
In IoT development, OTA upgrades (firmware update Over The Air) are essential features for modules. This article will introduce several common OTA solutions using the RTL8711, Espressif 8266 , and Qingke 3186 WiFi modules as examples, and provide a comparative summary.
RTL8711 OTA Upgrade Solution
Solution Overview
The flash partition of the 8711 is shown in the figure below:
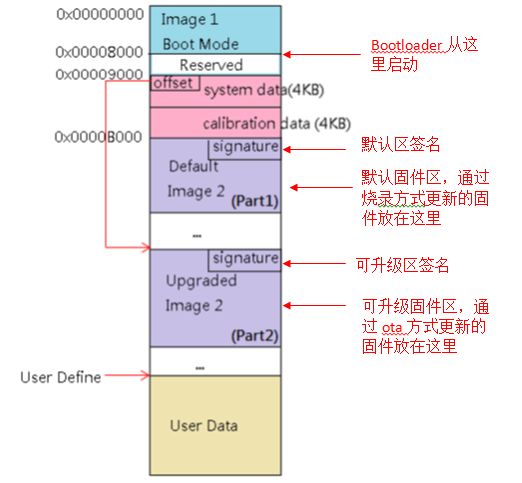
The RTL 8711AF flash is divided into bootloader, verification information area, system information area, default firmware area, and upgradable firmware area. The default firmware area stores firmware updated via programming, while the upgradable firmware area stores firmware updated via OTA upgrade. Only the upgradable firmware area can be used for OTA upgrades.OTA firmware upgrades are essentially IAP (In Application Programming), which generally includes two programs: Bootloader and APP programs. For the RTL8711AF, the chip starts from the Bootloader after power-up.
Bootloader is mainly responsible for:
(1) Reading the application signature information from each area;
(2) Determining which area the application should start from;
(3) Copying the application from the corresponding flash area to SRAM, and jumping to SRAM to run the application.
APP program is responsible for:
(1) Periodically sending HTTP requests to the server to obtain the latest firmware information;
(2) Comparing with the current firmware to determine if an update is needed. If an update is required, downloading the latest firmware from the server to the OTA flash area;
(3) Updating the flash area signature and performing a software reset.
During the firmware download process, a verification check is performed to ensure that the downloaded firmware is a complete and correct package.
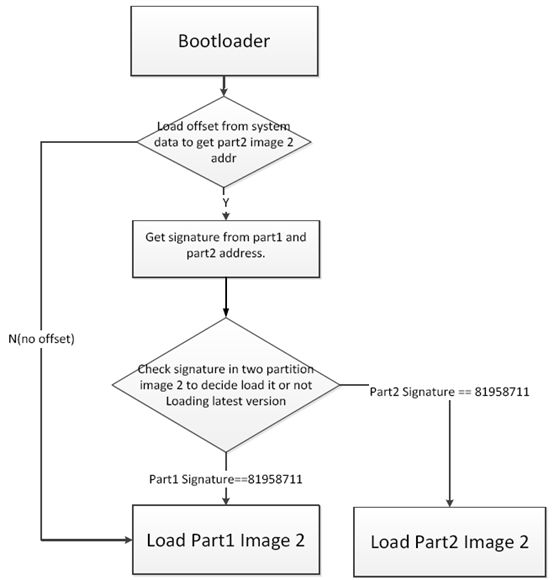
The flow of the 8711 bootloader program is shown in the figure below. After obtaining the addresses of the two flash areas storing firmware from the system parameters, it reads the signatures of these two areas and starts from the area with the signature “81958711“.
