 Weekly Linux Command (netstat)
Weekly Linux Command (netstat)
Command Overview (netstat)
netstat (network statistics) is a command-line tool used to display network connections (incoming and outgoing), routing tables, and various network interface (network interface controllers or software-defined network interfaces) and network protocol statistics. It can also be used to diagnose network issues, print status information about the network system in Linux, and view the overall network status of the Linux system.
The netstat tool is widely used across platforms, including Linux, Solaris, and Kylin, as well as Windows NT-based operating systems, including Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7/8/10.
# Syntax
netstat without syntax output, as shown:
root@valwell:~# netstat
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Active Internet connections (w/o servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
tcp 0 0postgres:58288 postgres:amqp ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0postgres:45566 postgres:6379 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0postgres:58312 postgres:amqp ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0postgres:36178 postgres:postgresql TIME_WAIT
Active UNIX domain sockets (w/o servers)
Proto RefCnt Flags Type State I-Node Path
unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 23733 /var/lib/haproxy/dev/log
unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 1594464 /run/user/1000/systemd/notify
unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 40530 /run/user/0/systemd/notifyAs shown above:<span>netstat</span> directly outputs two parts (for understanding only):
-
<span>Active Internet connections (w/o servers):</span>displays the established network connections on the host -
Active UNIX domain sockets (w/o servers): displays all active “Unix Domain” open sockets
# Practical Command Examples
1. List all ports and connections; the output will list established connections and services that are opening or listening
netstat -a 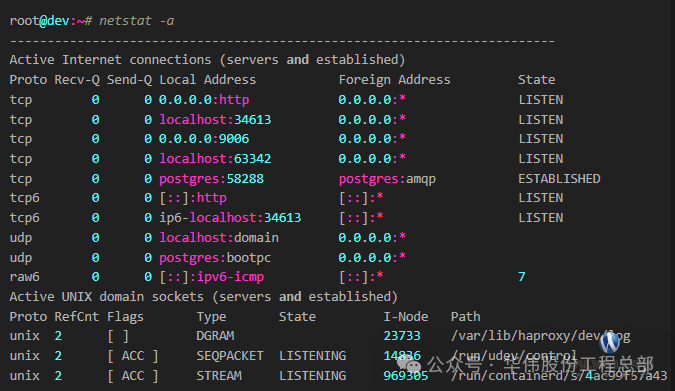
2. List all TCP ports
netstat -at 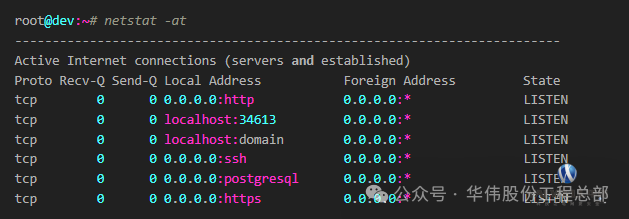
3. List all UDP ports
netstat -au 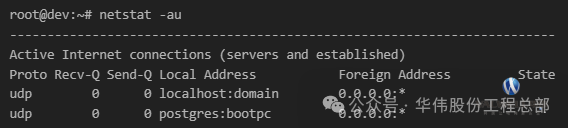
4. List listening ports
netstat -L
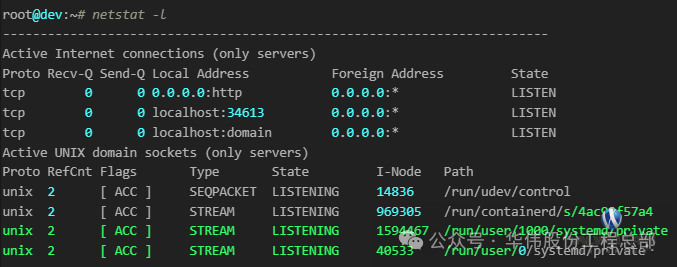
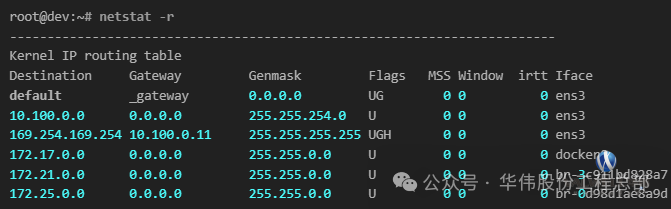
5. List kernel IP routing
netstat -r
6. Find the service process for a specific port
(1) Find by port
netstat -ano | grep ‘:[port_number]’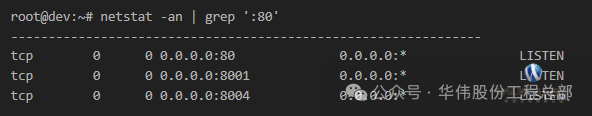
(2) Find by service name
netstat -ap | grep ‘:[service_name]’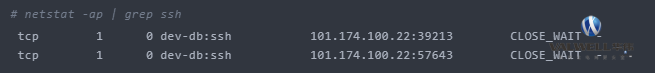
 END
END