The diversity of PCBs in materials, layers, and processes caters to different electronic products and their specific needs, resulting in a wide classification. Below, we summarize some common differentiation methods to briefly introduce the classification of PCBs and their manufacturing processes. Let’s analyze it from three aspects.
Materials
Organic Materials
① Phenolic Resin: Phenolic resin, also known as Bakelite, is originally a colorless or yellow-brown transparent material, often sold in red, yellow, black, green, brown, blue, and other colors with added coloring agents, available in granules or powder form.
Phenolic resin is resistant to weak acids and weak bases, decomposing in strong acids and corroding in strong bases. It is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents like acetone and alcohol. It is obtained by the polymerization of phenol and its derivatives. The image is as follows:

② Glass Fiber: Glass fiber (originally named glass fiber in English) is an excellent inorganic non-metallic material with a wide variety. Its advantages include good insulation, strong heat resistance, and good corrosion resistance, while its disadvantages are brittleness and relatively poor wear resistance.
It is manufactured from seven ores: talc, quartz sand, limestone, dolomite, boron-calcium stone, and boron-magnesite, through high-temperature melting, drawing, spinning, and weaving processes. The diameter of a single fiber ranges from a few microns to over twenty microns, equivalent to 1/20 to 1/5 of a human hair. Each bundle of fiber consists of hundreds or even thousands of single filaments.
Glass fiber is commonly used as a reinforcing material in composite materials, electrical insulation materials, thermal insulation materials, and circuit substrates across various sectors of the national economy. The image is as follows:

③ Polyimide: Polyimide resin, abbreviated as PI, appears as a transparent liquid, yellow powder, brown granules, and amber granules. Polyimide resin solutions, powders, and granules are produced, including thermoplastic polyimide resin solutions, thermosetting polyimide resin solutions, thermoplastic polyimide pure resin, and thermosetting polyimide pure resin. The molding methods for polyimide PI include: high-temperature curing, compression molding, impregnation, spraying, calendering, injection molding, extrusion, die-casting, coating, casting, laminating, foaming, transfer molding, and compression molding. The image is as follows.

Other organic materials include our epoxy resin and BT, etc.
Inorganic Materials
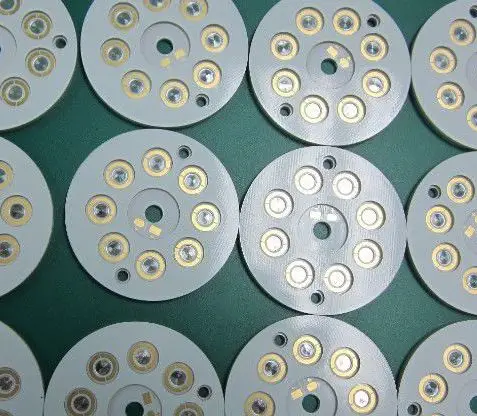
① Aluminum Baseboard: Aluminum baseboard is a type of metal-based copper-clad board with good heat dissipation functions, generally composed of a three-layer structure for single-sided boards.
It consists of a circuit layer (copper foil), an insulating layer, and a metal base layer. It is commonly found in LED lighting products. It has two sides; the white side is for soldering LED pins, while the other side shows the natural color of aluminum, typically coated with thermal conductive paste for contact with heat-conducting parts. There are also ceramic baseboards, as shown in the image below.

② Copper Baseboard: Copper baseboard is the most expensive among metal baseboards, with heat conduction performance much better than aluminum and iron baseboards. It is suitable for high-frequency circuits and areas with significant temperature fluctuations, as well as for heat dissipation in precision communication equipment and the construction decoration industry, as shown in the image below.

There are also ceramic baseboards that belong to inorganic materials, primarily for their heat dissipation functionality.
Finished Rigid and Flexible Boards
Rigid Board
Rigid boards are made from PVC. PVC rigid boards are widely used in industry, particularly in the chemical anti-corrosion sector.
PVC is a resin resistant to acids, bases, and salts, and due to its excellent chemical properties and relatively low cost, it is widely used in various industries such as chemicals, building materials, light industry, and machinery, as shown in the image below.

Flexible Board
Soft polyvinyl chloride extruded boards are made by adding plasticizers, stabilizers, etc., to polyvinyl chloride resin and extruding them into shape.
Mainly used as liners for corrosion-resistant equipment such as acid and alkali, it can also serve as general electrical insulation and sealing gasket materials, with a temperature range of -5 to +40°C, making it a widely used new environmentally friendly product, as shown in the image below.

