
In September 2022, security researchers discovered a rare new type of attack method known as Hyperjacking. Attackers deployed an infection implant within VMware virtualization software to control the infected virtual machine systems and evade detection.
It is important to emphasize that the danger of this attack lies not in exploiting external remote code execution vulnerabilities, but rather in the attackers hijacking the administrator-level privileges of the virtual machine system. Google’s Mandiant threat intelligence team has referred to it as a serious threat to virtual machine operations, describing it as a “new malware ecosystem” because once attackers gain super administrator privileges of a virtual machine, they can maintain persistent access to the hypervisor and execute arbitrary commands.
What is a Hyperjacking Attack?
From its English name, Hyperjacking is a combination of hypervisor and jacking attacks. Therefore, Hyperjacking attacks primarily refer to unauthorized high-level administrative control achieved through malicious attacks on virtual machines (VMs).
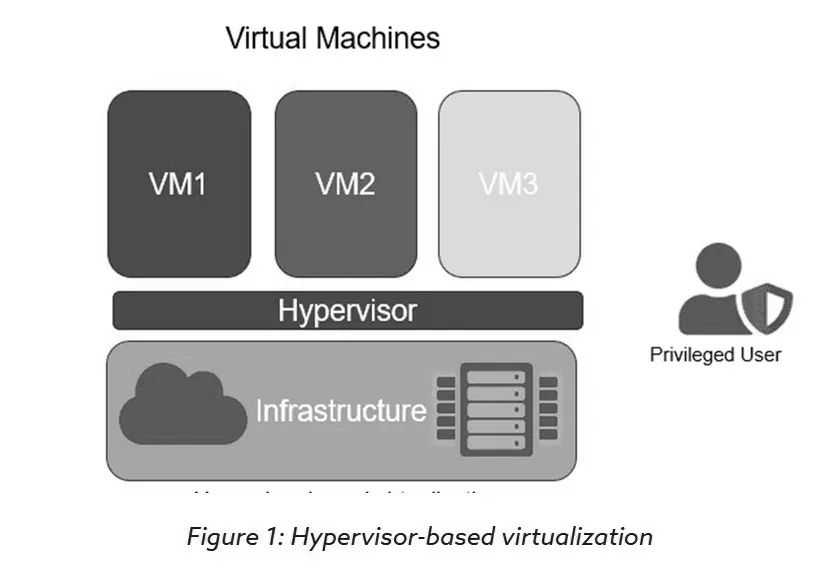
Hypervisor-based virtualization applications
Although virtual machines must exist on hardware servers, they need to operate using virtual components (such as virtual CPUs). The hypervisor is crucial for the normal operation of the virtual machine environment, as it is an intermediate software layer that runs between the underlying physical server and the operating system, allowing multiple operating systems and applications to share hardware. It is also known as a Virtual Machine Manager (VMM). The target of Hyperjacking attacks is precisely the hypervisor of the virtual machine.
Although security researchers have long suggested the possibility of Hyperjacking attacks occurring, this type of attack had not appeared in actual security incidents for many years. This may be because attackers, after weighing cost-effectiveness, found easier attack vectors, such as through more traditional malware. However, with the continuous evolution of technology and the strategies of cyber attackers, the risk of Hyperjacking attacks is increasing year by year.
Principle of Hyperjacking Attacks
The main target of Hyperjacking attacks is the hypervisor. In a typical attack, the original hypervisor is replaced by a malicious hypervisor controlled by the attacker, allowing the attacker to gain illegal control over the legitimate hypervisor and abuse the virtual machines.
By controlling the hypervisor of the virtual machine, attackers can also gain monitoring rights over the entire virtual machine server, meaning their malicious actions are more covert and difficult to detect. In the Hyperjacking attack case discovered in September of this year, hackers were found to use super administrator privileges to monitor victims.
According to Mandiant’s research report, attackers took the following actions when launching Hyperjacking attacks:
-
Maintain persistent management access to the hypervisor;
-
Send executable commands to the hypervisor that can route to client virtual machines (VMs);
-
Transfer files between the ESXi hypervisor and the clients running on it;
-
Tamper with logging services on the hypervisor;
-
Execute malicious operational commands from one client VM to another client VM running on the same hypervisor.
Researchers at VMware have also confirmed the discovery of a new variant of malware targeting vSphere in their virtualization application environment. When this malware is activated, attackers can exploit existing security vulnerabilities to harm client interests.
