

What do these parameters mean? How can you choose the right SSD from the myriad of products available? Today, we’re bringing you a brief introduction to the bus, protocol, and interface of SSDs, turning you into an SSD “veteran” in no time.

-
The bus is the pathway for data interaction between different functional components of a computer. For SSDs, the bus is the route data takes from the SSD to the CPU.
-
The bus is based on physical criteria, so it has a certain capacity limit. -
The total amount of data transmitted over a unit time is called bandwidth.

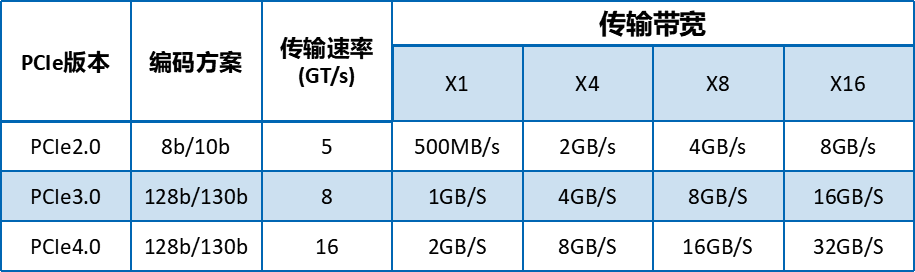
The bandwidth of the PCIe bus is commonly represented in speed units, where X indicates how many times X1.

The data in the table above may seem complex. The SAS bus is commonly used in servers, so we won’t discuss it further. The buses we usually deal with in daily life are SATA3.0, PCIe3.0, and PCIe4.0. To illustrate, consider a simple analogy: when a vehicle is driving on the road, there are three paths: SATA3.0, PCIe3.0, and PCIe4.0, as shown in the following image.
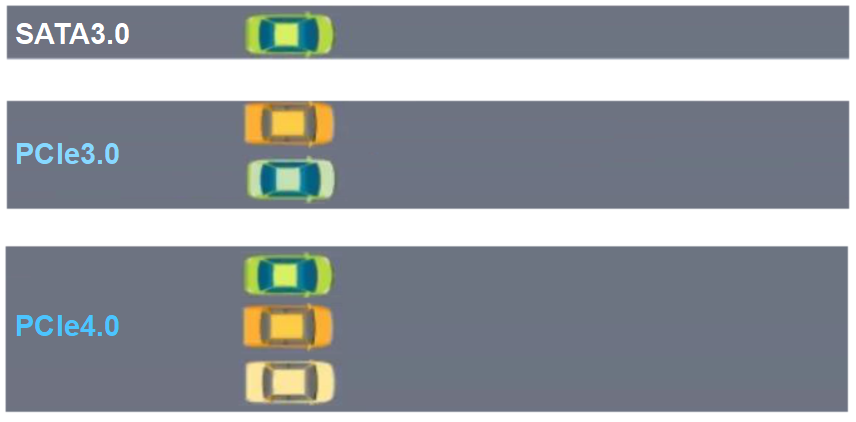
It can be seen that, within the same time frame, the SATA3.0 bus transmits the fewest vehicles, akin to a rural road. The PCIe3.0 and PCIe4.0 buses transmit more vehicles, resembling two wider highways, with PCIe4.0 being the widest.
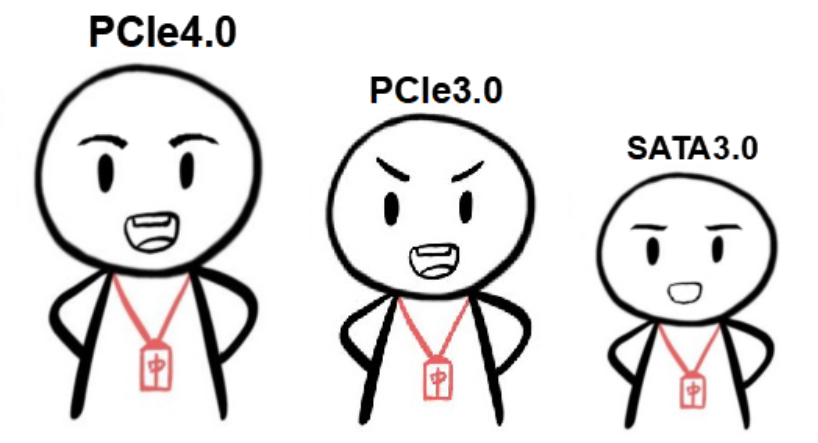

