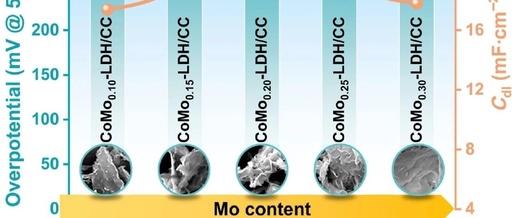
Nano Res.【OER】| Layered Cobalt-Molybdenum Double Hydroxide Arrays Enhance Efficient Oxygen Evolution Reaction
Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) based on transition metals have demonstrated high efficiency as catalysts in the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) during alkaline water electrolysis, which is crucial for sustaining hydrogen production. However, there is an urgent need to explore new LDH-based electrocatalysts that possess both high activity and good stability, which is essential for a … Read more