Overview of the Semiconductor Industry
The semiconductor downstream applications are extensive and closely related to economic development.

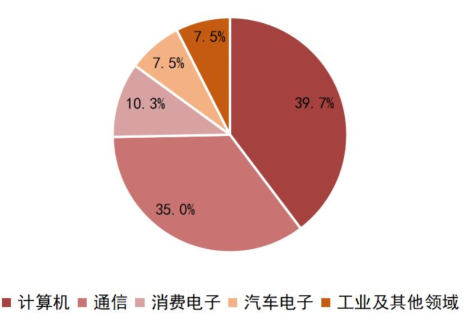
From the perspective of downstream demand structure, computers (mainly PCs and servers) and communication products (primarily smartphones) constitute the main sources of global semiconductor demand, accounting for nearly three-quarters combined. According to IC Insights data, in 2020, the sales revenue from the computer sector accounted for 39.7% of the semiconductor downstream proportion, while the communication sector accounted for 35.0%. This is followed by consumer electronics and automotive electronics, which accounted for 10.3% and 7.5%, respectively.
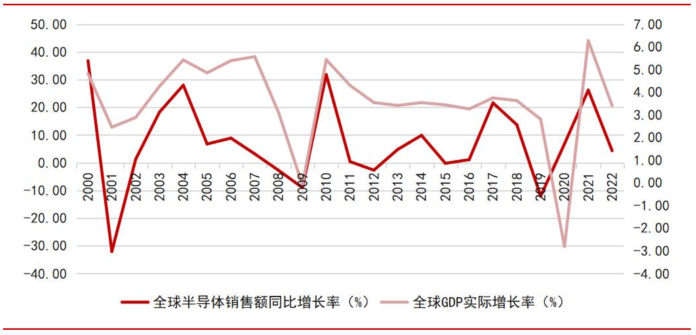
In the electronic information era, the sales of semiconductors are increasingly closely related to global economic growth, playing a significant role in economic development.
In the electronic information era, semiconductors play an increasingly important role in economic development, with semiconductor sales closely linked to global economic growth. According to data provided by WSTS and the International Monetary Fund, from 1987 to 1999, the correlation coefficient between global semiconductor sales growth rate and GDP growth rate was 0.13, while from 2000 to 2022, the correlation coefficient rose to 0.46, indicating a significant increase in correlation. With the continuous increase in silicon content in downstream PCs, servers, smartphones, and new energy vehicles, it is expected that the correlation between semiconductor sales and the level of economic development will continue to increase in the future.
Chart 2: Year-on-Year Growth Rate of Global Semiconductor Sales from 2000 to 2022, Actual Growth Rate of Global GDP
Review of Industry Sales Scale: Downstream Innovation Drives Industry Development, Industry Scale Grows Amid Fluctuations.
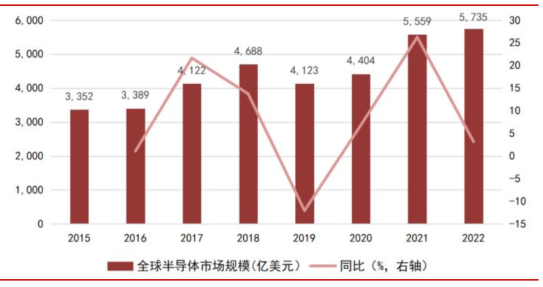
We reviewed the sales situation of semiconductors over the years and found that the market scale of the industry is primarily determined by downstream innovation. The sales situation of downstream terminals and the release of corporate production capacity jointly determine the cyclical fluctuations, showing overall growth amidst fluctuations. From 2015 to 2022, the global semiconductor sales scale grew from $335.2 billion to $573.5 billion, with a compound annual growth rate of 7.97%, higher than the global GDP growth rate during the same period.
2015-2018: Smartphones were still in a rapid penetration period, driven by strong demand for downstream consumer electronics such as smartphones and TWS, the global semiconductor market flourished, with the market scale growing from $335.2 billion to $468.8 billion, and a compound growth rate of 11.83% from 2015 to 2018; 2019: The market for smart terminals represented by smartphones declined, leading to a downturn in the global semiconductor cycle, compounded by intensified international trade frictions, with the global semiconductor industry market size at $412.3 billion, a year-on-year decline of 12.05%; 2020-2022: With the continuous expansion of 5G terminal scale, increasing demand for data centers, and the gradual expansion of AIoT and other intelligent scenarios, along with increased demand for remote work and home entertainment amidst the pandemic, the global semiconductor industry scale rose, with the global semiconductor market size at $440.4 billion, $555.9 billion, and $573.5 billion in 2020, 2021, and 2022, respectively, with year-on-year growth rates of 6.82%, 26.83%, and 3.17%.
Chart 3: Global Semiconductor Market Size from 2015 to 2022
Classification of the Semiconductor Industry.