Rigid-Flexible Combined Board
The birth and development of FPC and PCB have given rise to this new product called rigid-flexible combined boards. Therefore, rigid-flexible combined boards are formed by combining flexible circuit boards and rigid circuit boards through lamination and other processes, following relevant process requirements, resulting in circuit boards with characteristics of both FPC and PCB, as shown in the image below.
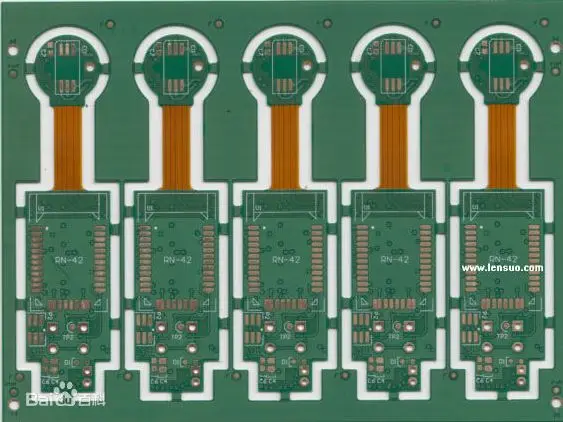
PCB Structure
Single-Sided Board
A single-sided board is a basic PCB where components are concentrated on one side, and the wires are concentrated on the other side. Since the wires only appear on one side, we call this type of PCB a single-sided board.
Because single-sided boards have many strict limitations in circuit design (as there is only one side, the wiring cannot cross and must follow a unique path), this type of board was only used in early circuits, as shown in the image below.
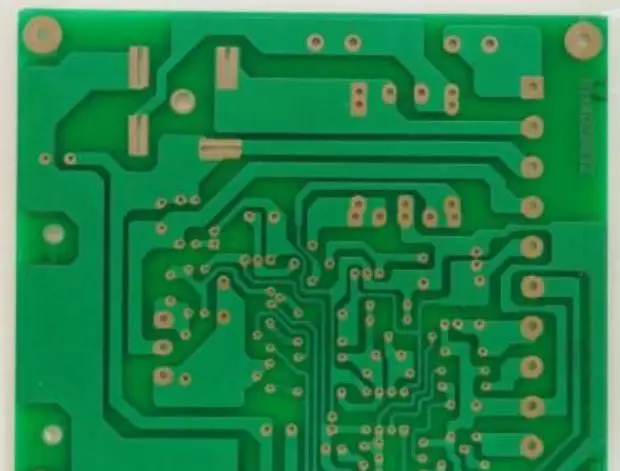
Double-Sided Board
A double-sided board includes both the Top (upper layer) and Bottom (lower layer) with copper on both sides, allowing for wiring and soldering on both sides. The middle layer is an insulating layer, making it one of the most commonly used types of printed circuit boards.
With wiring possible on both sides, the difficulty of wiring is greatly reduced, leading to widespread adoption, as shown in the image below.
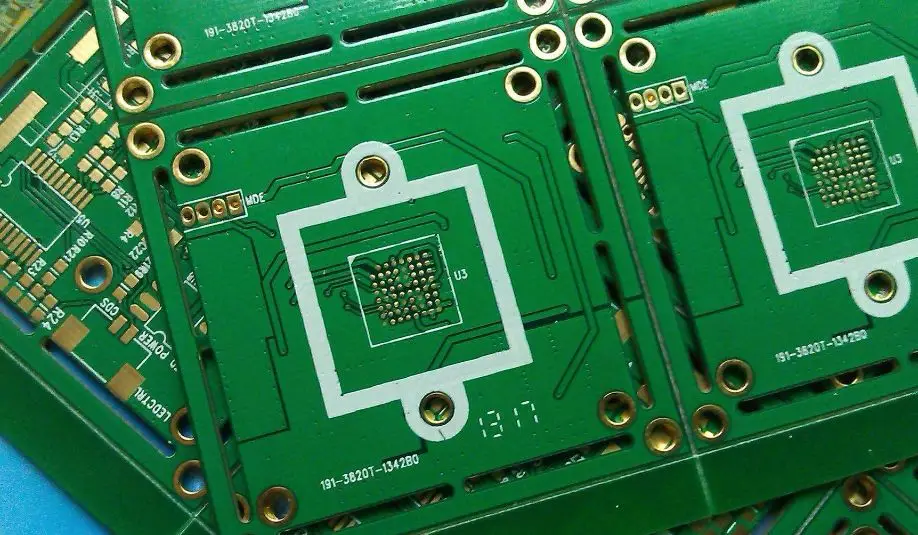
Multi-Layer Board
The manufacturing method for multi-layer boards generally involves first creating the inner layer pattern, then using printing and etching methods to create single-sided or double-sided substrates, incorporating them into designated layers, and then heating, pressurizing, and bonding them. The subsequent drilling process is similar to the plated through-hole method used for double-sided boards, as shown in the image below.

