
Comprehensive Understanding of Hall Sensors
In magnetic sensors, sensors made using the Hall effect are called Hall sensors. Hall sensors can be divided into Hall elements that directly output the Hall voltage (VH) obtained from the Hall effect, Hall ICs that process the output of Hall elements through subsequent ICs to output high and low level digital signals, and linear Hall ICs that output linear signals after amplifying the output of Hall elements.

What is a Hall Element?
A Hall element is a component made using the Hall effect, spelled as Hall in English. The name Hall comes from Dr. Hall, who discovered the Hall effect. The Hall effect refers to the phenomenon where a potential difference is generated perpendicular to the direction of current flow when a magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the current.
When current flows through a semiconductor film, a voltage is generated that corresponds to the magnetic flux density and its direction, according to the Hall effect. This component, which detects magnetic fields based on the Hall effect, is called a Hall element. (The schematic diagram of an N-type semiconductor Hall element is shown in Figure 2.)
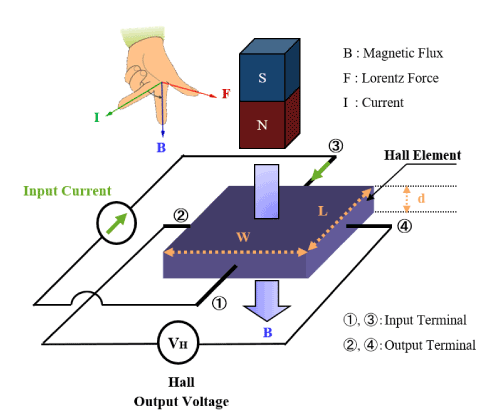
Figure 2 Schematic of Hall Element (N-type Semiconductor)
Even in a static magnetic field where the magnetic flux does not change, the Hall element can detect its presence, which is why Hall elements are used in various applications, such as non-contact switches used with magnets, angle sensors, current sensors, etc. Hall elements are widely used in geomagnetic sensors in smartphones and other fields.
Hall Element
Characteristics
As a basic type of sensor, it can be applied to both digital and analog types depending on the design of its subsequent circuit. It can obtain output voltage signals ranging from tens to hundreds of mV.
Hall Element
Distinctive Features
The output voltage is proportional to the strength of the magnetic field applied perpendicularly to the sensor, and it outputs positive and negative voltages based on the direction of the magnetic field. When no perpendicular magnetic field is applied, its output voltage is 0 V (*1).
(*1 In reality, there is a bias voltage even when no magnetic field is applied.)
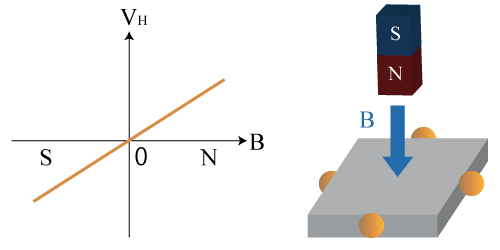
Figure 1 Output Characteristics of Hall Element
Hall Element
Usage
The input terminals are two pins for control voltage (control current) and GND, while the output terminals are two pins for differential output, totaling four pins. As long as the maximum rated values are not exceeded, both constant voltage and constant current driving can work.
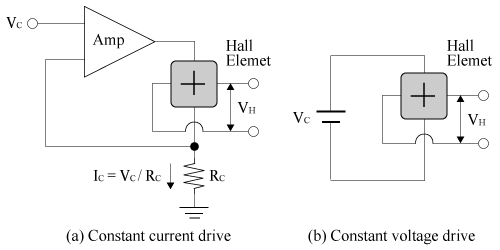
Working Circuit Diagram (Reference Example)
Hall Element
Applications
Used in DCBL motors, smartphones, and digital camera lens drives.