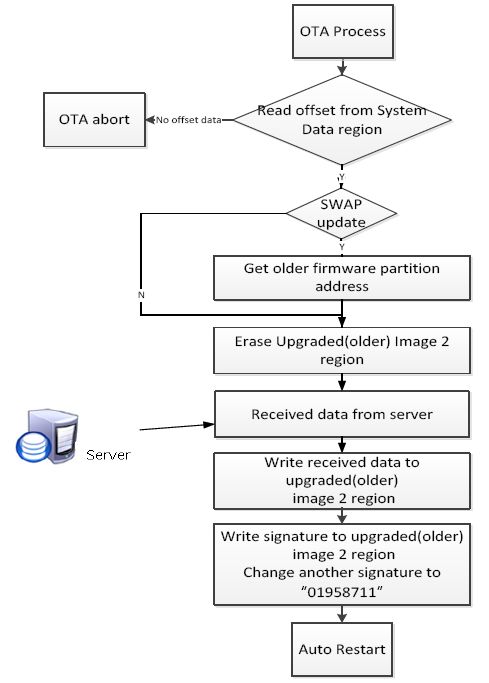
The flowchart of the 8711 OTA APP program is shown below. After obtaining the address of the upgradable area from the system parameters, it erases that area, then downloads the new firmware from the server and writes it to the flash, and finally updates the signature of that area and the signature of the other area.

Advantages and Disadvantages of the 8711 OTA Solution
The 8711 OTA solution divides the flash into two areas, one fixed for programming and the other for OTA upgrades, which is relatively simple and easy to implement. The disadvantage is that if a power outage or network failure occurs during an OTA upgrade after the product leaves the factory, the flash may be corrupted, and upon power-up, it can only run the firmware from the other programming area, which is the first firmware version programmed at the factory, and cannot run the previous version.
Can both areas be used for OTA upgrades, with this upgrade using area A and the next upgrade using area B, alternating upgrades, so that if an upgrade fails, it runs from the other area? In this case, it would be the previous version. Yes, but it requires redesigning the entire solution.
Fixing one area for programming and one area for OTA upgrades is simple to implement, but if designed for alternating upgrades in both areas, is it feasible? It is relatively complex because:
1. The firmware compilation conditions for different areas are different. During compilation, the starting address and size of the corresponding flash area must be set, so the generated firmware is also different. Two firmware versions need to be released during the release process.
2. If designed for both areas to be capable of OTA upgrades, there needs to be system information to record which partition the current program is running on. During the OTA upgrade, it must first obtain which area the current program is running in, then download the corresponding firmware for the other area from the server. The bootloader also needs to know which area to start from, which is relatively cumbersome.

Espressif ESP8266 OTA Solution
Solution Overview
The Espressif solution adopts the dual-area alternating upgrade solution mentioned above. The figure below shows the flash partitioning of the Espressif 8266, where both partition 1 and partition 2 can perform OTA upgrades.
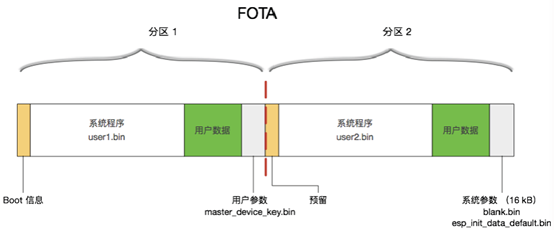
The system parameter area stores a flag indicating which area the system should run after startup (i.e., either user1.bin or user2.bin). Upon system startup, it first runs the boot, which reads this flag and then goes to the corresponding area to read and run the firmware.
For example, in the initial state, it runs version V0.1 of user1.bin, and the system parameter area flag indicates using user1.bin. When an upgrade is needed, the firmware versions V0.2 of user1.bin and user2.bin are uploaded to the cloud server. When the ESP8266 WiFi board performs the upgrade, it first reads the system flag to determine that it is currently using user1.bin, then downloads user2.bin from the server to store in partition 2. If user2.bin is the correct firmware and the download is successful, it modifies the system parameter area flag to partition 2 and then restarts. Upon restart, it first reads this flag, finds it is partition 2, and then starts from partition 2.
If the download process is interrupted due to a network failure or power outage, causing the download to fail, then when the system starts again, the partition flag indicates using user1.bin, and it will run the previous version instead of the first version programmed at the factory.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Espressif Solution
The advantage of the Espressif solution is that it allows reverting to the previous version in case of an upgrade failure, rather than reverting to the first version. The disadvantage is that each time a version is released, two upgrade files must be released simultaneously, which is somewhat cumbersome. If a mistake is made in the release, such as swapping user1.bin and user2.bin, it could lead to a situation where the downloaded upgrade file does not match the partition, causing the WiFi board to become bricked with no recovery options.

