
Since the National Development and Reform Commission and eight other ministries first proposed the construction of smart hospitals in 2014, the development of smart hospitals in China has gone through nearly ten years. With the introduction of guiding policies and the establishment of evaluation systems, the “Action Plan for Promoting High-Quality Development of Public Hospitals (2021-2025)” explicitly proposed the construction of a smart hospital information system that integrates smart medical services, smart management, and smart services. The continuous promotion of policies and increasing construction achievements have allowed more and more hospitals to experience the benefits of smart hospital construction, transforming from passive to proactive, and engaging in the wave of smart hospital construction. This includes many well-known public hospitals. Many newly established hospital campuses are dedicated to building smart hospitals from the outset.
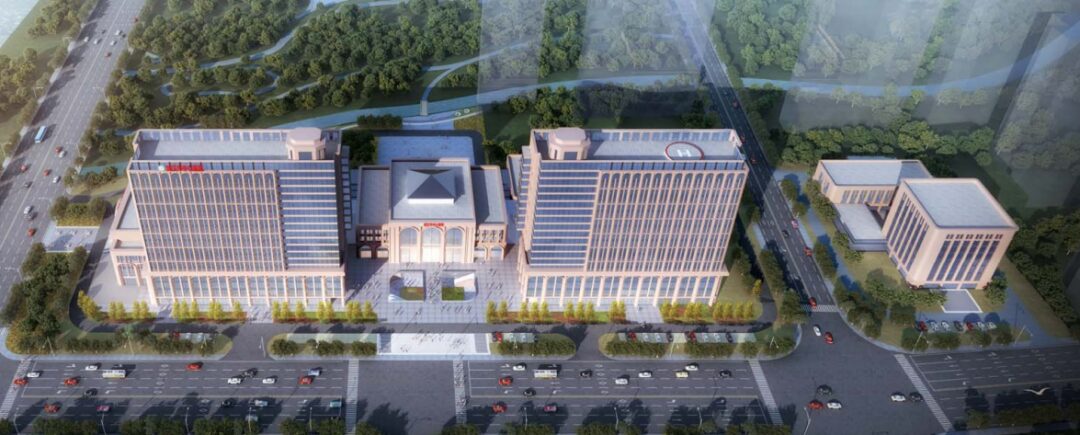
Following the guiding policies for the development of smart hospitals, the Yangchunhu Campus of Wuhan Central Hospital officially opened in August 2023 and has conducted many explorations in smart hospital construction, achieving remarkable results. The construction of the Internet of Things (IoT) platform and IoT applications is an important component of the smart hospital at Yangchunhu Campus. Enke Information Technology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. undertook the wireless IoT platform and IoT application project for this campus. Multiple IoT application systems have been launched at the Yangchunhu Campus of Wuhan Central Hospital, including wireless infusion systems, vital signs monitoring, patient positioning, infant anti-theft, asset positioning in the operating room, energy consumption management, safe nursing, and outpatient infusion systems. Through the joint efforts of Wuhan Central Hospital’s Yangchunhu Campus and Shanghai Enke Company, the “smart” concept has permeated all aspects of hospital management. The goal is to create a new benchmark for IoT application scenarios in hospitals at both regional and national levels.

01
Ensuring Sustainable Upgrades: IoT Platform Accelerates Smart Hospital Construction

In recent years, Wuhan Central Hospital has made significant progress in clinical, medical technology, and logistics information construction. Building on the development of the Houhu Campus, the Yangchunhu Campus drew on the experiences of leading hospitals in the country and set high standards and strict requirements for the design of each system from the outset. The hospital’s information center conducted extensive research and feasibility studies in the early stages of the project.
Market research found that common technical standards for IoT in hospitals include WiFi, LoRaWAN, ZigBee, RFID, BLE, Thread, 802.15.4, and some proprietary communication protocols, with operators using NBIoT, Cat.1, 2G/4G/5G, etc. Common indoor positioning technologies include Bluetooth iBeacon, Bluetooth gateways, Bluetooth AoA, UWB, 125K RFID, infrared, etc. Different technology protocols vary in coverage, transmission rates, accessible terminals, and power consumption. Industry solution companies choose based on their understanding of technology and the matching of technology with usage scenarios. Currently, some technology protocols are defined by solution companies, and products from different manufacturers are generally not compatible. Overall, the IoT industry is characterized by a multitude of standards and is currently in a phase of diverse development.
During the hospital’s infrastructure phase, WiFi and other IoT technologies are typically designed and planned as a whole, forming an integrated wireless + IoT solution. Currently, many data communication manufacturers usually bind ecological partners to provide comprehensive solutions to hospitals, which can limit hospitals in choosing suppliers.
For hospitals, during the network construction phase, it is essential to consider which technical standards can meet future clinical business needs or to choose a platform with high inclusivity and openness to support various technologies, avoiding issues related to incompatible standards.
Through feasibility studies and on-site testing, the Yangchunhu Campus of Wuhan Central Hospital ultimately chose the “One Network, Unlimited” data distribution platform solution from Enke Information Technology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. This platform is suitable for a wide range of environments and can be deployed in all areas of the hospital, including wards, operating rooms, ICUs, CCUs, and outpatient services. On the other hand, Enke’s “One Network, Unlimited” data distribution platform supports operation across the full frequency range from 400MHz to 7125MHz, integrating WiFi networks, IoT sensor networks, and positioning networks. Additionally, the data distribution system has the capacity to expand with operator 5G, allowing for on-demand access. According to the latest plans from the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the 6425-7125MHz range will be used for 6G network communications, making the data distribution platform technically capable of 6G access, thus being referred to as the “All-Network Data Distribution Platform.”
The data distribution platform offers free open interfaces to third-party systems, allowing hospitals to connect third-party applications as needed. The Yangchunhu Campus of Wuhan Central Hospital has already integrated third-party systems such as hand hygiene systems and in-hospital navigation, and all systems are currently operating well. This has truly realized the expected goal of sustainable upgrade and development.

