Introduction to the Core Component of OpenWrt: libubox (1)
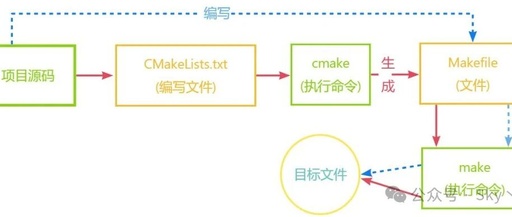
During the project development process, many applications require common I/O operations, data structures, and algorithms. If each application needs to rewrite these functionalities, it will inevitably reduce development efficiency and increase the possibility of code instability. Therefore, many large projects develop basic libraries or services for other applications to use. These components are referred to … Read more