Qingke EMW3165 Solution
Solution Overview
The Qingke solution not only addresses the issue of being unable to revert to the previous version in case of an upgrade failure but is also very simple. Similar to the above, it is divided into bootloader and app programs, but the steps for firmware startup and execution are slightly different.
Similarly, in the APP program, an HTTP request is initiated to check if there is a new firmware version on the server and to download it, which is then stored in the external flash area, modifying the firmware parameter information, and rebooting. Upon reboot, the first thing it does is check the firmware parameter information to see if there is a new firmware. If there is, it moves the firmware from the external flash area to the internal flash area and jumps to run from there.
The flash area planning for Qingke 3165 is shown in the figure below:
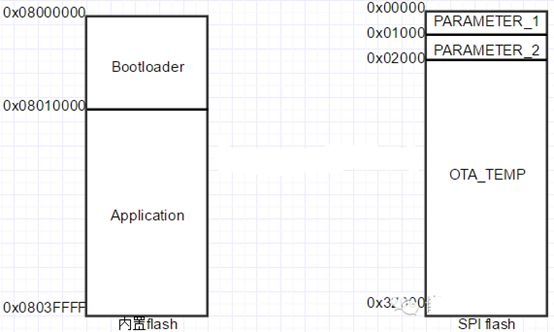
The Bootloader is placed at the internal Flash address 0x08000000, with a size of 64K. After powering on the device, it first jumps here to execute;
The Application is placed at the internal Flash address 0x08010000; PARAMETER_1 and PARAMETER_2 (for backup) are areas that record firmware parameter information, and they are placed in the external Flash;
The OTA_TEMP area is the storage area for OTA firmware, located in the external Flash. The Application downloads the bin file from the network and writes it to this area, while the Bootloader moves the firmware from this area to the Application area.
Upgrade process:
(1) The Application checks the server for new firmware to download, and if available, downloads it to the OTA_TEMP area;
(2) Modifies the PARAMETER_1 parameter to record firmware information;
(3) Reboots
(4) The Bootloader reads the PARAMETER_1 parameter to determine if there is new firmware in the OTA_TEMP area that needs to be updated;
(5) If there is, it moves the firmware from the OTA_TEMP area to the internal flash area;
(6) Jumps to the Application program to execute.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Qingke Solution
The advantages are clear; this method ensures that if the upgrade process fails, the next power-up runs the previous version, and it is very simple. When releasing a version, only one firmware needs to be released, unlike the complexity of the Espressif solution.
The clever part is that it separates the two flash areas, one specifically for downloading and storing firmware, and the other specifically for running programs. This avoids the need to release two firmware versions during the release process and eliminates the need to determine which area to start from upon power-up. If the firmware download process fails due to a power outage, upon the next startup, it first checks the firmware parameters and finds no new version, so it runs the original firmware in the internal flash, which is the previous version.
No disadvantages have been found so far; perhaps the time taken to move the firmware upon power-up might be slightly longer? The modules used by Gubei also employ this solution, and from the user experience, there is no noticeable delay.
1. Chang’e 4 successfully landed on the far side of the moon, achieving the first soft landing of a human probe on the moon’s far side!
2. At 36 years old, he won the Turing Award! 80-year-old algorithm master Donald Knuth plans to finish “The Art of Computer Programming” at 105.
3. Alibaba Damo Academy released the top 10 technology trends of 2019; let’s see who made the list?
4. For MCUs, timers are crucial!
5. Master these 5 skills, and you can thrive in the engineering circle!
6. It’s not embedded systems that let you down; it’s you who let down embedded systems.
Disclaimer: This article is a network reprint, and the copyright belongs to the original author. If there are any copyright issues, please contact us, and we will confirm the copyright based on the copyright certificate you provide and pay for the manuscript or delete the content.