ARMv8/v9-GIC Virtual Interrupt Direct Injection System Architecture
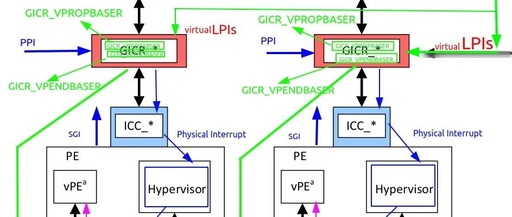
ver0.2 Introduction In the previous article, we introduced the basic architecture and routing mechanism of LPI-type interrupts. I believe everyone is now somewhat familiar with LPI-type interrupts, at least understanding the difference between bus-based (Message) and hardwired (Signal) interrupt types. We also discussed the basic architecture and working principles of GIC physical interrupt virtualization. However, … Read more