When we think of OLED screens, our impression often revolves around screen burn-in. Why do OLED screens suffer from burn-in while LCD screens rarely do? What are the actual differences between these two types of screens? Today, let’s take a closer look at what LCD screens are and what OLED screens are.
LCD and OLED are currently the two main screen materials in use today. Almost all the smartphones you see are made with one of these two materials. Terms like TFT, IPS, AMOLED, and PMOLED are enhancement technologies based on these two materials. Just remember this when shopping, and you can avoid being overwhelmed by the complex classifications of screens.
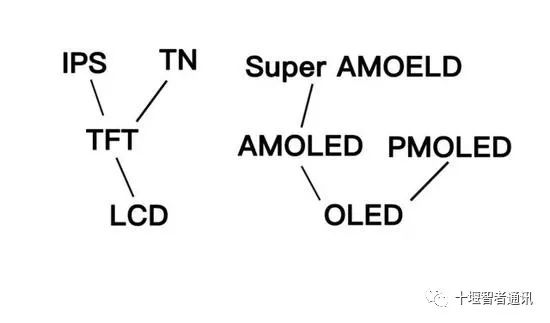
In fact, most smartphone screens now use various technologies to enhance screen performance, but unfamiliar terms can often confuse users. So, let’s return to the basics of LCD and OLED and focus on smartphone screens.
Differences Between LCD and OLED Screens
The construction of LCD screens is not particularly impressive; it consists of a liquid crystal layer sandwiched between two “glass” plates, with a thin-film transistor on the lower substrate and a color filter layer on the upper substrate. Under the influence of voltage, the liquid crystal layer produces different optical characteristics, which are then projected through the color filter layer to create various colors.
On the other hand, OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) has the characteristic of self-illumination, consisting of a very thin layer of organic materials. When current passes through, these diodes can emit light individually.
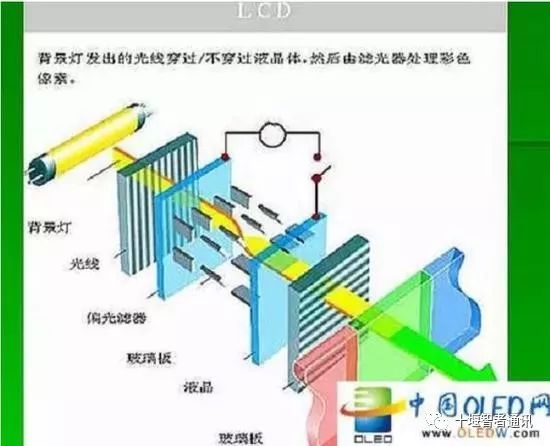 Image from China OLED Network
Image from China OLED Network
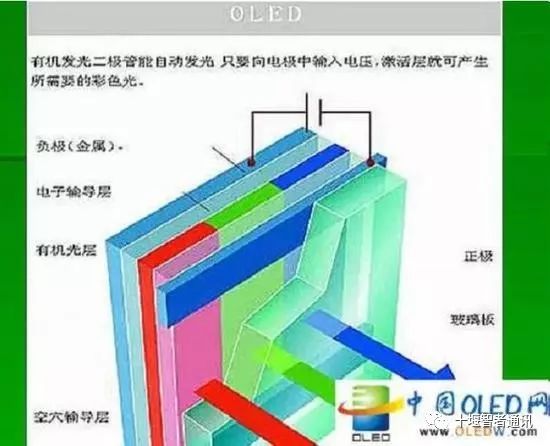 Image from China OLED Network
Image from China OLED Network
To simply understand, LCD is like watching a shadow play, where the “light source” or actors are behind the scenes, separated by a membrane, while OLED is like a live performance, where you can see the actors directly.
The light source of LCD is fixed and cannot emit light independently. If black is to be displayed, the liquid crystal cannot completely block the light source, resulting in a visual appearance of gray.
So, is OLED better than LCD?
Yes, but it’s not an all-around domination. While OLED screens offer outstanding colors, they have notable drawbacks in flickering and pixel performance. Due to the varying lifespans of different color pixels, early OLED screens had a certain risk of burn-in.
However, manufacturers have now implemented algorithms to periodically shift the areas of constant display (like taskbar icons) or increase the area of short-lifespan LEDs to average the lifespan of screen pixels.
Currently, most smartphones using OLED screens do not experience burn-in issues. Of course, aside from burn-in, OLED also faces flickering issues related to its light-emitting principles. Please refer to another article, “DC Dimming Suddenly Becomes Popular, But OLED Screens First Need to Solve This Problem.”
