Whether it’s a board made by someone else or a PCB board designed and produced by yourself, the first thing to do upon receiving it is to check the integrity of the board, such as issues with soldering, cracks, short circuits, open circuits, and drilling. If the function of the board is relatively strict, it’s advisable to also check the resistance value between the power supply and ground.
In general, for boards made by yourself, components will be installed after soldering is completed, while for boards made by others, they will just be a bare soldered PCB with holes, requiring you to install the components yourself when you receive it.
Some people have a lot of information about the PCB boards they design, so they prefer to install all the components at once before testing. However, it is recommended to do it step by step.
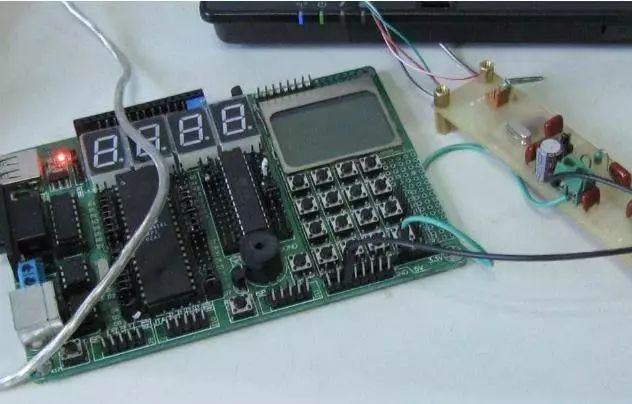

Debugging PCB Circuit Board
New PCB debugging can start from the power supply section. The safest method is to add a fuse and then connect the power supply (it’s best to use a regulated power supply just in case).
Set the overcurrent protection current on the regulated power supply, then slowly increase the voltage of the regulated power supply. This process requires monitoring the board’s input current, input voltage, and output voltage.
If the voltage is increased without triggering overcurrent protection and the output voltage is normal, it indicates that there is no issue with the power supply section of the board. If the output voltage exceeds normal or triggers overcurrent protection, then the fault must be investigated.
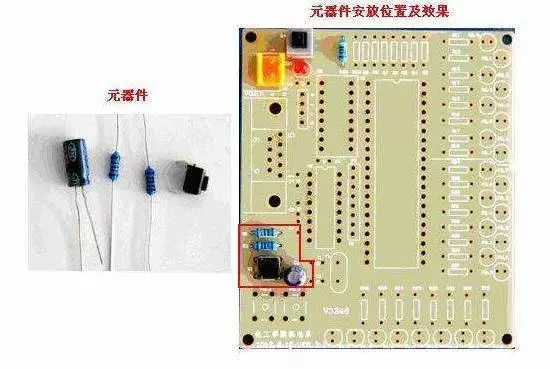
Component Installation on Circuit Board
During debugging, gradually install the modules. Each time you install one or several modules, follow the above steps to test, which helps avoid hidden errors in the initial design or incorrect component installation that could lead to overcurrent damage.
If a fault occurs during installation, the following methods can generally be used for troubleshooting:
Troubleshooting Method One: Voltage Measurement Method

Voltage Measurement Method
When overcurrent protection occurs, do not rush to disassemble the components. First, confirm the voltage levels at the power pins of each chip to see if they are within the normal range. Then check the reference voltage, working voltage, etc.
For example, the voltage at the BE junction of a silicon transistor will be around 0.7V when conducting, while the CE junction is generally at 0.3V or lower.
If during testing, the BE junction voltage is higher than 0.7V (excluding special transistors like Darlington), it may indicate an open circuit at the BE junction. By checking the voltage at various points, faults can be eliminated.
Troubleshooting Method Two: Signal Injection Method
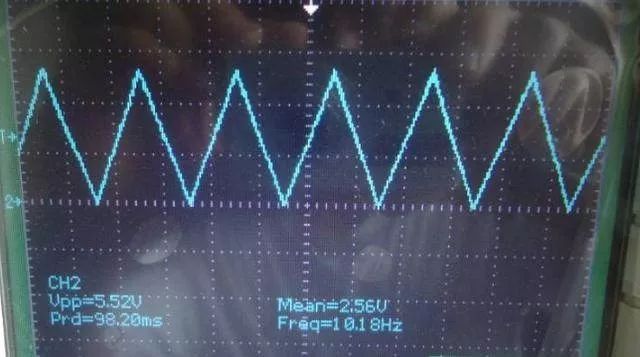
Signal Injection Method
The signal injection method is more complicated than voltage measurement. When delivering the signal source to the input, we need to measure the waveforms at each point downstream to find the fault point from the waveforms.
Of course, tweezers can also be used to detect the input end. The method is to touch the input end with tweezers and observe the response of the input end. This method is generally used in audio and video amplification circuits (Note: Do not use this method in hot ground circuits and high-voltage circuits to avoid electric shock accidents).
If this method detects that the previous stage is normal while the subsequent stage has a response, then the fault is not in the subsequent stage but in the previous stage.
Troubleshooting Method Three: Others
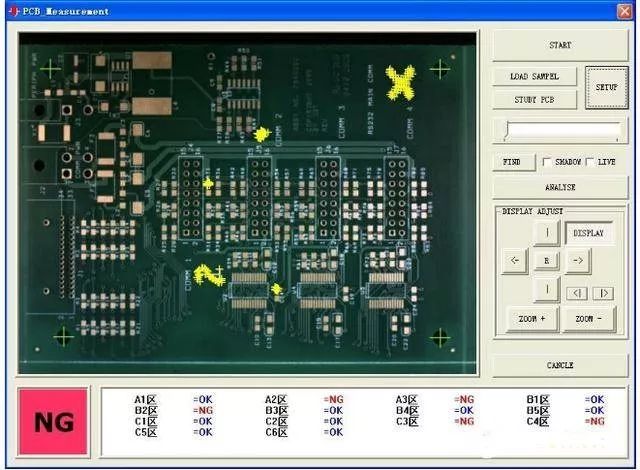
PCB Circuit Board Appearance Inspection Machine
The above two methods are relatively simple and straightforward. Additionally, methods like looking, smelling, listening, and touching require some experience from engineers to detect problems.
Generally, “looking” does not mean checking the status of the testing instruments but rather examining whether the components are intact; “smelling” mainly involves checking for any unusual odors from the components, such as burnt smells or electrolytic liquid smells. Typically, components emit unpleasant burnt smells when damaged.
“Listening” primarily involves listening to whether the sounds from the board in operation are normal; regarding “touching,” it does not mean checking if components are loose but rather using your hand to feel whether the component temperatures are normal. For instance, a component that should be cold is hot, while a component that should be hot is abnormally cold. During the touching process, be careful not to directly squeeze with your hand to avoid burns from high temperatures.
Disclaimer: This article’s copyright belongs to the original author and does not represent the views of the association. Articles promoted by the “Jiangxi Province Electronic Circuit Industry Association” are for sharing purposes only and do not represent the stance of this account. If there are copyright issues, please contact us for removal.
