Last week, I introduced the history of television technology. The development of TV display technology has spanned nearly a century, evolving from CRT technology to the current mainstream TFT-LCD technology. However, just as TFT-LCD technology began to take hold, OLED technology started to emerge, along with various new display technologies such as QD-LCD, QLED, Mini-LED, and Micro-LED. What exactly are these technologies that display giants are competing to develop? In this article, I will provide a brief introduction.

Mini-LED
:
First, let’s talk about Mini-LED technology. Mini-LED refers to millimeter-scale light-emitting diodes (Mini LED) in flat panel displays. The Mini LED technology transforms the backlight source of the display screen from dozens of LED chips on the side to thousands or even tens of thousands of chips in direct backlighting. It is estimated that a 55-inch TV’s backlight unit (BLU) requires about 40000 mini LEDs, while a smartphone panel requires about 9000 mini LEDs.
Mini-LED technology is merely an enhancement of the backlight for existing LCD display technology, significantly improving the color performance and contrast of the display panel, but it also greatly increases the cost of the display panel. Currently, there are no mass-produced products on the market using mini-LED technology; according to online news, mass production products may be launched in 2018.

Micro-LED
:

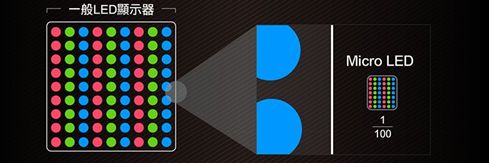
After discussing Mini-LED , let’s talk about Micro-LED. In simple terms, Micro-LED is a miniature version of outdoor LED advertising boards, integrating individual LED lights onto semiconductor chips through semiconductor technology, forming a high-density array of tiny LED lights, where each MicroLED is a pixel that can be individually driven to light up, with pixel distances at the micrometer level.
Since Micro LED is a self-emitting technology, its advantages include low power consumption, high brightness, ultra-high resolution and color saturation, fast response time, energy efficiency, long lifespan, and high efficiency. Its power consumption is about 10% of LCD and 50% of OLED. Moreover, structurally, Micro-LED is much simpler than TFT-LCD and OLED.
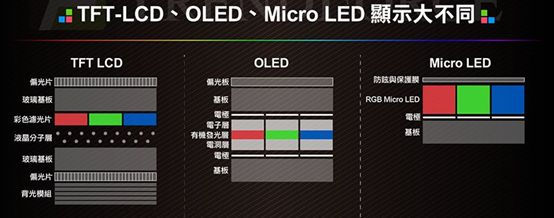
In terms of production technology, Micro LED Display integrates the characteristics of both TFT-LCD and LED technologies. The development of materials, processes, and equipment is relatively mature, but several key production steps still need breakthroughs.
Due to the high specifications of Micro-LED technology products compared to current TFT-LCD or OLED, giants like Apple are actively researching and developing this technology and its products.

QD-LCD
:
After discussing LED emission, let’s talk about quantum dot emission. Quantum dots are inorganic semiconductor nanocrystals, usually composed of zinc, cadmium, selenium, and sulfur atoms. Their structure consists of three layers: core, shell, and ligand. When stimulated by light or electricity, quantum dots emit light, and the color of the light is determined by the composition and size of the quantum dots. Ideally, by controlling the continuous variation in the diameter of the quantum dot materials, a continuous spectral effect close to natural light can be achieved.
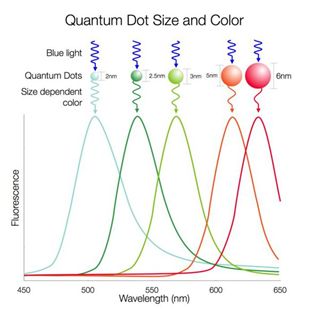
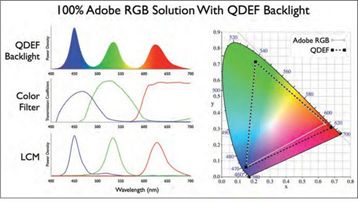
QD-LCD refers to applying quantum dot films to traditional LCD screens, using quantum dot technology to replace the yellow phosphor in blue LED optical packaging materials to enhance color gamut and brightness. The light emitted by blue LED backlights is transformed into red and green light through quantum dot films, achieving full-color display. QD-LCD technology is an improvement of LCD display technology, which still fundamentally relies on backlight sources.
3M and Nanosys have jointly developed quantum dot films that have been applied in the LCD display field, enabling full-color display.
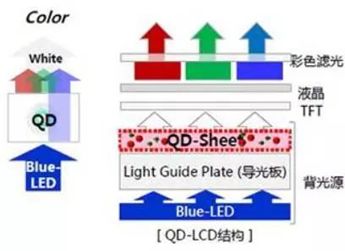
The greatest advantage of quantum dot films is their high reliability, as they can be compatible with traditional LCD backlight structures. By simply replacing the white light source in LCDs with blue LEDs, the display panel can be transformed. The greatest advantage of QD-LCD technology is that it can fully utilize the production lines of TFT-LCD to reduce production costs.

QLED
:
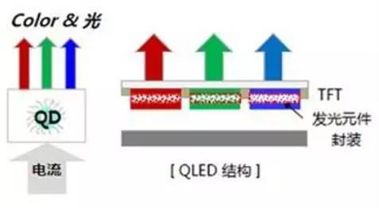
Based on the electroluminescent properties of quantum dots, QLED technology uses the self-emission of quantum dots under electrical drive as the display basis, utilizing the quantum dot materials themselves as the light-emitting materials of the diodes to achieve image display. Its structure is very similar to OLED technology, with the main difference being that the light-emitting center of QLED is composed of quantum dot materials. QLED technology has advantages such as strong contrast, energy efficiency, wide viewing angles, and high color saturation, making products thinner and lighter, and it is a display technology with great development prospects. However, limited by the research and development of related materials and processes, QLED is still in the laboratory research stage.
It is said that today’s display technology has entered an era of fierce competition; which technology will emerge as the dominant one remains to be seen.