According to the World Semiconductor Trade Statistics (WSTS), semiconductor products are categorized into four main types: Integrated Circuits, Discrete Devices, Optoelectronic Devices, and Sensors. Among them, integrated circuits account for over 80% of the industry scale, with subfields including logic chips, memory chips, microprocessors, and analog chips, which are widely used in industries such as 5G communication, computers, consumer electronics, network communication, automotive electronics, and the Internet of Things, making them a core component of most electronic devices.
According to WSTS data, in 2022, the global market sizes for integrated circuits, discrete devices, optoelectronic devices, and sensors were $479.988 billion, $34.098 billion, $43.777 billion, and $22.262 billion, respectively, accounting for 82.7%, 5.9%, 7.5%, and 3.8% of the global semiconductor industry. Among these semiconductor product distributions, integrated circuits are the most technologically challenging and fastest-growing sub-product, making them the most important component of the semiconductor industry.
Chart 4: Classification of Semiconductors
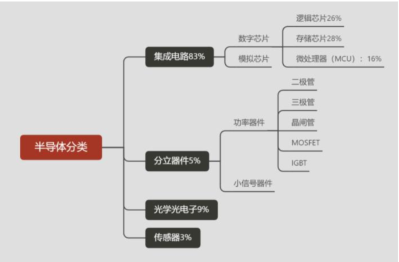
Chart 5: Sales Proportion of Semiconductor Subcategories (2022)
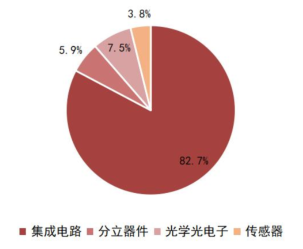
Chart 6: Market Size Changes of Semiconductor Subcategories from 2011 to 2022
Integrated Circuits: Integrated circuits (IC) are a type of microelectronic device or component that uses specific processes to interconnect the necessary transistors, resistors, capacitors, and inductors in a circuit onto a small piece or several pieces of semiconductor wafers or medium substrates, which are then encapsulated in a housing, forming a microstructure with the desired circuit function, also known as a chip.
Based on the type of signal processed, integrated circuits can be divided into digital integrated circuits and analog integrated circuits. Digital integrated circuits are used for arithmetic and logical operations on discrete digital signals, including logic chips, memory chips, and microprocessors, which are digital logic circuits or systems made by integrating components and connections on the same semiconductor chip; analog integrated circuits mainly refer to integrated circuits that consist of capacitors, resistors, transistors, etc., and are used to process analog signals. According to WSTS data, in 2020, logic chips, memory chips, microprocessors, and analog chips accounted for 32.78%, 32.52%, 19.29%, and 15.41% of the integrated circuit market size, respectively.
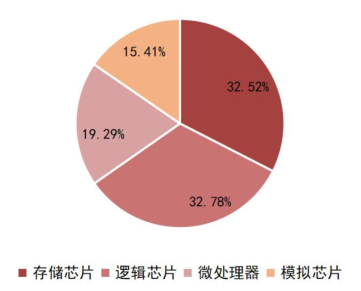
Chart 8: Comparison of Analog Integrated Circuits and Digital Integrated Circuits
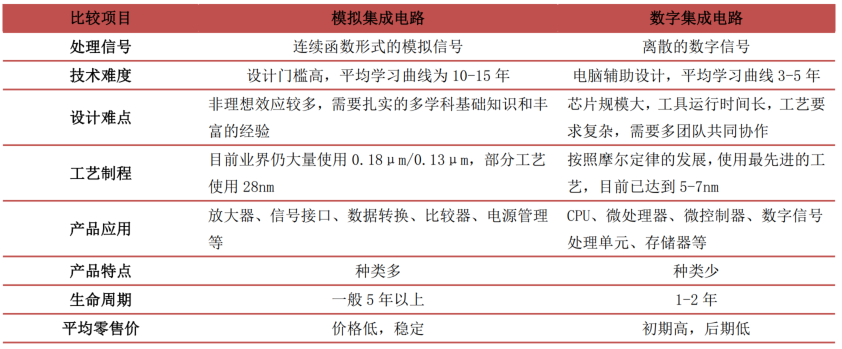
Chart 9: Discrete Device – Diode

Chart 10: Discrete Device – Transistor

Chart 11: Discrete Device – IGBT

Chart 12: Some Types of Discrete Devices

Chart 13: Types of Optoelectronic Devices
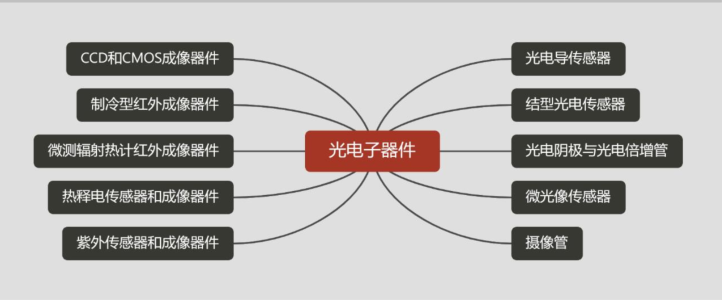
Chart 14: Classification of Sensors
Structure of the Semiconductor Industry

From the production process perspective, semiconductor production is mainly divided into design, manufacturing, and packaging/testing processes, requiring upstream semiconductor equipment and materials for support. Integrated circuits, represented by various products, have extensive downstream applications, and the demand growth driven by downstream innovation is the core driving force behind the rapid development of the semiconductor industry.

