Skip to content
ADCs (Antibody-Drug Conjugates) and RDCs (Radionuclide Conjugates) are innovative drugs that have gained significant attention in recent years, demonstrating enormous potential in the field of oncology. They are referred to as the “magic bullets” of tumor-targeted therapy because they enable precise treatment while avoiding damage to normal cells.
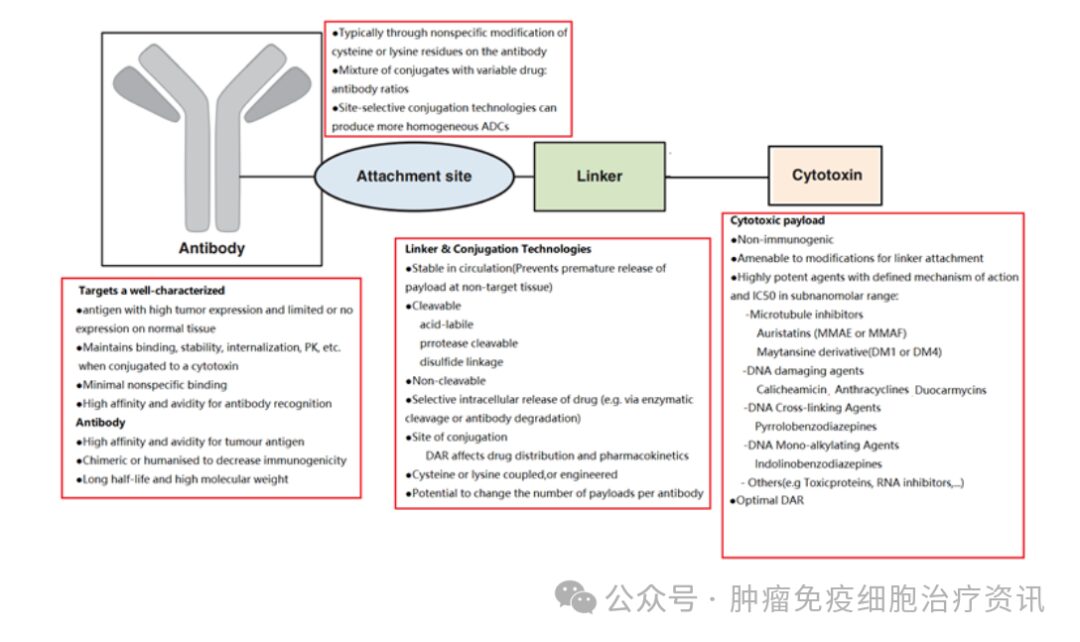
ADC drugs link antibodies with known effective toxic molecules through a linker, forming a conjugate that combines the characteristics of targeted drugs and chemotherapy drugs. This type of drug can avoid harming normal cells and achieve precise treatment. A complete ADC drug consists of three structural modules: antibody, linker, and small molecule drug. The antibody has a large molecular weight, and research can be conducted using mass spectrometry (MS). Narrowly defined ADC compounds only contain the drug and linker, with various types of drugs and linkers composed of PEG units, peptide units, and rigid six-membered rings. These compounds can be analyzed in terms of their structure using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR).
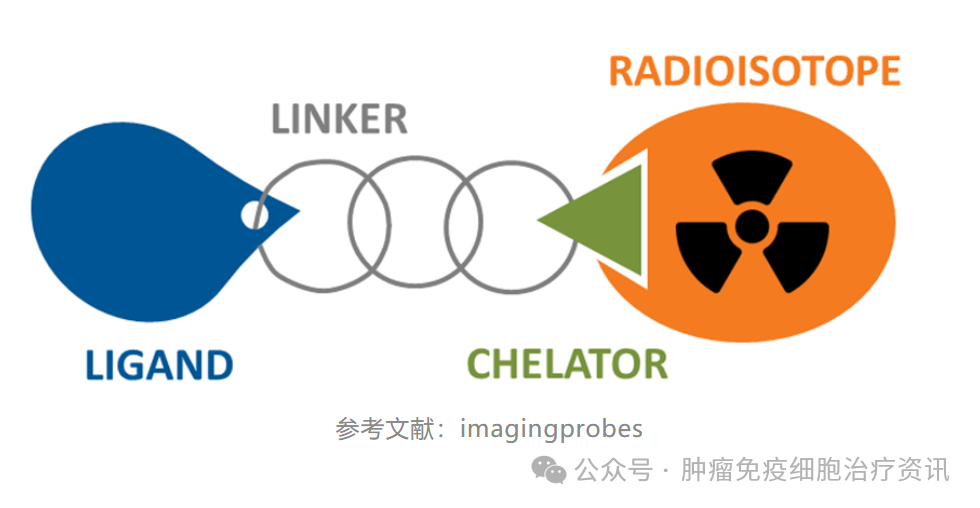
RDC drugs are structurally similar to ADC drugs and also possess the ability to deliver precisely to tumors, being used for both imaging diagnosis and treatment. RDCs mainly consist of antibodies or small molecules (Ligands), linker arms, chelators, and radioactive isotopes. The biggest difference from ADCs lies in the drug payload, as RDCs use radioactive nuclides instead of small molecule drugs. Different medical nuclides can achieve various functions, including imaging and treatment, and some nuclides even possess both capabilities.
Although the development of ADC drugs has been hotter than that of RDC drugs, the number of FDA-approved RDC drugs has gradually increased in recent years, showing the potential and development trend of the RDC field. This indicates that the development of RDC drugs may be gaining traction.
In summary, both ADCs and RDCs have enormous potential in the field of tumor-targeted therapy. They can achieve precise treatment while avoiding damage to normal cells, and there are some structural differences in terms of drug payload and the nuclides used. With continuous technological advancements and deeper research, ADCs and RDCs are expected to achieve greater breakthroughs and applications in tumor treatment.
1. Chari RVJ, Miller ML, Widdison WC. Antibody-drug conjugates: an emerging concept in cancer therapy. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 2014;53(15):3796-3827.
2. Reilly SW, Wester H, Ploeger B. Antibody cocktails: A strategy to combat tumor heterogeneity? Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2020;156:78-87.
3. Seneviratne DS, Lau JL, Murphy SJ, Buggy CJ. The Current status of antibody-drug conjugates in cancer chemotherapy. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2020;156:112-132.
4. Pillai MRA. Nanoparticle-formulated alpha-particles-injectable Rhenium-188 for radionuclide therapy. Nanomedicine. 2017;12(12):1387-1389.






