Basic Programming Algorithm – Insertion Sort
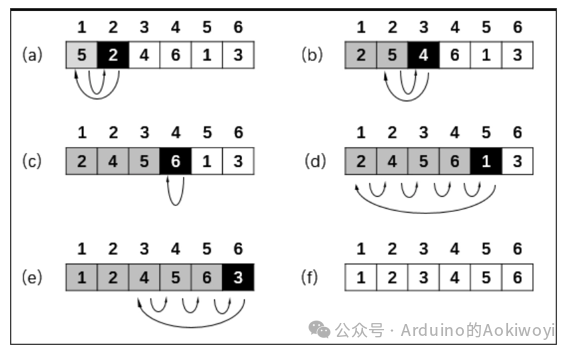
Insertion Sort: Insertion sort builds a sorted sequence by scanning the unsorted data from back to front in the sorted sequence, finding the appropriate position and inserting it. Insertion sort is generally referred to as direct insertion sort. It is an effective algorithm for sorting a small number of elements [1]. Insertion sort is one of the simplest sorting methods, and its basic idea is to insert a record into an already sorted list, thus creating a new sorted list with one more record. The implementation uses a double loop, where the outer loop iterates over all elements except the first one, and the inner loop searches for the insertion position in the sorted list before the current element and performs the necessary movements.
void setup() {Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
while (!Serial); // Wait for serial connection (only for boards like Leonardo that require manual serial activation)
int arr[] = {5, 2, 4, 6, 1, 3}; // Array to be sorted
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); // Calculate array length
Serial.println(“Original array:”);
printArray(arr, n);
// Execute insertion sort
insertionSort(arr, n);
Serial.println(“\nSorted array:”);
printArray(arr, n);
}
void loop() {// Empty loop, sorting only needs to be executed once
}
// Insertion sort function
void insertionSort(int arr[], int n) {// Start traversing from the second element
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
// The current element to be inserted
int key = arr[i];
int j = i – 1;
// Move elements greater than key backwards
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j–;
}
arr[j + 1] = key; // Insert element at the correct position
// Optional: Display the result of each sorting pass
/*Serial.print(“Pass “);
Serial.print(i);
Serial.print(” sorting result:”);
printArray(arr, n);*/
}
}
// Print array function
void printArray(int arr[], int n) {for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Serial.print(arr[i]);
Serial.print(” “);
}
Serial.println();
}
Code Explanation:
1. Initialization and Array Definition:
– Initialize serial communication in setup()
– Define the array to be sorted {5, 2, 4, 6, 1, 3}
– Automatically calculate the array length n
2. Core Algorithm of Insertion Sort:
– Outer loop: Start traversing from the second element (i starts from 1)
– Inner loop: Compare the current element with the sorted part to find the appropriate insertion position
– Element shifting: Move elements backwards when a larger value than the current element is found
– Insertion operation: Insert the current element at the correct position
3. Output Demonstration:
– Print the original array before sorting
– Print the result array after sorting
– (Optional) Uncomment to see the result of each sorting pass
4. Auxiliary Function:
– printArray() is used to format the output of the array contents
Upload and Test:
1. Upload the code to the Arduino development board
2. Open the serial monitor (baud rate 9600)
3. Observe the output results:
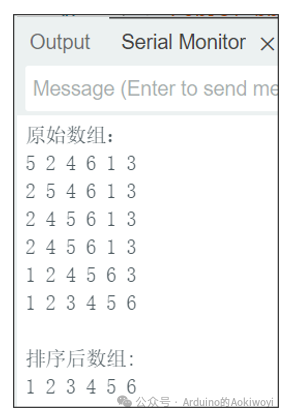
Original array:
5 2 4 6 1 3
Sorted array:
1 2 3 4 5 6
This example demonstrates how to implement a classic sorting algorithm on the Arduino platform and visually display the sorting process through serial output. You can test the sorting effect with different datasets by modifying the initial array.