Liquid crystal display technology continues to advance, from the most commonly heard LCD, LED, and OLED, to the currently hottest display technologies in the industry: Micro LED, Mini LED, and Micro OLED. Have you ever wanted to understand them but found it confusing? Here, we will briefly introduce the characteristics of these next-generation display technologies from a popular science perspective, as well as their differences from older technologies.
1 What are the differences between LCD, LED, and OLED?
LCD stands for “Liquid Crystal Display”. Currently, most of the market uses “Thin Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display” (TFT-LCD) technology, which consists of two glass substrates sandwiching a layer of liquid crystal. The upper glass substrate is a color filter, while the lower glass is embedded with transistors. When current passes through the transistors, the electric field changes, causing the liquid crystal molecules’ original rotational arrangement to twist, thereby altering the degree of light rotation passing through and projecting different colors onto the color filter.
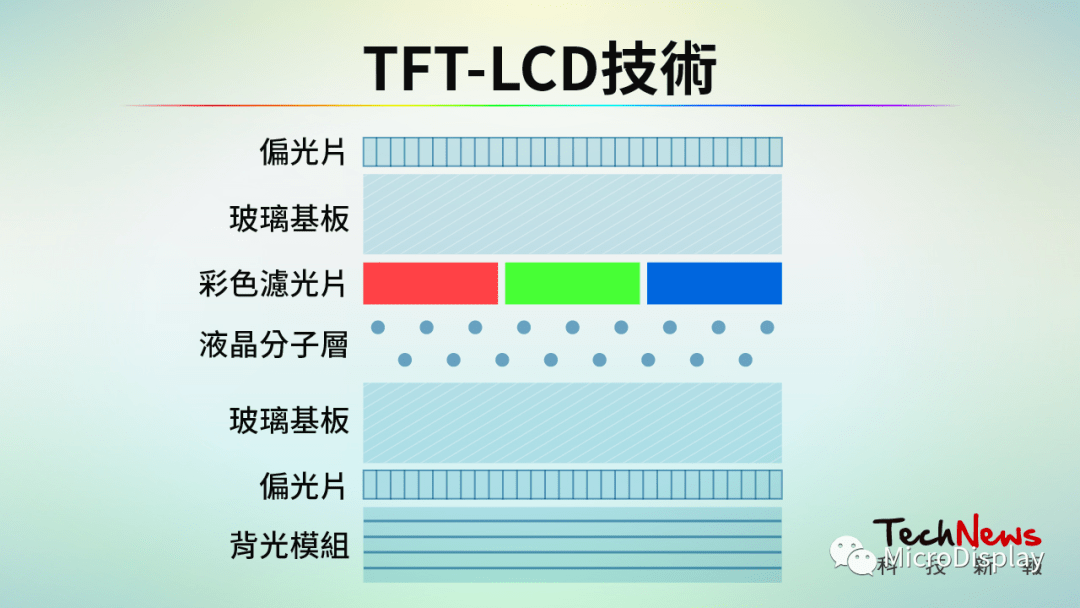 The most commonly used LCD panel technology is TFT-LCD (Source: Technology News Report)
The most commonly used LCD panel technology is TFT-LCD (Source: Technology News Report)
Currently, LCD technology is quite mature, used in general computer and television screens, and is cost-effective, becoming a foundational technology for consumer products.
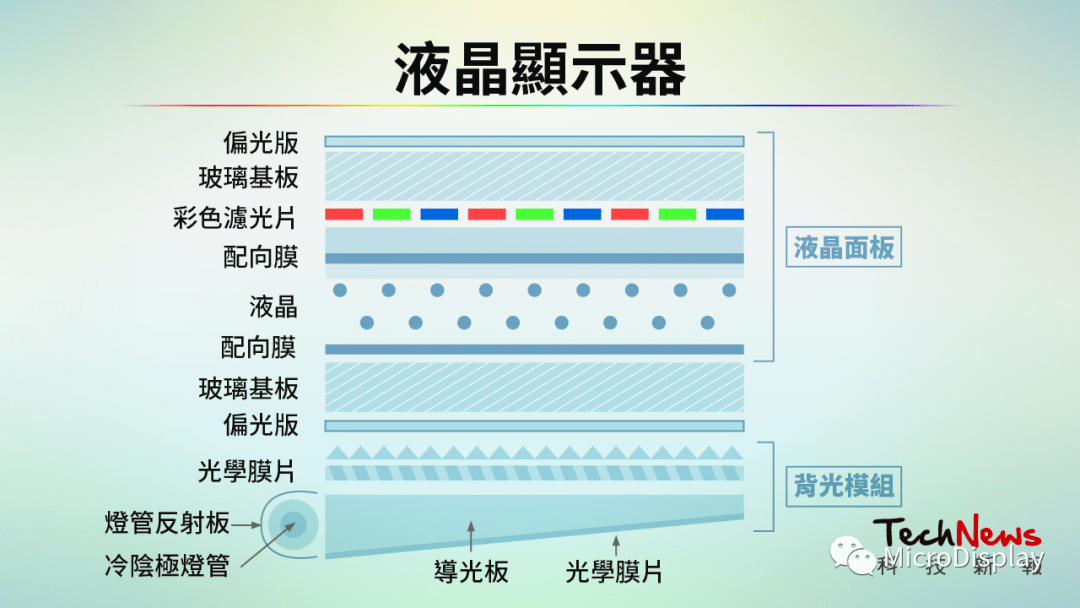 The imaging principle of a typical LCD (Source: Technology News Report)
The imaging principle of a typical LCD (Source: Technology News Report)
After understanding LCD, let’s introduce LED and OLED.
