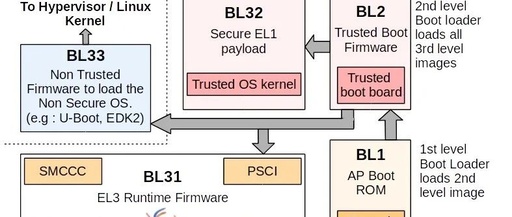
Exception and Interrupt Model of Armv8/Armv9
Click the blue "Arm Selection" in the upper left corner and select "Set as Favorite" 1 Introduction This article introduces the exception and privilege model in Armv8-A. It covers the different types of exceptions in the Arm architecture and the behavior of the processor when an exception is received. This article is relevant for developers … Read more