What is a Hall IC?
A Hall IC consists of a Hall element and a signal processing IC, which compares the output voltage of the Hall element and converts it into high/low level digital signals for output (as shown in the figure). Therefore, Hall ICs cannot output detailed information such as “the magnitude of the applied magnetic field” like Hall elements, but can quickly provide digital signal outputs such as “whether a magnet is present”.
The output voltage range of Hall ICs is determined by the pull-up voltage of the output, so when using a pull-up power supply voltage, matching the power supply voltage of the Hall IC with the input voltage range of the backend microcontroller can help the microcontroller better receive signals.
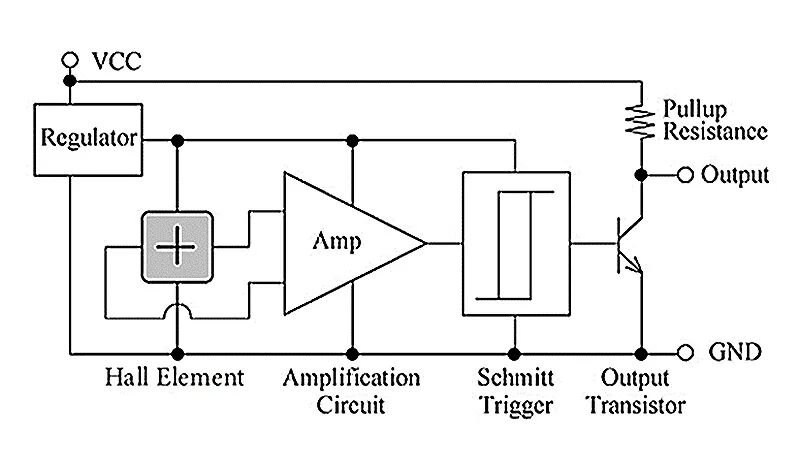
Hall IC
Characteristics
The output of the Hall element is compared with a set threshold and outputs high and low level signals. Since the output voltage range is determined by the power supply, the output signal is easily processed by the subsequent controller. It can be divided into switch types that detect magnetic field strength and latch types that detect magnetic field polarity.
Hall IC
Output Characteristics
The output voltage is divided into high and low outputs based on the strength of the magnetic field applied perpendicularly to the Hall sensor. Additionally, there are types for detecting S poles, N poles, and bipolar detection.
When the magnetic field strength exceeds Bop, the output becomes low, and when it falls below Brp, the output becomes high. The relationship between Brp and Bop is
Brp < Bop (due to hysteresis).
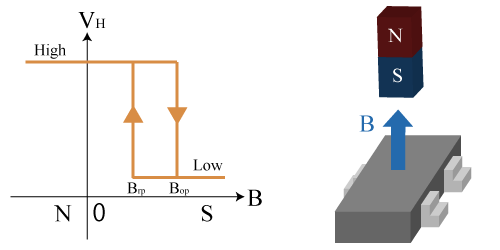
Output Characteristics of S Pole Detection Type Hall IC
Hall IC
Usage
There are two input terminals VCC, GND, and one output pin. Combine the Hall element with the IC shown in Figure 4 and use it in a constant voltage driving mode.
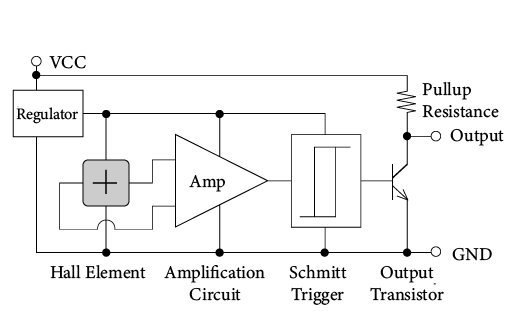
Hall IC
Applications
Switch type Hall ICs are used in appliance switches, while latch type Hall ICs are used in DCBL motors, rotating magnetic field detection, etc.

What is a Linear Hall IC?
Linear Hall IC
Characteristics
The output voltage of the Hall element is amplified by an amplifier to achieve linear output. (*2) Since the output voltage range is specified by the power supply, the output signal is easily processed by the subsequent controller.
(*2 The output at this time is rail-to-rail output.)
Linear Hall IC
Output Characteristics
The output voltage is proportional to the strength of the magnetic field applied perpendicularly to the Hall sensor. When no magnetic field is applied, the output voltage is set to VCC / 2 (*3), and it outputs a voltage from 0 V to VCC based on the direction of the magnetic field.
(*3 In reality, there is a bias voltage even when no magnetic field is applied.)
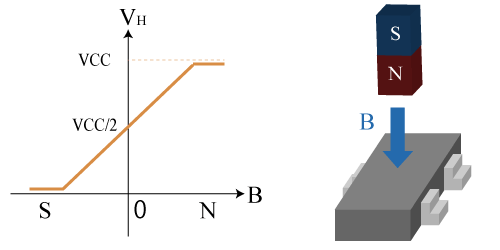
Output Characteristics of Linear Hall IC
Linear Hall IC
Usage
There are two input terminals VCC, GND, and one output pin. Combine the Hall element with the IC shown in Figure 6 and use it in a constant voltage driving mode.
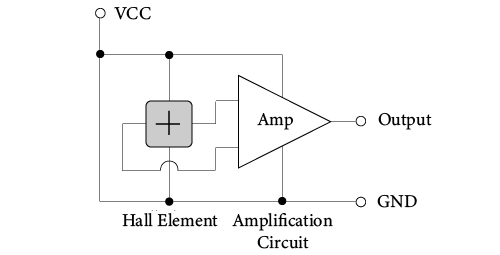
Working Circuit Diagram (Reference Example)
Linear Hall IC
Applications
Used in level gauges, current sensors, and angle detection.
The article is an excerpt from AKM, intended for sharing technical knowledge. If there is any infringement, please contact us for removal.
Shenzhen Junmin Technology Co., Ltd.
A high-tech enterprise focused on technology development, solution provision, and component sales, based in Shenzhen and established in 2008. Offices are located in Suzhou, Foshan, Wuhan, and Hong Kong. We always adhere to the corporate spirit of “innovation and efficiency”. With a generous mindset, we provide competitive solutions and services, continuously creating maximum value for our customers.
Products include motor driver ICs, Hall ICs, memory ICs, MCUs, SOCs, MOS, IPMs, sampling resistors, temperature and humidity sensors, VCM voice coil motors, etc.
Contact us: 18926468515 (WeChat same number)
806, Building C, Rongchuang Zhihui Building, Shangfen Community, Longhua District, Shenzhen