-
A protocol is a set of rules agreed upon by both parties for communication, including how to connect and how to identify each other.
-
For two electronic devices to effectively transmit data, they must have the same or compatible protocols.
-
Efficient protocols require hardware support.
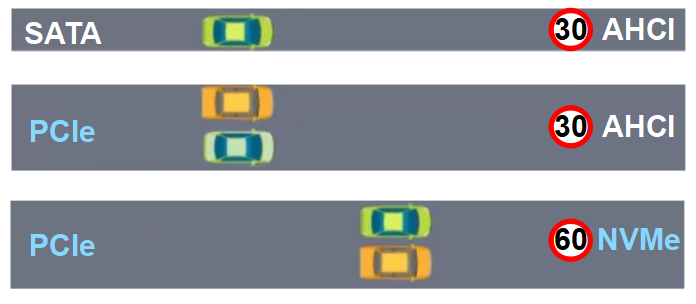
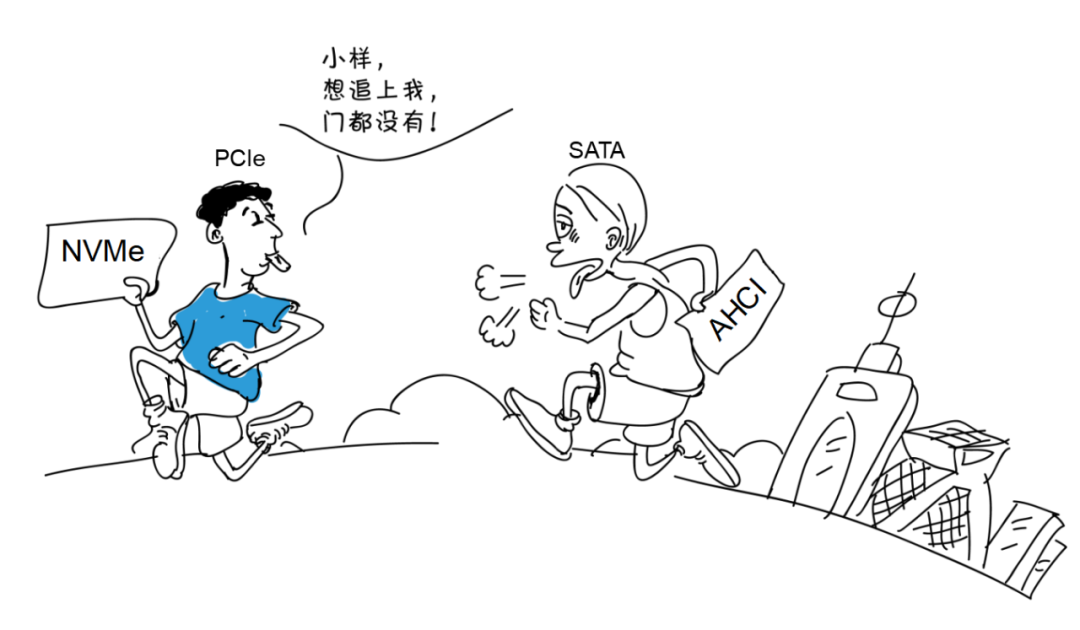
As shown in the image above, the AHCI protocol can be used with both SATA and PCIe buses. Although the PCIe bus represents a “wider” road, due to the limitations of the AHCI protocol, the rate improvement of PCIe over SATA is limited.
The NVMe protocol can be used with the PCIe bus. The “high-speed” NVMe protocol, combined with the “wide” PCIe bus, greatly increases the data transmission rate.
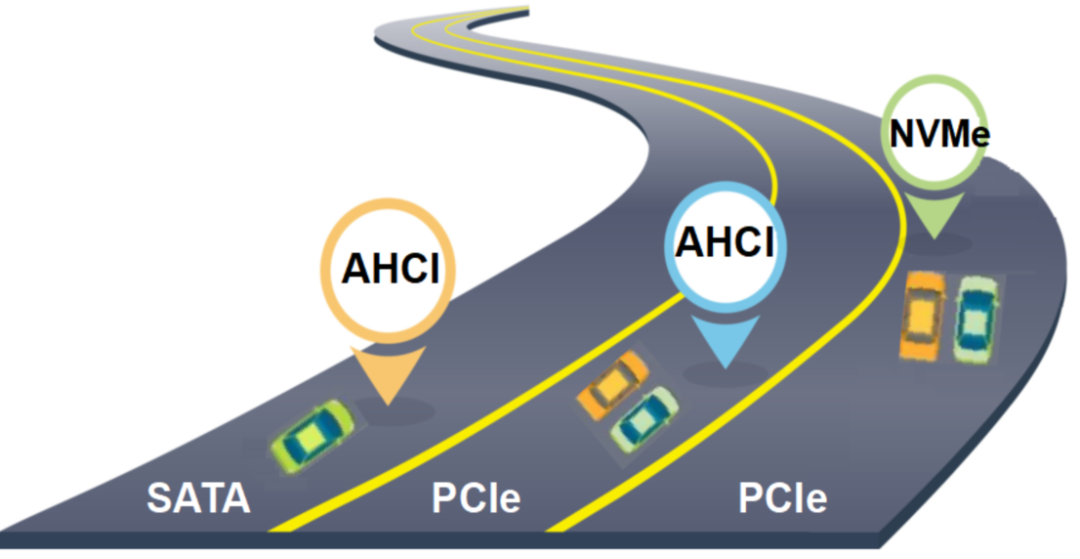
In summary, in terms of data transmission rates, we can simply understand it as:NVMe protocol transmits data faster than AHCI protocol.
-
The interface is the bridge between the hard drive and the motherboard. -
The interface, bus, and protocol in SSD products complement each other, and the theoretical speed limit of the SSD interface can be determined by the bus’s carrying capacity. -
The actual speed of the interface is also related to materials and craftsmanship.
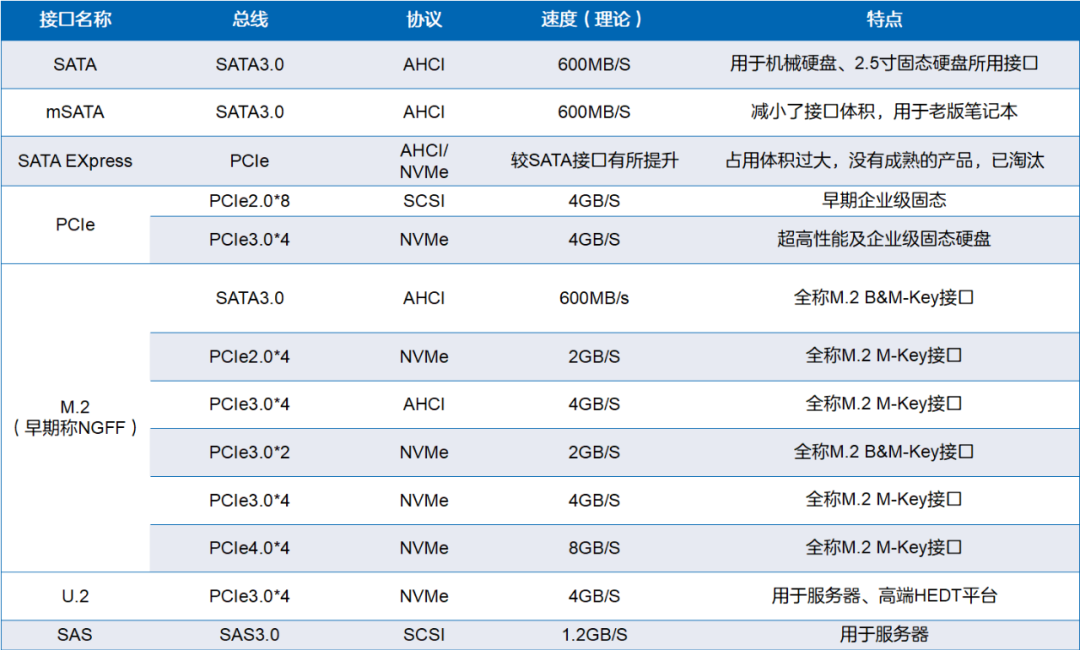
The following image summarizes the common SSD interfaces and their corresponding protocol and bus situations.
-
