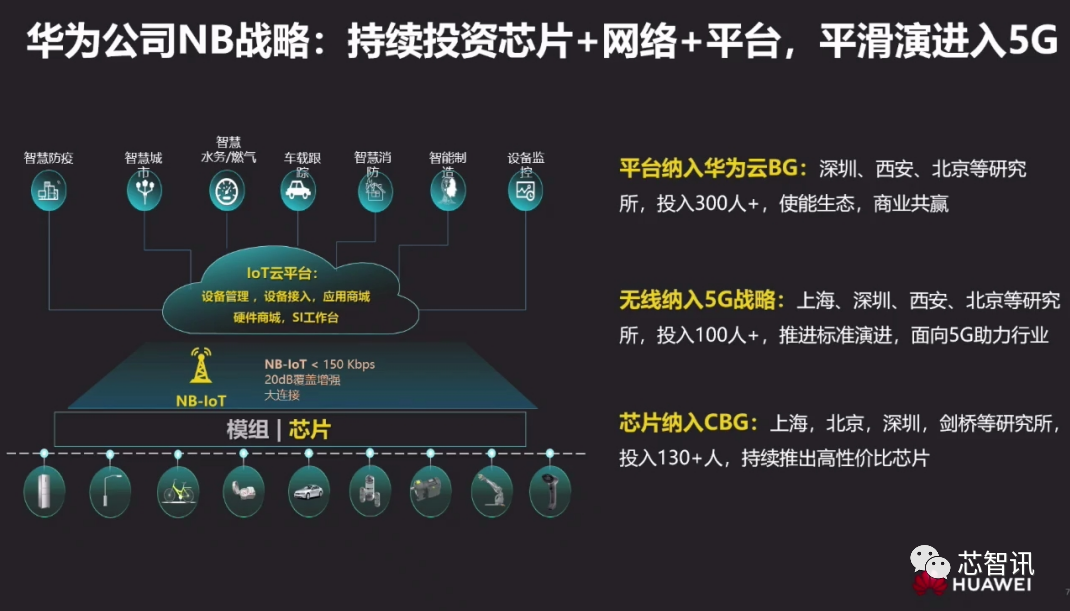
Yang Tao, Vice President of Huawei’s China Operator Business Department, also stated that Huawei’s NB strategy is to continuously invest in chips + networks + platforms, promoting the smooth evolution of NB-IoT into 5G. The upcoming Boudica200 from HiSilicon is designed for this purpose, supporting the latest 3GPP R15/16 version and enabling future connections of 1 billion devices.
Previous related articles: “The Birth of the Internet Celebrity ‘Cat.1’: Why Chip Manufacturers/Module Manufacturers/Operators Are All ‘In Love’?”
Editor: Chip Intelligence – Lang Ke Jian
Note: Due to the extensive content of the conference, this is only a整理 based on the article’s needs, and many contents have not been included. If there are any errors or omissions, please feel free to comment and correct. Thank you! Additionally, we are preparing to establish a WeChat group for IoT discussions; those interested can first join our larger QQ group 221807116 for communication.
Previous Exciting Articles
76,000 people stop work! Toshiba announces closure of all factories in Japan
Accelerating IGBT localization! BYD Semiconductor to be listed independently, with a market value of up to 30 billion yuan!
5G Patent Competition: Huawei ranks first in quantity, but overall quality is lower than Intel, Samsung, ZTE, etc.
Fastest mass production by the end of the year! Yangtze Memory’s 128-layer QLC flash memory released: 1.6Gbps, single capacity of 1.33Tb
To encourage US companies to withdraw from China, US officials propose 100% subsidies!
The Japanese government invests 243.5 billion yen to encourage Japanese companies to withdraw production from China
Domestic localization rate only 12%! A comprehensive understanding of key semiconductor raw materials and electronic special gases
For industry exchanges and cooperation, please add WeChat: icsmart01Chip Intelligence official exchange group: 221807116