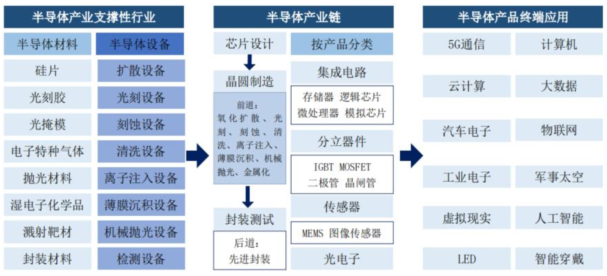

It refers to designing the required circuit diagram according to established functional requirements, with the final output being the mask layout. The integrated circuit design industry in our country started relatively low, but relying on huge market demand and favorable industrial policy environment, it has become a new force in the global integrated circuit design industry.
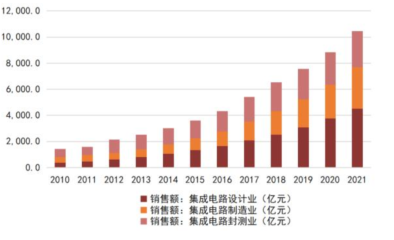
In terms of industry scale, the sales scale of integrated circuit design in mainland China grew from 38.3 billion yuan in 2010 to 451.9 billion yuan in 2021, with a compound annual growth rate of about 25.15%. The gradual improvement of the local industrial chain has also provided wafer manufacturing support for domestic startup chip design companies, coupled with industrial funding and policy support, as well as the return of overseas talent, the number of chip design companies in our country has rapidly increased. According to data from the China Semiconductor Industry Association, since 2010, the number of chip design companies in our country has significantly increased from 582 in 2010 to 3,243 in 2022, with an average compound growth rate of about 15.39% from 2010 to 2022.

Chart 16: Growth of Chip Design Enterprises in China from 2010 to 2022
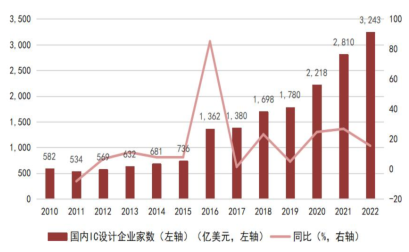
Chart 17: Sales Revenue and Year-on-Year Growth Rate of Integrated Circuit Design Industry in China
Integrated Circuit Manufacturing:

Integrated circuit manufacturing refers to the process of transferring the designed circuit diagram onto substrate materials such as silicon wafers, that is, fabricating the necessary transistors, diodes, resistors, and capacitors on a small piece of silicon, glass, or ceramic substrate using certain processes, and then interconnecting them using appropriate techniques, followed by packaging them in a housing, significantly reducing the overall circuit size and the number of lead and solder points.
From a process perspective, the integrated circuit manufacturing process is generally divided into front-end (Front End of Line, FEOL) and back-end (Back End of Line, BEOL). The front-end process generally refers to the manufacturing process of devices like transistors, mainly including isolation, gate structure, source-drain, and contact hole formation processes. The back-end process primarily refers to forming interconnection lines that transmit electrical signals to various devices on the chip, mainly including dielectric deposition between interconnection lines, metal line formation, and contact pad preparation processes.
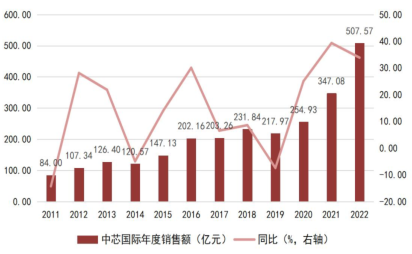
In recent years, benefiting from the rise of local wafer foundries like SMIC and Hua Hong Semiconductor, as well as the establishment of leading foundry companies like TSMC in mainland China, the market scale of integrated circuit manufacturing in our country has achieved rapid growth. According to data from the China Semiconductor Industry Association, from 2010 to 2021, the market scale of integrated circuit manufacturing in mainland China grew from 40.9 billion yuan to 317.63 billion yuan, with a compound annual growth rate of 20.48%. Among them, SMIC’s annual revenue grew from 8.4 billion yuan to 50.757 billion yuan, with a compound annual growth rate of 17.77% from 2011 to 2022.

