Key Techniques for Circuit Board Repair
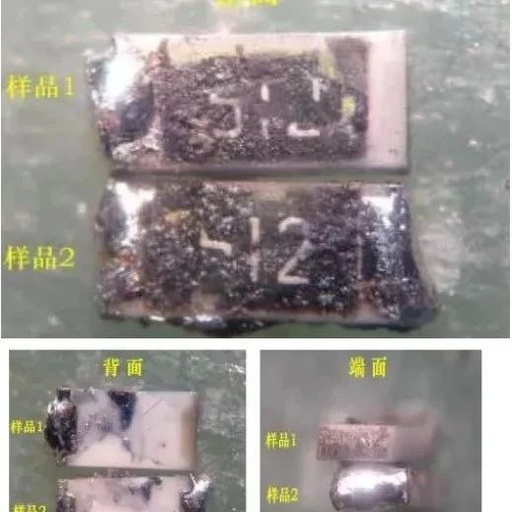
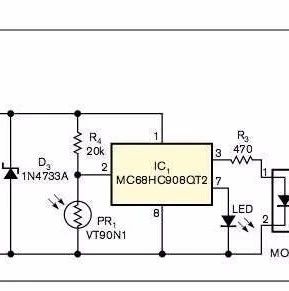
1. Faults Caused by Capacitor Damage Capacitor damage is the most common fault in electronic devices, particularly with electrolytic capacitors. Signs of capacitor damage include: reduced capacitance; complete loss of capacitance; leakage; short circuit. Different capacitors serve various roles in a circuit, leading to distinct fault characteristics. In industrial control circuit boards, digital circuits dominate, … Read more