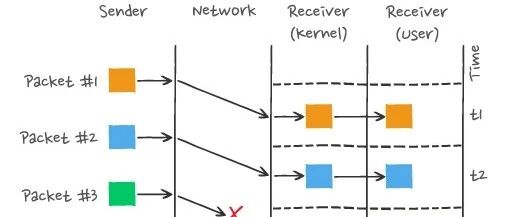
What are HTTP Long Connections and Pipelining Principles? What is Head-of-Line Blocking? How does HTTP/2 Multiplexing Solve Head-of-Line Blocking? What Optimizations Does HTTP/3’s QUIC Protocol Provide?
This article belongs to the collection: Interviewing the Interviewer Series For more interview questions, feel free to add the assistant’s WeChat at the end of the article! This article overview includes: What are the main differences between HTTP/1.1 and HTTP/1.0? Can you elaborate on how HTTP long connections are implemented, their advantages, and disadvantages? Can … Read more