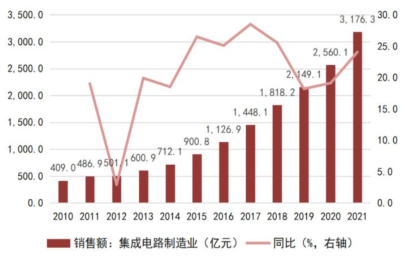
Chart 19: Annual Revenue and Year-on-Year Growth Rate of SMIC from 2011 to 2022
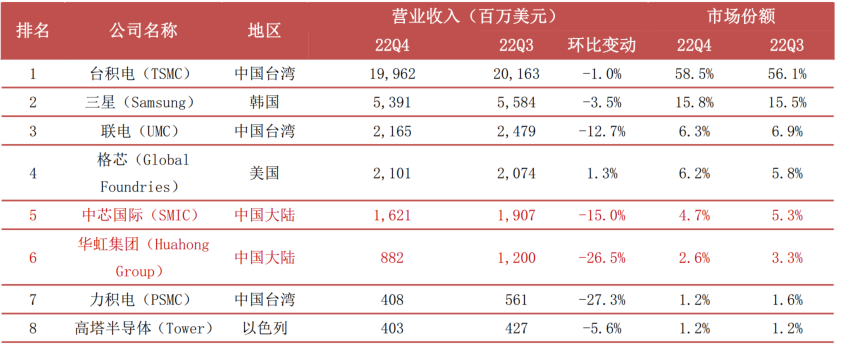
TSMC dominates the market, while SMIC and Hua Hong Semiconductor are rapidly rising. Integrated circuit manufacturing requires thousands of steps, and the close coordination and error control between each link require substantial experience accumulation. Any error in one step can significantly reduce the chip yield, thus presenting extremely high technical barriers. In addition to technology, the semiconductor manufacturing process also has very high capital requirements, with the capital expenditure to build a wafer factory requiring billions or even hundreds of billions of dollars. The extremely high technical and financial barriers lead to a very high industry concentration, with TSMC currently exhibiting a competitive landscape of dominance, maintaining dual leadership in process technology and market share. According to Trendforce data, in Q4 2022, TSMC achieved revenue of $19.962 billion, with a market share of 58.5%, an increase of 2.4 percentage points year-on-year, far ahead of other wafer foundry companies; on the domestic front, mainland semiconductor manufacturing is represented by SMIC and Hua Hong Semiconductor, which have continuously improved their process technology and expanded production scale, achieving rapid growth. In Q4 2022, SMIC and Hua Hong Semiconductor achieved revenues of $1.621 billion and $882 million, ranking fifth and sixth globally, respectively.
Chart 20: Revenue Rankings of the Top Ten Global Wafer Foundries in Q4 2022

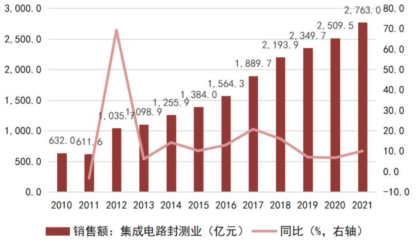
The packaging and testing industry is located downstream of the semiconductor manufacturing process and requires substantial equipment and personnel investment, making it a capital-intensive and labor-intensive industry. Compared to other areas of integrated circuits, the packaging and testing threshold is relatively low, making it the most technologically mature and easily replaceable area in the domestic semiconductor industry chain. Over the past decade, due to semiconductor industry transfer, human resource cost advantages, tax incentives, and other factors, global integrated circuit packaging and testing capacity has gradually shifted to the Asia-Pacific region. China’s IC packaging industry started early, leveraging labor cost advantages and a broad downstream market to take on a large number of transferred packaging orders, thus developing rapidly, with the market scale steadily increasing in recent years. In recent years, the global integrated circuit packaging and testing industry has entered a steady development phase, with a compound annual growth rate of 4.27% from 2014 to 2021, while China’s growth rate has outpaced the global average due to the booming development of downstream terminal applications such as smartphones. According to data from the China Semiconductor Industry Association, the annual sales of China’s integrated circuit packaging industry grew from $125.6 billion in 2014 to $276.3 billion in 2021, with a compound growth rate of about 11.92% from 2014 to 2021, far exceeding the global average level, indicating vast growth potential for the domestic packaging industry as downstream applications continue to develop and advanced packaging processes continue to progress.
