Theoretical Speed
• Wi-Fi speed continues to improve with updates to the Wi-Fi protocol.
Wi-Fi speed has undergone a development process from slow to fast. The initial theoretical wireless transmission speed of Wi-Fi was only 11 Mbit/s, and after several updates, we have achieved the current results.
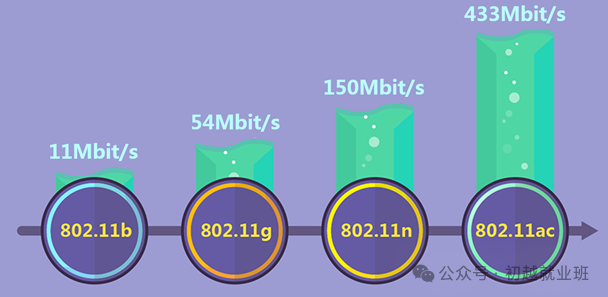
• Wi-Fi speed is further enhanced with the application of MIMO technology.
MIMO (multiple-input multiple-output) refers to multiple input multiple output, which is an antenna system consisting of m transmitting antennas and n receiving antennas, allowing signals to be transmitted and received through multiple antennas at the transmitting and receiving ends, thereby improving communication quality. MIMO achieves multiple sending and receiving through multiple antennas, significantly increasing the system channel capacity without increasing spectrum resources and antenna transmission power, showing obvious advantages and is regarded as the core technology of the next generation of mobile communication.
Under different spatial stream counts, the theoretical air interface rates achievable by 802.11n/802.11ac are shown in the table below:
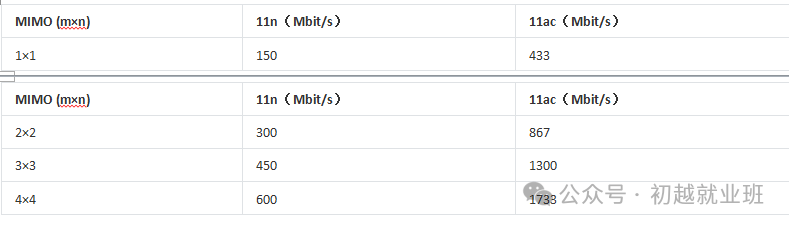
Therefore, the high speeds advertised by some dual-band routers are calculated as follows:
733 Mbit/s = 300 Mbit/s (11n 2×2) + 433 Mbit/s (11ac 1×1)
1167 Mbit/s = 300 Mbit/s (11n 2×2) + 867 Mbit/s (11ac 2×2)
1750 Mbit/s = 450 Mbit/s (11n 3×3) + 1300 Mbit/s (11ac 3×3)
Factors Affecting Wi-Fi Speed
Wi-Fi theoretical speed only represents the speed in an ideal state and does not equal the actual data transmission speed. In practice, Wi-Fi speed is affected by various factors.
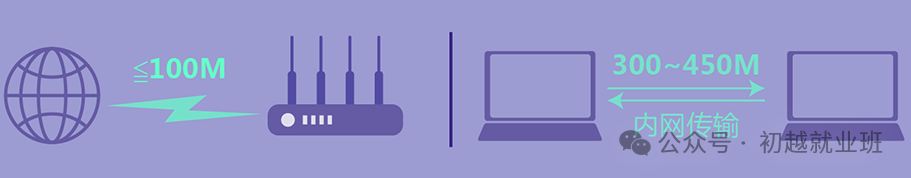
• Wi-Fi speed is limited by the bandwidth provided by the carrier and the performance of the connected devices’ network cards.
Currently, the broadband provided by service providers generally does not exceed 100M. The commonly mentioned 300M and 450M wireless transmission speeds refer to the transmission speed within the local area network, while the internet speed mainly depends on the external bandwidth (i.e., provided by the service provider).
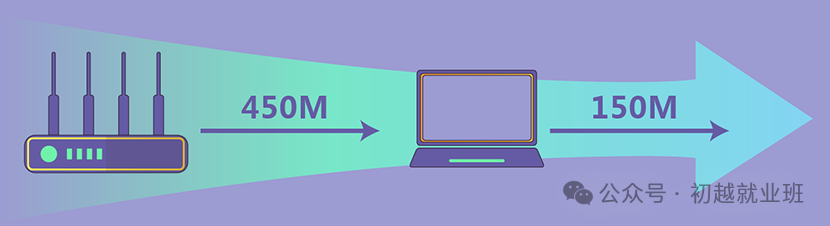
When wireless devices (such as mobile phones, laptops, etc.) connect to a wireless signal, they negotiate a wireless transmission speed with the router. The higher the speed supported by the device’s wireless network card, the higher the negotiated wireless transmission speed will be.
Currently, most mobile phones on the market support speeds of 54Mbit/s and 72Mbit/s, while most laptops come with wireless network cards that support speeds of 144Mbit/s. This means that even when connected to a 450M wireless router, the theoretical maximum wireless transmission speed achievable by a laptop is 150Mbit/s.
Additionally, the age of the wireless network card drivers may also affect the wireless transmission speed.
• Wi-Fi speed is influenced by the strength and quality of the Wi-Fi signal.
The strength of the Wi-Fi signal is related to speed; the better the signal strength, the higher the speed.
Therefore, while 802.11ac increases speed, it also uses MIMO to enhance signal strength. Before each transmission, a channel measurement is actually performed, and based on the channel quality, an appropriate sending rate is selected from the MCS table for transmission, allowing for real-time speed adaptation.