Linux | Red Hat Certified | IT Technology | Operations Engineer
👇 Join the technical exchange QQ group with 1000 members, note 【public account】 for faster approval

1. The Origin and Development of Linux
1. Initial Motivation: Linux is a powerful open-source operating system developed and released by Linus Torvalds, a student at the University of Helsinki. Linus Torvalds started writing Linux to learn about the Unix operating system. However, due to the high cost of purchasing a Unix workstation, he decided to create a Unix-like operating system that could run on the 386 processor, which became the prototype of Linux.
2. Release and Growth: On October 5, 1991, Linus Torvalds released the first version of Linux on the Usenet newsgroup comp.os.minix. Since then, Linux has continuously updated and iterated, attracting more and more developers and users to participate.
3. Open Source Spirit: From the very beginning, Linux has followed the spirit of the GPL (GNU General Public License), with its kernel being free and open. This open-source spirit has allowed Linux to quickly attract a large number of developers who contribute to its development.
2. Features of Linux
1. Open Source: The source code of Linux is publicly available, allowing users to freely view, modify, and distribute it, which gives Linux a high degree of transparency and customizability.
2. Stability: The Linux operating system is designed to be very stable and reliable, with its kernel having undergone rigorous testing and validation, capable of running stably for long periods even in extremely harsh environments.
3. Security: Linux provides multi-layered security protections, including access control and permission management, making it the preferred operating system for many security-sensitive applications.
3. Applications of Linux
1. Server Domain: Linux is widely used in the server domain, especially in network servers and cloud computing. Due to its efficiency, stability, and security, Linux has become the operating system of choice for many enterprises and organizations.
2. Desktop Systems: Although Linux has a relatively small market share in the desktop system domain, many users still choose Linux as their daily operating system. This is mainly because Linux offers a wealth of free software resources, as well as high customizability and security.
3. Embedded Systems: Linux is also widely used in embedded systems, such as smartphones and routers. This is mainly because the Linux system has low hardware resource requirements while providing good stability and scalability.
4. Linux Distributions
1. Ubuntu
Features: Ubuntu is one of the most popular Linux distributions, focusing on ease of use and user-friendliness. It provides an attractive graphical user interface and powerful package management tools, such as APT (Advanced Packaging Tool), making software installation and upgrades very convenient. Ubuntu also has a large community support, where users can get help and share experiences.
Use Cases: Suitable for beginners and general desktop users, also widely used in servers and cloud computing platforms.
2. CentOS
Features: CentOS (Community Enterprise Operating System) is a distribution based on the source code of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). It focuses on stability and security and is widely used in enterprise and server environments. CentOS provides long-term support (LTS), with a relatively long update and patch release cycle, ensuring system stability. CentOS uses YUM (Yellowdog Updater, Modified) as its package management tool.
Use Cases: Mainly aimed at the server market, especially for enterprise applications.
3. Fedora
Features: Fedora is a community-driven distribution sponsored by Red Hat, dedicated to providing the latest software and technologies. Fedora adopts a rolling update model, regularly releasing new versions and providing an advanced package management system, DNF (Dandified Yum). Fedora also aims to promote innovation in the open-source community and is a pioneer of many new technologies and projects.
Use Cases: Suitable for desktop users and servers, especially those who want to use the latest technologies and features.
4. Debian
Features: Debian is a very stable, reliable distribution with extensive software package support. It emphasizes the principles of free software and offers various choices, such as the X Window System and GNOME desktop environment. Debian’s package management tool APT is very powerful, allowing for quick installation, updates, and uninstallation of packages. Debian is also the foundation for many other distributions, such as Ubuntu.
Use Cases: Suitable for users pursuing stability and free software, whether in server or desktop environments.
5. openSUSE
Features: openSUSE is an open-source distribution launched by the German company SUSE, including Leap (stable version) and Tumbleweed (rolling release). It provides YaST, a comprehensive system configuration tool, making system configuration and management simple and convenient.
Use Cases: Provides desktop and server versions, suitable for users who need stability and ease of management.
6. Arch Linux
Features: Arch Linux is a rolling release distribution aimed at advanced users. It emphasizes simplicity, modernity, and user customization, providing the latest packages through the Pacman package manager and AUR community repository. Arch Linux encourages users to build their systems from the ground up.
Use Cases: Suitable for advanced users and tech enthusiasts with high requirements for Linux.
7. Kali Linux
Features: Kali Linux is designed for network security and penetration testing, containing numerous security auditing and attack tools.