Chart 21: Global Integrated Circuit Packaging Industry Market Scale and Year-on-Year Growth Rate from 2014 to 2021
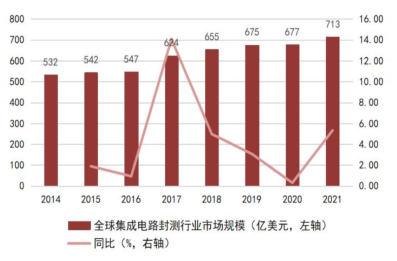
Chart 22: Sales Revenue and Year-on-Year Growth Rate of China’s Integrated Circuit Packaging Industry from 2014 to 2021
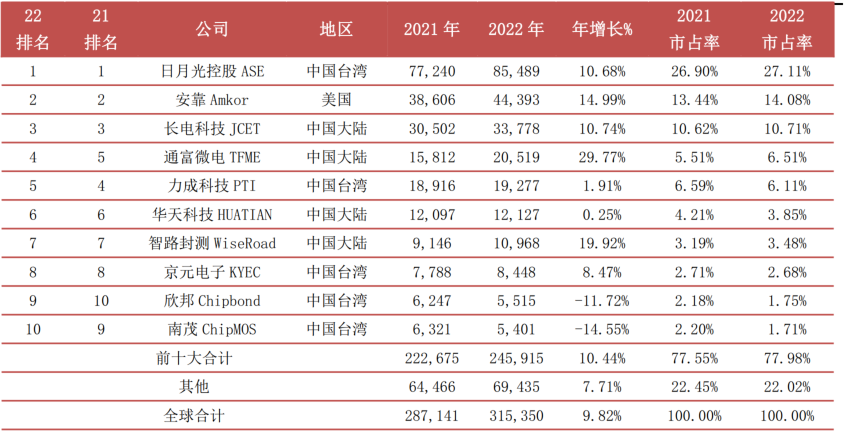
Currently, the overall domestic self-sufficiency rate in the integrated circuit field is relatively low, especially in the semiconductor equipment, materials, and wafer manufacturing segments, with significant gaps compared to international leading levels. However, packaging and testing is the most competitive segment in China’s integrated circuit field. In recent years, several domestic packaging and testing leaders, represented by Changdian Technology, have strengthened their market competitiveness through independent research and development and mergers and acquisitions in the advanced packaging field, making them capable of participating in international market competition. According to data from the Chip Thought Research Institute, in 2022, four companies in mainland China entered the global top ten packaging and testing companies, namely Changdian Technology, Tongfu Microelectronics, Huatian Technology, and Zhilu Packaging, ranking third, fourth, sixth, and seventh globally for annual revenue.
Chart 23: Estimated Rankings of Global Packaging and Testing Leaders in 2022
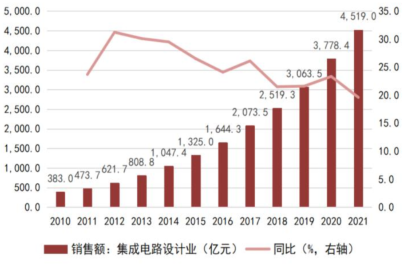
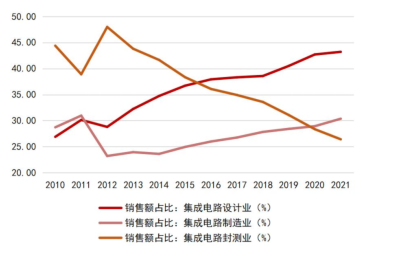
China’s integrated circuit market continues to grow, with an increasingly optimized industrial structure. According to data from the China Semiconductor Industry Association, from 2010 to 2021, China’s integrated circuit sales revenue grew from 142.4 billion yuan to 1,045.83 billion yuan, with a compound annual growth rate of 19.87%. After experiencing global industrial transfers and multiple industry mergers, the integrated circuit packaging industry has become the most globally competitive subfield of China’s semiconductor sector, ranking first in sales revenue among the three segments before 2016. In recent years, domestic IC design companies represented by Huawei HiSilicon have rapidly risen, driving a rapid increase in the sales revenue share of the IC design industry, surpassing the packaging industry to rank first in sales scale in 2016. The rise of local wafer foundries like SMIC and Hua Hong Semiconductor has also driven the market scale of China’s integrated circuit manufacturing industry to grow, surpassing the IC packaging industry to rank second in 2020. The increasing share of higher value-added integrated circuit design and manufacturing industries indicates that China’s IC industry structure is gradually optimizing, transitioning from a model dominated by packaging to a complete integrated circuit industry chain with balanced development across IC design, manufacturing, and packaging.
