
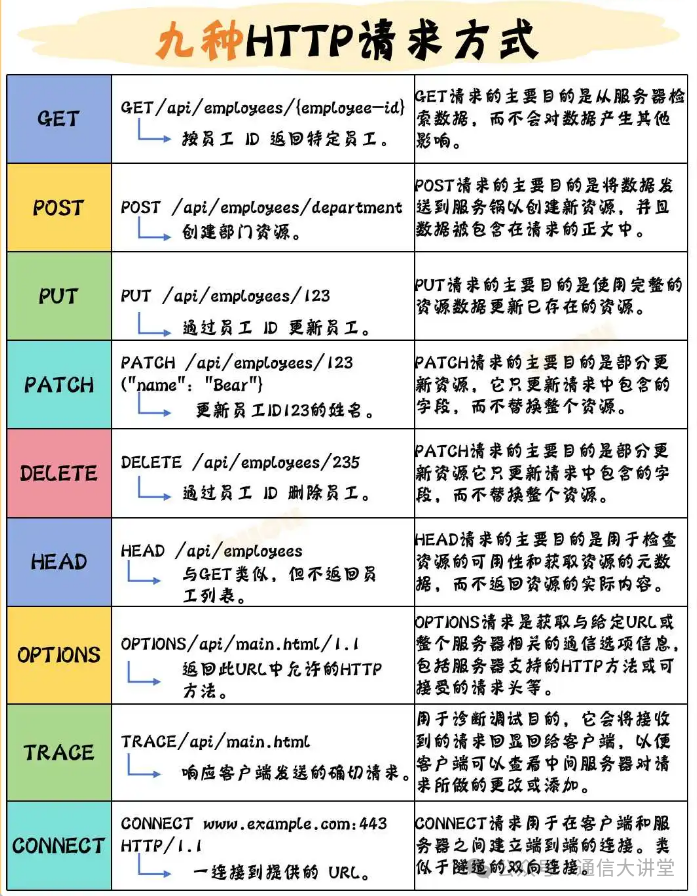
HTTP requests are an important means of communication between the front-end and back-end, and as developers, it is essential to master them. Today, I will introduce the 9 common types of HTTP request methods, along with their respective uses and differences:
- GET
Retrieve specific employee information by employee ID. GET is the primary method for reading data from the server and does not affect the data in any other way. - POST
Create department resources. POST sends data to the server to create a new resource, and the request includes a complete data package. - PUT
Update employee information by employee ID. PUT replaces the existing resource data, ensuring that the resource is completely present or overwritten. - PATCH
Update specific fields of an employee, such as changing the name of the employee with ID 123. PATCH only modifies part of the content in the resource without affecting other fields. - DELETE
Delete an employee by employee ID. DELETE requests are used to remove specified resources. - HEAD
Similar to GET, but does not return the employee list, only retrieves metadata. HEAD is often used to check the status of a resource. - OPTIONS
Returns the HTTP methods allowed for a URL, used to detect the communication options supported by the server. - TRACE
Echoes the request sent by the client, useful for debugging and tracing the request path. - CONNECT
Used to establish a tunnel connection between the client and server, commonly seen in HTTPS connections.
Each request method has its unique purpose, and learning to use them correctly can make our APIs more efficient and secure!


Some screenshots from electronic books

Complete set of hardware documentation collection