Use Cases: It is one of the preferred tools for security professionals.
8. Raspbian (Raspberry Pi OS)
Features: Raspbian is a Debian derivative specifically designed for the Raspberry Pi, providing optimizations and features tailored for Raspberry Pi hardware.
Use Cases: Suitable for Raspberry Pi single-board computers.
Setting Up a Linux Environment
1. Ways to Set Up a Linux Environment
There are mainly three ways:
1. Directly install on a physical machine. However, since using Linux on the desktop is very unfriendly, it is not recommended.
2. Use virtualization software to set up Linux on a virtual machine. However, due to some bugs in current virtualization software (like VMWare), various inexplicable issues may arise in the environment, which can be quite troublesome.
3. Use cloud servers, where you can directly purchase a cloud server from providers like Tencent Cloud, Alibaba Cloud, or Huawei Cloud.
Next, I will introduce the third method.
2. Purchasing a Cloud Server
Taking Huawei Cloud as an example, other server providers are similar.
Visit the official website: https://activity.huaweicloud.com
Log in to the website; if you are a new user, you should register first.
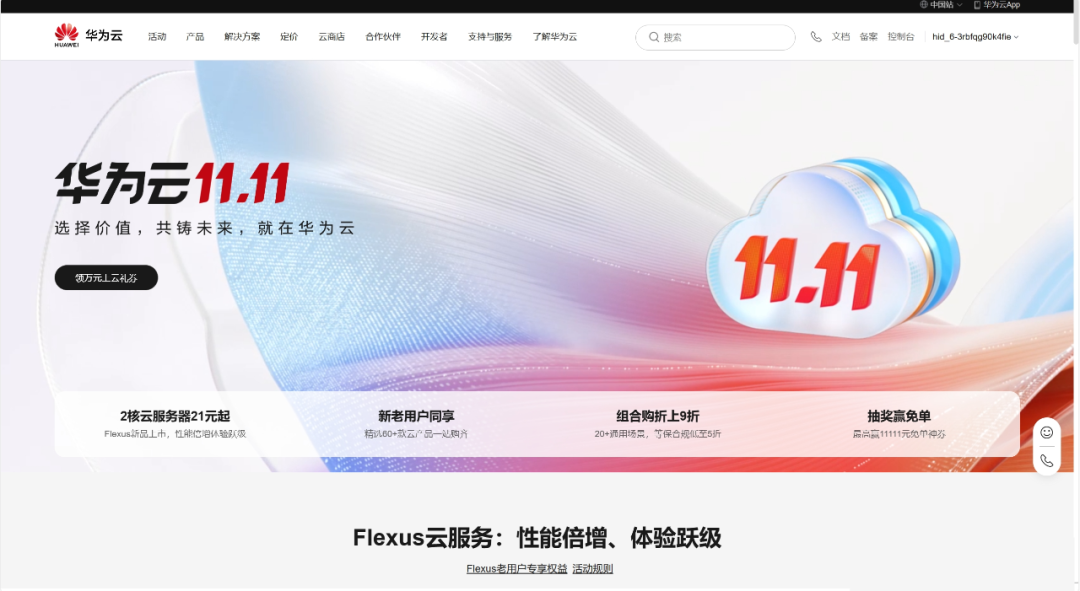
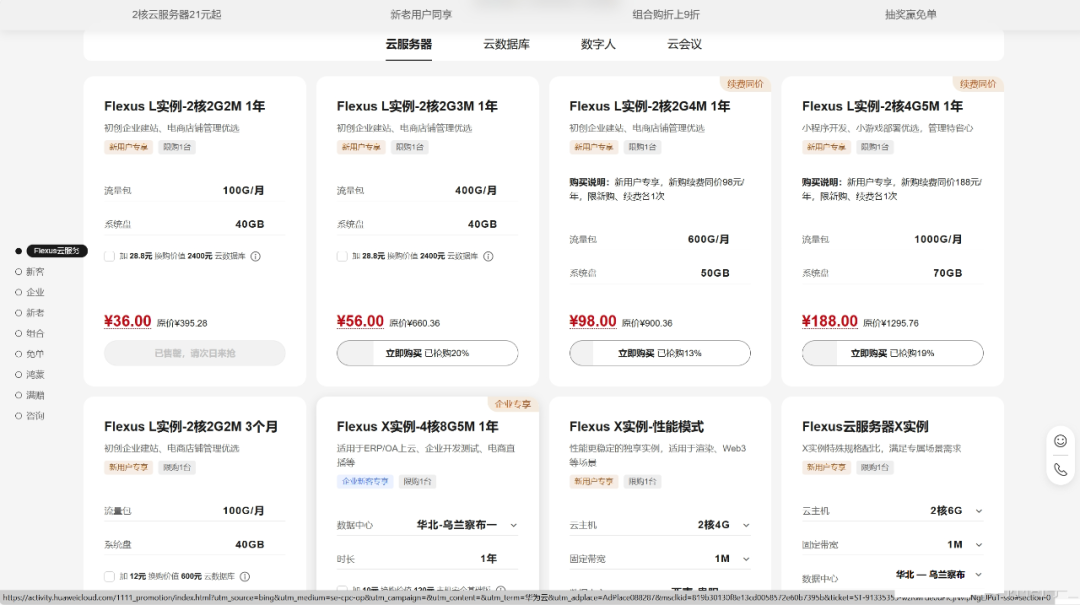
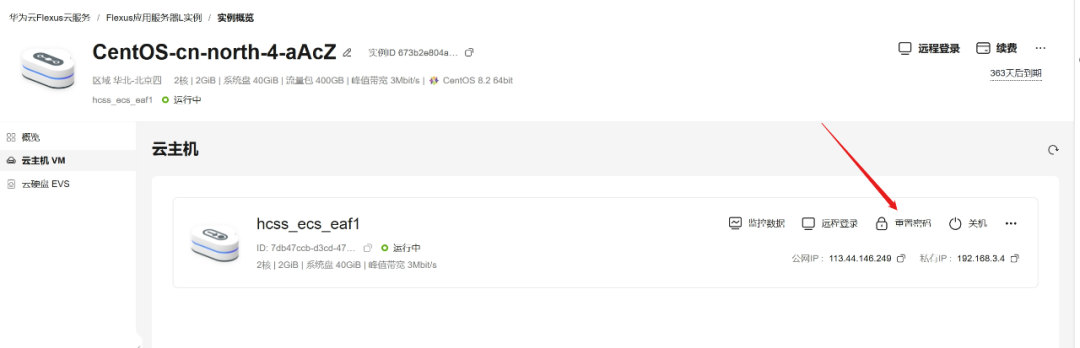
Purchase the cloud server you need based on your requirements.
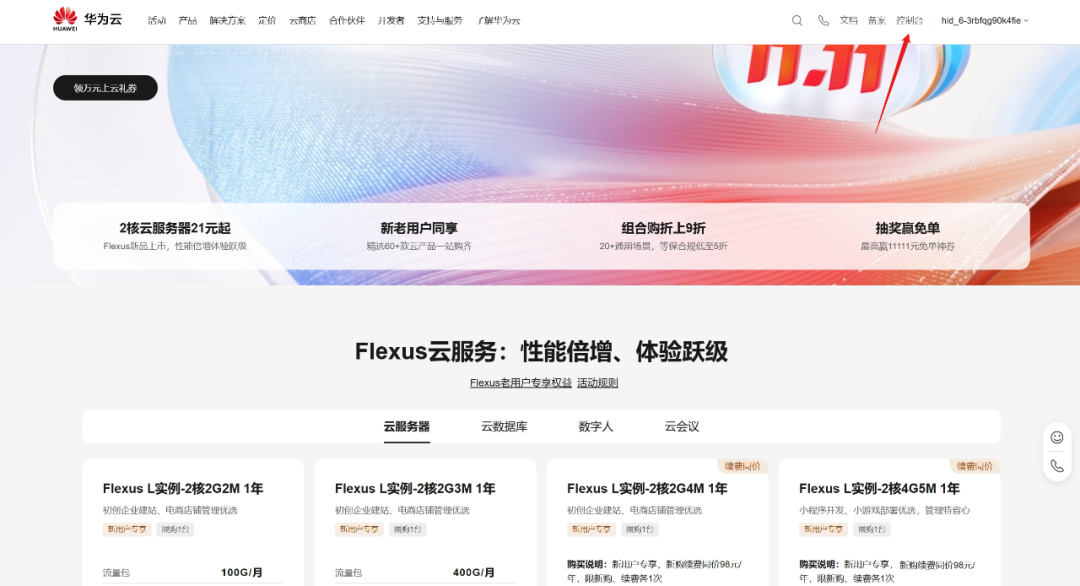
After purchasing, you can find your server in the console. Clicking on it will show the server’s IP address.