02
Enhancing Nursing Management: IoT Systems Improve Quality and Efficiency

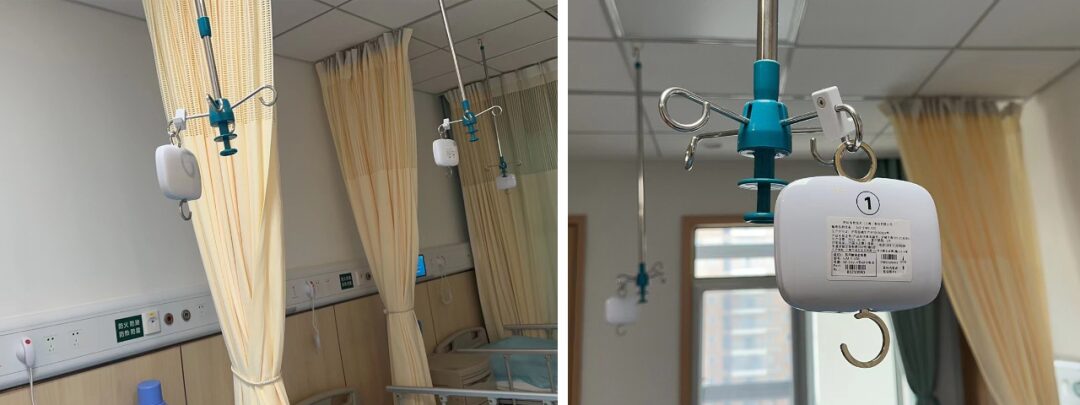
Improving management efficiency, enhancing the quality of medical services, and increasing patient satisfaction are among the goals of high-quality development in hospitals. Through IoT technology, achieving a tighter nursing management loop is a significant embodiment of the application of IoT technology in hospitals.
Taking intravenous infusion, one of the most common nursing scenarios, as an example, the complete process of intravenous infusion includes three checks and seven confirmations, disinfection, puncture, adjusting the infusion speed, changing the dressing midway, and removing the needle, which adds to the already significant daily nursing workload, making it difficult for nurses to devote more energy to higher-quality nursing processes.
In response, the Yangchunhu Campus of Wuhan Central Hospital has launched a wireless infusion monitoring system, which has a Class II medical device registration certificate. This system is capable of real-time monitoring of each hospitalized patient’s infusion status, such as drip rate and expected end time, and transmits the collected data to the backend for processing via the “One Network, Unlimited” data distribution platform. The computation results are displayed on a centralized IoT dashboard at the nurse station, intelligently reminding nurses to pay attention to each patient’s infusion status. When the infusion is about to finish, the system can prompt for a dressing change in advance. This transition from waiting for patients to ring the bell to proactively changing the dressing has significantly improved patients’ perception of inpatient medical services.
In addition to the wireless infusion monitoring system, the Yangchunhu Campus has also adopted a vital signs monitoring system, which also has a Class II medical device registration certificate. It uses high-precision and high-sensitivity sensors to ensure the accuracy of temperature data collection, attaching sensors to patients’ armpits using medical adhesives to achieve 24/7 real-time monitoring of patient temperatures, allowing for timely detection of patient deterioration and providing “ICU-style” monitoring services for general ward patients. This is one of the embodiments of high-quality medical development. In infection wards, reducing contact between nurses and patients during vital sign measurements further lowers the risk of cross-infection between medical staff and patients.
03
Making “People/Equipment” Movements Visible: Data Empowering Smart Management