Semiconductor Market Size
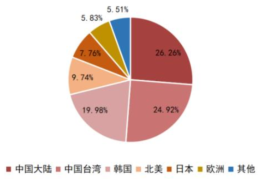
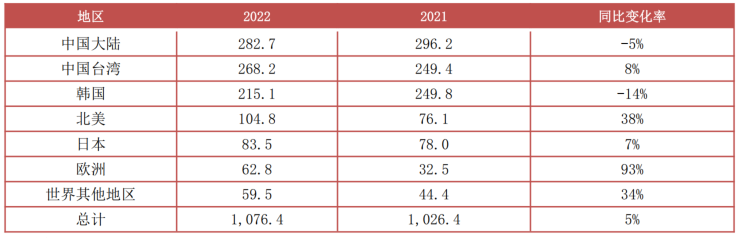
Throughout the development history of the global semiconductor industry, it has undergone several rounds of industrial transfer from the United States to Japan, to South Korea, and to Taiwan and mainland China. Currently, mainland China has become one of the most important semiconductor application and consumption markets globally. According to IC Insights data, in 2022, there were 23 12-inch wafer fabs in production in mainland China, with a combined monthly capacity of approximately 1.042 million wafers. The International Semiconductor Industry Association (SEMI) predicts that by 2026, the monthly capacity of 12-inch wafer fabs in mainland China is expected to reach 2.4 million wafers, increasing its global share to 25%. Generally, the cycle from establishing a new wafer fab to production is about 2 years, so it is expected that the wafer manufacturing capacity in our country will continue to grow in the coming years, driving the development of upstream semiconductor equipment and materials.

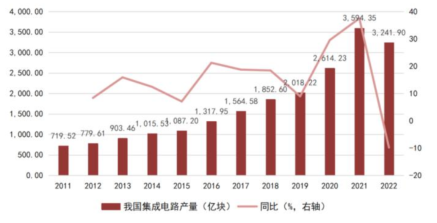
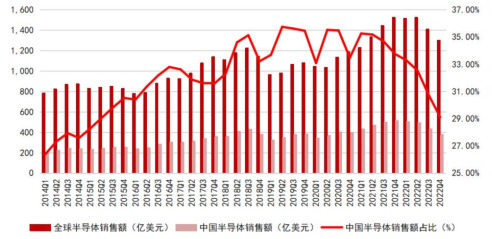
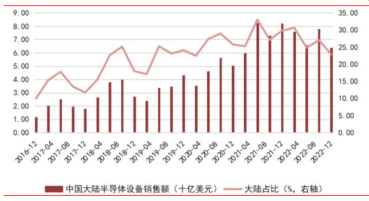
Benefiting from the booming development of consumer electronics, PCs, and continued promotion of domestic substitution, from 2016 to 2022, China’s integrated circuit output grew from 71.952 billion pieces to 324.19 billion pieces, with a compound annual growth rate of 12.08%; in terms of market scale, the sales revenue of China’s semiconductor industry has grown faster than the global average, increasing its global share. In the second quarter of 2014, China’s semiconductor sales revenue accounted for 26.37% of the global share, which increased to 35.52% by the second quarter of 2020. Although the share has decreased since 2022, it still remains around 30%.
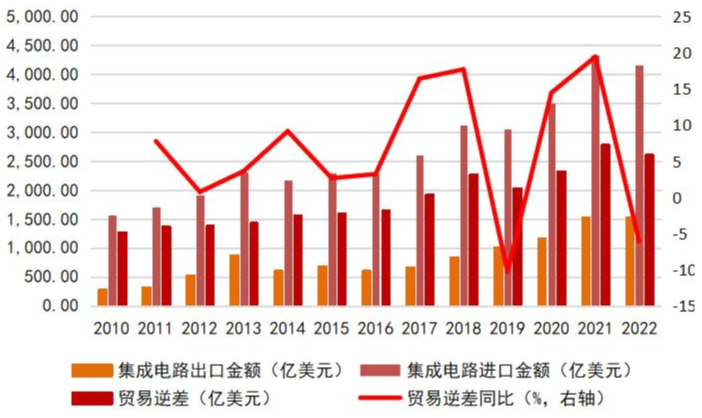
In recent years, the import value of integrated circuits has exceeded that of crude oil, complete automobiles, and automotive parts, becoming the largest category of imports in China. According to data from the General Administration of Customs, the import value of integrated circuits has rapidly increased in recent years, with the trade deficit expanding year by year, from $127.74 billion in 2010 to $261.661 billion in 2022, creating a significant gap between strong downstream market demand and a low self-sufficiency rate. Due to the enormous supply gap and trade deficit in the integrated circuit industry, the development of China’s integrated circuit industry is urgent, presenting opportunities for related enterprises in the industry chain.
From the detailed components of imports and exports published by the General Administration of Customs (processors, controllers, memory, amplifiers, other integrated circuits, and integrated circuit parts), the import value of processors and controllers is $205.1 billion, accounting for 49.2%, with a year-on-year growth of 2.7%; the import value of memory is $101.3 billion, accounting for 24.3%, with a year-on-year decline of 7.1%. The trade deficit for processors and controllers is $152.8 billion, while the trade deficit for memory has decreased to $31 billion. This indicates that China has improved its self-sufficiency level in the field of memory, while still maintaining a high degree of reliance on imports for processors and controllers.