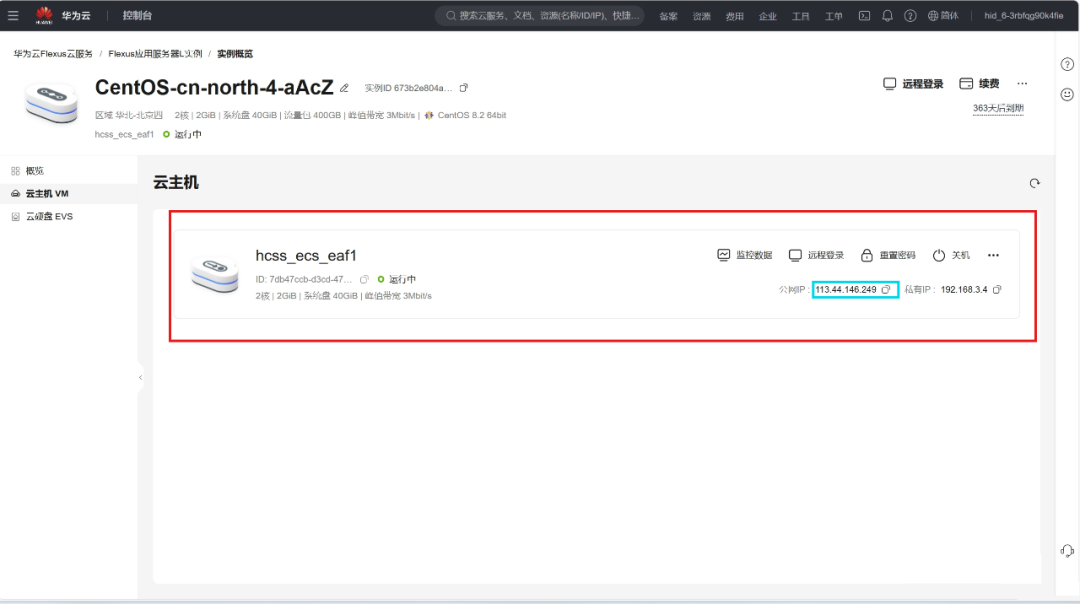
The blue box indicates the public IP address, which we will use to log in to the server later.
Set the root password: Click on reset password (this step may require SMS verification). It is recommended to set a slightly complex root password to avoid being hacked.
Summary:
In this step, the most important information we need is:
The server’s external IP
The administrator account of the server (fixed as root)
The administrator account password (set on the Tencent Cloud website)
With these three pieces of information, you can use XShell for remote login.
3. Using XShell to Remotely Log in to Linux
1. Download and Install Xshell
XShell is a remote terminal software.
Download from the official website.
When installing, choose “home/school” for the free version.
2. Check the IP Address of the Linux Host
Refer to the “Purchasing a Cloud Server” section above.
3. Use XShell to Log in to the Host
In the XShell terminal, type:
ssh root@your_public_IP
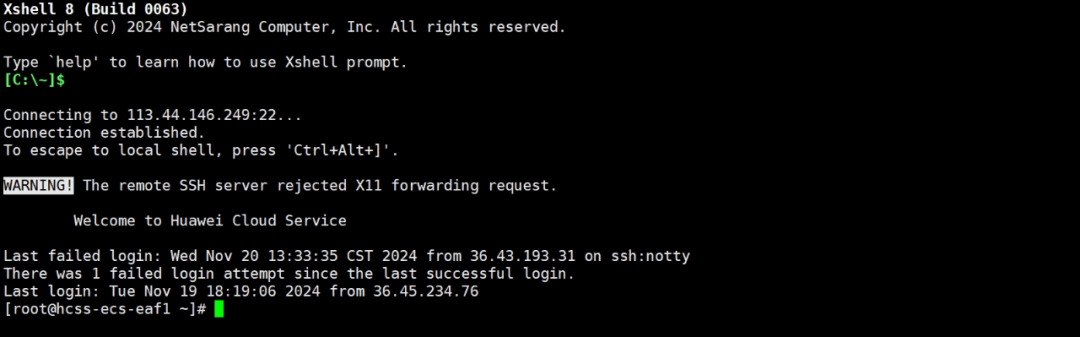
The interface after a successful login should look like this:
For course inquiries, add: HCIE666CCIE
↓ Or scan the QR code below ↓
If you have any technical points or content you want to see, please leave a message below!