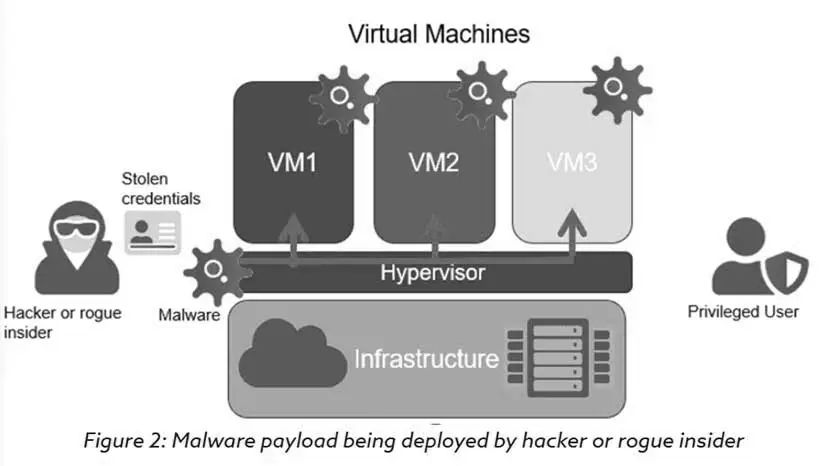
Malware payload deployed by attackers or malicious insiders
Protection Strategies Against Hyperjacking Attacks
Fortunately, compared to very popular attack strategies like phishing and ransomware, Hyperjacking attacks are still a relatively new form of cybercrime. However, it is likely to quickly gain popularity among criminal organizations to achieve their objectives of monitoring victims and stealing data assets. Therefore, if enterprises are using one or more virtual machines, they should strengthen their protective measures as soon as possible to avoid becoming victims of Hyperjacking attacks.
1. Authentication and Authorization
Enterprises often overlook the establishment of appropriate access control policies when deploying virtual infrastructure. System administrators typically have unrestricted access to the root directories of large virtual machines, making enterprises more susceptible to Hyperjacking attacks. By applying basic principles of defense in depth and adopting a least privilege model, such attacks can be effectively prevented. As part of the least privilege model, the use of strong password policies and multi-factor authentication can help mitigate these attacks.
2. Role-Based Access Control
In addition to using the least privilege model, enterprises should implement role-based access control policies before deploying virtual machines to prevent the threat of Hyperjacking attacks. By defining detailed, fine-grained role-based access controls, the least privilege access principle can be used to limit the capabilities of super administrators. These measures can also help determine who can access content within the virtual environment.
3. Secondary Approval
Secondary approval can enforce additional audits before users perform sensitive, destructive operations on resources. For example, if certain privileged users are executing actions such as deleting or shutting down virtual machines, editing firewalls, or creating edge gateway services, the system can require secondary approval. Additionally, privileged users cannot approve requests they initiate themselves, even if they are in the audit group.
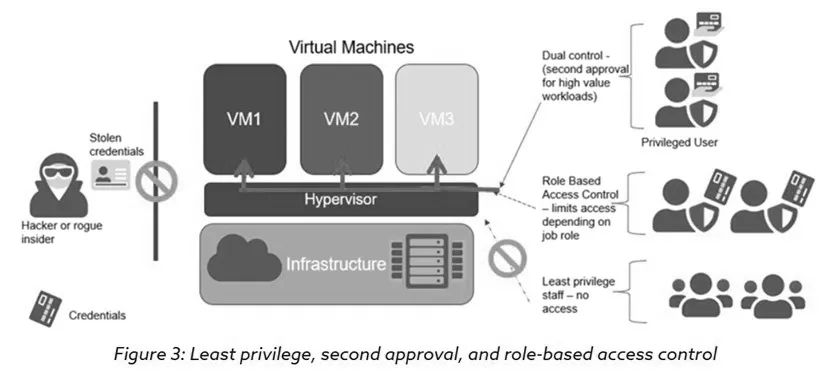
Least privilege, secondary approval, and role-based access control
4. Host Authentication
Host authentication is another key measure to prevent Hyperjacking attacks. Virtual environment administrators can use it to help block attackers in certain scenarios. For example, host authentication can ensure that during the host boot cycle, the current trusted state of the virtual machine system can be determined by leveraging a “fingerprint” or a set of unique host measurements.
5. Strengthening Basic Security Measures
Enterprises should always ensure that robust basic protective measures are in place for virtual machine application systems. For instance, firewalls can be used to isolate each virtual machine, and host devices should have adequate antivirus protection. When attackers gain control over virtual machines, they can use them to access other hardware. Therefore, efforts should be made to avoid linking virtual machines to unnecessary devices to prevent attackers from further exploiting them after completing their attacks.
Organizations should also ensure that the hypervisor is regularly patched to prevent malicious actors from exploiting bugs and vulnerabilities in the software. This is one of the most common ways cybercriminals carry out attacks, and often, they cause significant damage before software vendors are aware of the security vulnerabilities.
Reference Links:
https://cloudsecurityalliance.org/blog/2022/11/29/preventing-hyperjacking-in-a-virtual-environment/
https://www.makeuseof.com/what-is-hyperjacking-attack/
Related Articles
Implementing Large-Scale Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: DNS Hijacking
UK Media Reports Chinese Hackers Hijacking Forbes Website

Cooperation Phone: 18311333376Cooperation WeChat: aqniu001Submission Email: [email protected]