Based on the “One Network, Unlimited” data distribution platform’s positioning system, the Yangchunhu Campus of Wuhan Central Hospital has achieved real-time “positioning” of personnel and materials, establishing management for patient safety, medical staff, and the usage of medical equipment.
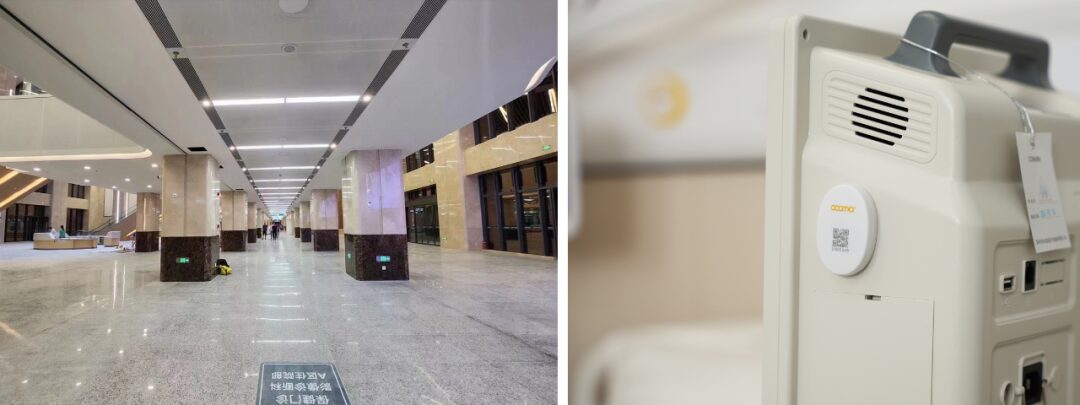
By combining positioning and energy efficiency sensors, real-time statistical analysis of the usage of high-value medical equipment in hospitals is provided, enabling analysis of equipment investment returns. Asset positioning saves medical staff time in locating medical equipment and facilitates preventive maintenance, enhancing maintenance efficiency. It assists equipment management departments in conducting cost-benefit analyses, fine management, preventive maintenance, clinical application evaluations, and intelligent diagnostics. In the event of abnormal removal of equipment positioning/energy efficiency sensors, timely anti-tampering alerts can also be issued. Utilizing IoT technology, the Yangchunhu Campus of Wuhan Central Hospital will build an equipment sharing center to achieve unified management of essential devices that are used disorderly and unpredictably in clinical settings, providing feasible pathways for sharing and utilization throughout the hospital.
04
In Patient Management, Safety Services are Crucial

“Safety and controllability” is the primary factor to consider in patient management within wards. The Yangchunhu Campus of Wuhan Central Hospital has implemented a patient positioning management system to achieve precise management of the entire process of patient diagnosis and treatment activities within the hospital, allowing for tracking of action trajectories and alert management for special patients entering and exiting. In the obstetrics ward, the infant anti-theft system offers a new management model for the safety of newborns. Infants are fitted with anti-theft ankle bands at birth, which automatically trigger an alarm at the exit if they are taken out of the ward without authorization, significantly enhancing the hospital’s safety level. The application system supports integration with HIS for automatic synchronization of patient information, eliminating the need for nurses to manually operate admission and discharge registrations in the system.
In terms of medical staff safety services, the Safe Nursing System effectively assists medical personnel in quickly responding to emergencies. When an urgent request for help arises, the SOS button on the staff ID badge can pinpoint the location of the medical personnel in real-time, while linking to the security monitoring system, allowing the security center to monitor the scene conveniently for rapid response.


Conclusion
To facilitate the daily operation and maintenance management of IoT devices and systems, Enke Company provides a visual IoT comprehensive operation and maintenance system for the Yangchunhu Campus of Wuhan Central Hospital, achieving real-time monitoring of the operational status of IoT application systems and network devices, as well as real-time online handling of anomalies.
With the acceleration of smart hospital construction, the Yangchunhu Campus of Wuhan Central Hospital will further establish a “quality medical service circle” at the doorstep for nearly 4 million residents, benefiting a large number of patients. The “One Network, Unlimited” data distribution platform builds a “two-way multi-lane highway” for the smart hospital construction of the Yangchunhu Campus, facilitating daily work for medical staff, achieving more precise closed-loop management of medical quality, improving patient hospitalization experiences, and providing diversified and multi-faceted data support for hospital management, ultimately delivering higher-quality diagnosis and treatment service experiences for patients.

END
Source | Company Contribution



Email for New Media Department:

If you find the content of this article meaningful, please give us a like