PCIe can serve as both a data-carrying bus and an interface. When used as an interface, it is referred to as a PCIe slot.
-
The SATA bus can only use the AHCI protocol, while the PCIe bus can use AHCI, NVMe, and SCSI protocols.
-
For M.2 interfaces, there are B&M-Key and M-Key interfaces, which often have distinguishing notches. Typically, B&M-Key drives have notches on both sides, while M-Key drives have a notch on the right side. However, it is important to note that one cannot solely determine the type of M.2 interface based on the position of the notch. 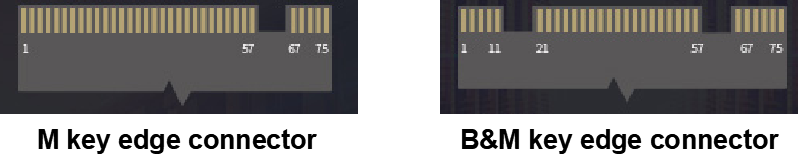
Today, we introduced the concepts of bus, protocol, and interface related to SSDs, summarized as follows:
-
The PCIe bus has stronger data transmission capabilities than the SATA bus.
-
The NVMe protocol has higher transmission speeds than the AHCI protocol.
-
Each interface has corresponding buses and protocols, and the theoretical speed of the interface can be determined by the bus type.

Step 1: Understand the interface and protocol types supported by your computer’s motherboard.
Step 2: Refer to the summary table above and check the bus types supported by your computer’s interface.
Step 3: Find an SSD that meets the criteria, and choose based on price and actual needs.
The reproduced content only represents the author’s views.
It does not represent the position of the Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Source: ZTE Document
Editor: Paarthurnax
Recent Popular Articles Top 10