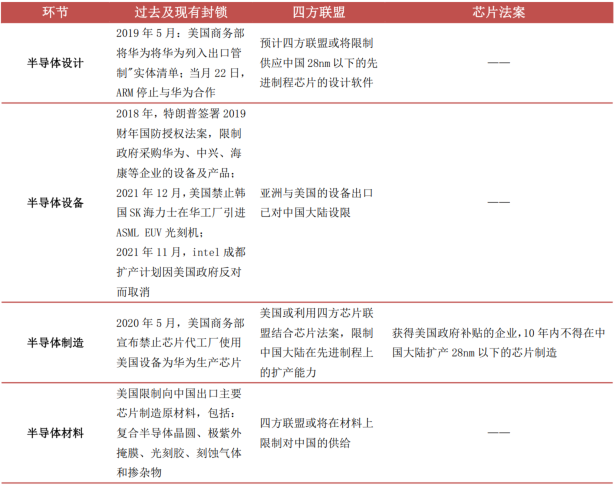
In recent years, US-China tensions have intensified, with the US increasing restrictions on China in high-tech fields, attempting to limit the development of the domestic integrated circuit industry through increased sanctions. In December 2020, the US placed SMIC on the “Entity List,” restricting the company from expanding production of semiconductors with processes below 14nm; in August 2022, the US signed the “CHIPS and Science Act,” primarily aimed at enhancing the competitiveness of domestic wafer foundries, explicitly stating that companies receiving US government subsidies are not allowed to expand production of chips below 28nm in mainland China for 10 years. The signing of the “CHIPS Act” further exacerbates the decoupling between the US and China in high-tech fields, leading to restrictions on the development of advanced processes for domestic chips.
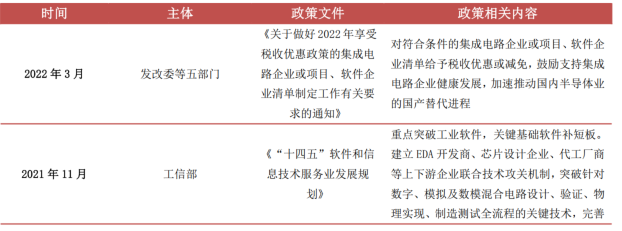
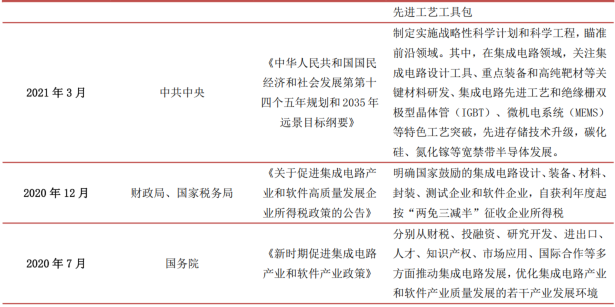
Integrated circuits hold a significant strategic position, and to encourage the development of the integrated circuit industry, promote self-sufficiency, and break free from dependency, the government has successively introduced a series of policies related to investment tax reductions and government subsidies for the integrated circuit industry, mobilizing national resources to ensure supply chain security and promote healthy industry development.
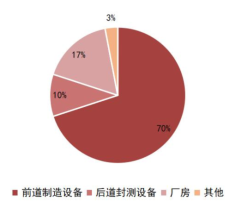
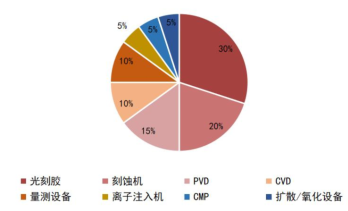
Semiconductor equipment is divided into front-end wafer manufacturing equipment and back-end packaging equipment, where front-end equipment includes photolithography machines, etching machines, CVD equipment, PVD equipment, ion implantation equipment, and CMP polishing equipment, while back-end equipment includes testing machines, probe stations, and sorting machines. According to SEMI, in a semiconductor production line, semiconductor equipment investment accounts for up to 80%, while facilities and other expenditures account for only 20%. In the front-end manufacturing equipment, the top three investment proportions are photolithography machines, etching machines, and PVD equipment, accounting for 30%, 20%, and 15%, respectively, followed by CVD, measurement equipment, ion implantation machines, CMP, and diffusion/oxidation equipment.
Semiconductor equipment requires extremely high quality, parameters, and operational stability, resulting in high technical barriers in the industry. A significant amount of capital must be invested in research and development, as well as in purchasing raw materials and components. Downstream customers are unlikely to easily switch manufacturers after certification, leading to a certain level of customer stickiness. Companies that have gained first-mover advantages are more likely to maintain and solidify their advantages.
