I'm Lao Wen, an embedded engineer who loves learning.
Follow me to become even better together!
Memory is divided into two main categories: RAM and ROM, and this article primarily discusses ROM. Initially, ROM could not be programmed; it retained whatever content it was manufactured with, making it inflexible.
Later, PROM was introduced, which could be written once. If you made a mistake, you had to replace it and accept your misfortune.
As human civilization progressed, the erasable programmable ROM (EPROM) was developed, which could be erased multiple times. Each time you needed to erase it, you had to place the chip under ultraviolet light for a while. Imagine you uploaded a program to a microcontroller and later realized you needed to add a line.
For this, you had to put the microcontroller under the UV lamp for half an hour before you could upload it again. This process could take a whole day just to make a few changes.
As history progressed, the great EEPROM emerged, saving a large number of programmers who could finally modify the content of ROM at will.
The full name of EEPROM is “Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory.” It is a type of ROM that can be erased electrically, as opposed to UV-erasable ROM.
However, today there are many variants of EEPROM, which have become a generic term for a class of memories.
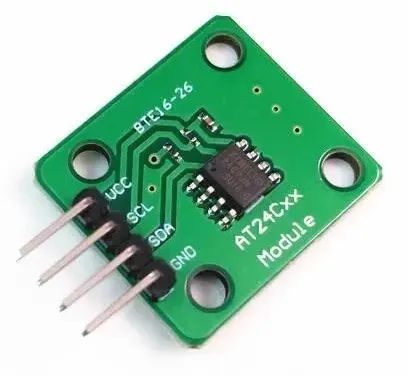
This type of ROM can randomly access and modify any byte. You can write 0 or 1 to each bit. This is the most traditional type of EEPROM, which retains data for up to 100 years after power loss and can be erased and written to 1 million times.
It has high reliability, but the circuit is complex and costs are high.Therefore, current EEPROMs range from tens of kilobytes to hundreds of kilobytes, with very few exceeding 512K.
For example, the commonly seen 24C02:
FLASH belongs to the broad sense of EEPROM because it is also electrically erasable ROM. However, to distinguish it from the general byte-wise erasable EEPROM, we call it FLASH.
FLASH improves by erasing in blocks instead of bytes, simplifying the circuit, increasing data density, and reducing costs. ROMs with MB capacities are generally FLASH.
For example, W25Q128JVSIQ:
FLASH is divided into NOR-FLASH and NAND-FLASH.
NOR-FLASH has separate data and address lines, allowing for random addressing like RAM, enabling reading of any byte.However, erasure still has to be done in blocks.Still using W25Q128JVSIQ.
NAND-FLASH is also erased in blocks, but it reuses data and address lines, which means it cannot utilize address lines for random addressing.Reading can only be done page by page.(NAND-FLASH is erased in blocks and read in pages, while NOR-FLASH does not have pages.)

Due to the multiplexing of pins in NAND-FLASH, the reading speed is slightly slower than NOR-FLASH, but the erasure and writing speeds are much faster than NOR-FLASH.
NAND-FLASH has a simpler internal circuit, allowing for higher data density, smaller size, and lower cost.Thus, large-capacity FLASH is mostly of the NAND type.Small-capacity FLASH, from 2 to 12M, is mostly of the NOR type.
In terms of lifespan, NOR-FLASH can be erased many more times than NAND.Moreover, NAND-FLASH can mark bad blocks, allowing software to skip them.Once NOR-FLASH is damaged, it cannot be used again.
Because NOR-FLASH allows for byte addressing, programs can run within NOR-FLASH.Embedded systems often use a small capacity NOR-FLASH to store boot code and a large capacity NAND-FLASH to store the file system and kernel.
-END-
Previous Recommendations: Click the image to read.
Have you noticed that more and more people are getting into embedded systems?
Embedded C language, memory mapping of various data types.
The intelligent robot by Zhihui Jun has popularized this embedded operating system and core board…
I’m Lao Wen, an embedded engineer who loves learning.
Follow me, to become even better together!