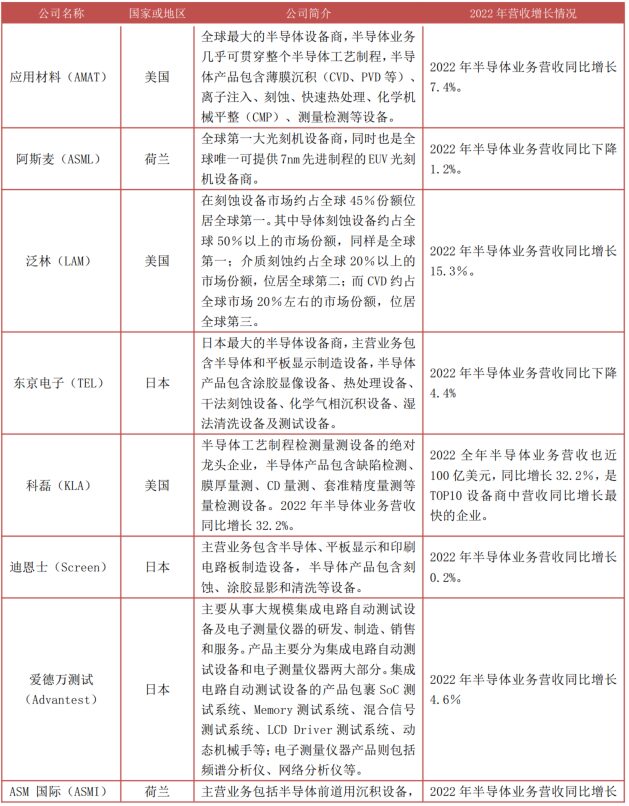
From the perspective of industry competition, the global semiconductor equipment market is highly concentrated, with major participating manufacturers for a single piece of equipment generally not exceeding 5. The US, Japan, and Europe maintain technological leadership, with representative manufacturers including Applied Materials (USA), ASML (Netherlands), Lam Research (USA), and Tokyo Electron (Japan). According to data from CINNO Research, in 2022, the combined revenue of the top ten publicly listed semiconductor equipment companies reached $103 billion, a year-on-year growth of 6.1%, and all are from the US, Japan, and the Netherlands. In terms of revenue, the top four equipment manufacturers’ semiconductor businesses all exceeded $16 billion in revenue for the entire year of 2022.

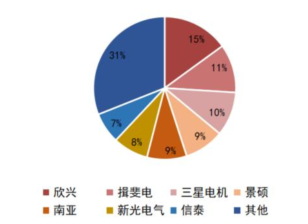
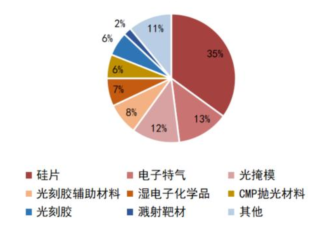
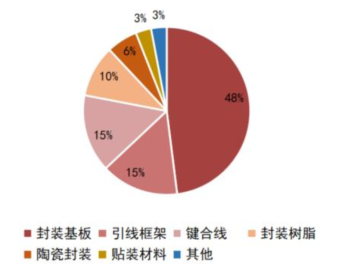
The semiconductor materials industry is located upstream in the semiconductor industry chain, being the segment with the most subfields, encompassing over a hundred sub-industries. Broadly categorized, semiconductor materials mainly include wafer manufacturing materials and semiconductor packaging materials, where wafer manufacturing materials include silicon wafers, photomasks, photoresists, specialty gases, target materials, and CMP polishing materials (polishing liquids and pads), while packaging materials include packaging substrates, lead frames, bonding wires, and packaging resins. According to data from the International Semiconductor Industry Association (SEMI), in 2020, the top five global wafer manufacturing materials by value were: silicon wafers (35%), specialty gases (13%), photomasks (12%), photoresist auxiliary materials (8%), and wet electronic chemicals (6%); the top five packaging materials by market size were: packaging substrates (48%), lead frames (15%), bonding wires (15%), packaging resins (10%), and ceramic packaging (6%).
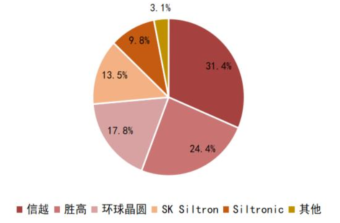
The technology barriers for core semiconductor materials are extremely high, and the vast majority of domestic products have low self-sufficiency rates, with the market monopolized by overseas manufacturers from the US, Japan, Europe, South Korea, and Taiwan. For example, in the semiconductor silicon wafer market, which has the largest share, the top five manufacturers account for over 95%, with the top three—Shin-Etsu Chemical, SUMCO, and GlobalWafers—holding a combined global share of 74% (2020 data, SEMI). Domestic enterprises, represented by Shanghai Silicon Industry, still have a significant gap compared to international leading levels; in the relatively dispersed packaging substrate field, the top seven manufacturers also account for nearly 70%, primarily occupied by Taiwanese, Japanese, and South Korean manufacturers. Domestic semiconductor material companies have only achieved self-production and sales in certain areas, with significant breakthroughs in target materials, specialty gases, and CMP polishing materials, and some products reaching international first-class technical standards, with local production lines achieving large-scale supply.