LED stands for “Light Emitting Diode”. It converts electrical energy into light energy. When a voltage is applied across the two terminals of a semiconductor, the current causes electrons and holes to combine, releasing the remaining energy in the form of visible light. Depending on the materials used, the photon energy will produce light of different wavelengths. Direct-view LEDs are commonly used in outdoor television walls or traffic lights, while LED chips are currently the mainstream products for television, screen backlighting, and lighting.
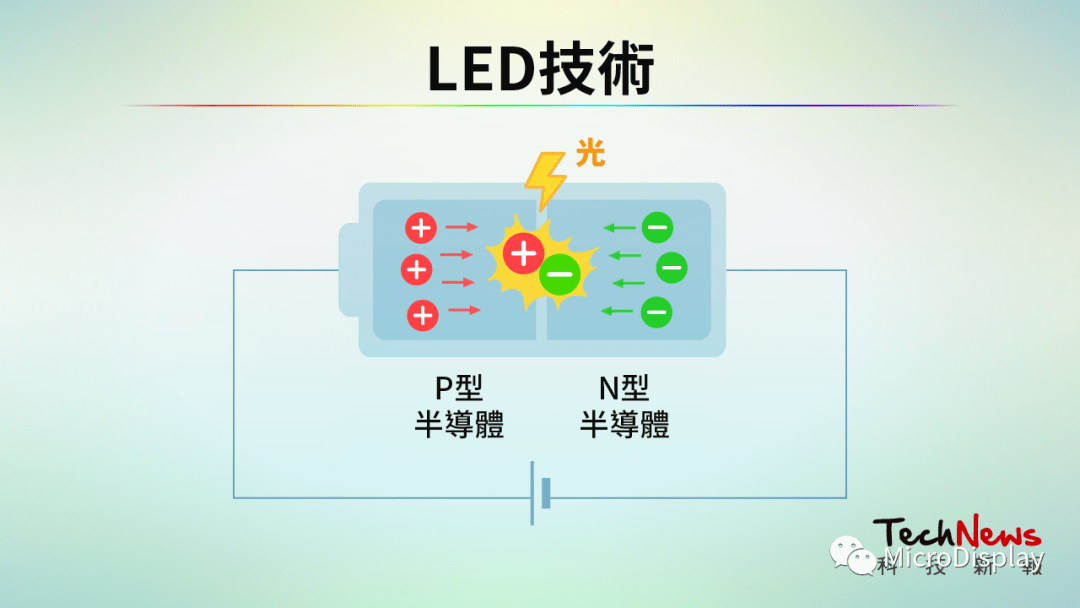 LED technology converts electrical energy into light energy. (Source: Technology News Report)
LED technology converts electrical energy into light energy. (Source: Technology News Report)
LED and OLED have similar driving concepts, but the materials used are completely different. OLED stands for “Organic Light Emitting Diode”. Its basic structure consists of a layer of organic material light-emitting layer made on indium tin oxide (ITO) glass, covered by a layer of low work function metal electrode. Driven by external voltage, the positive hole and negative electron combine in the light-emitting layer, generating energy and emitting light. Due to the different material properties, the primary colors R, G, and B are produced to form basic colors.
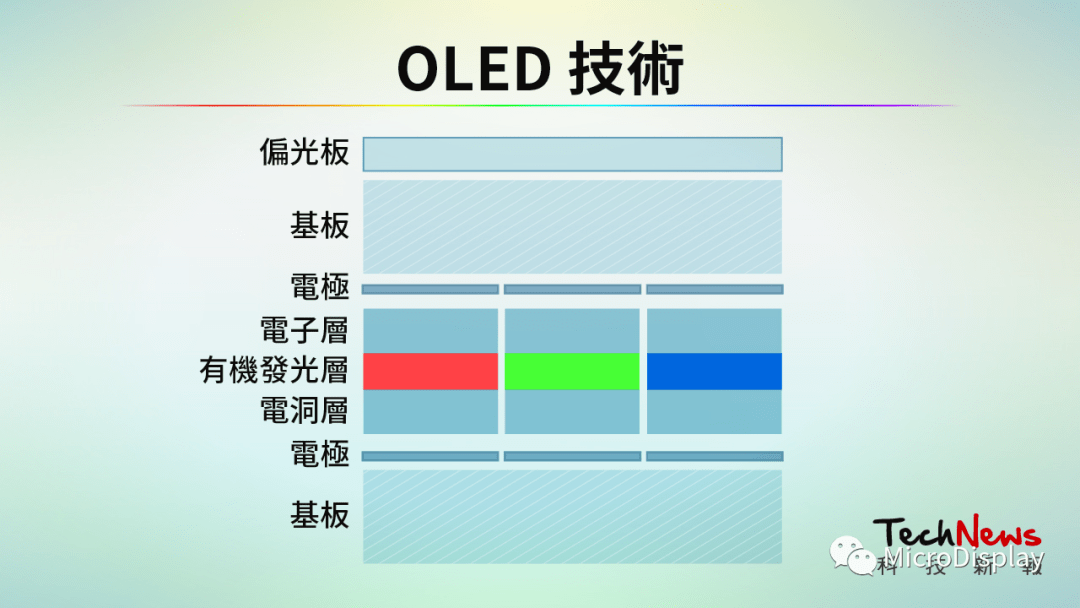 OLED technology (Source: Technology News Report)
OLED technology (Source: Technology News Report)
The biggest difference between OLED and LCD is whether it can emit light by itself. LCD requires an LED backlight and filter, while OLED can emit light by itself.
Although OLED displays vibrant images, consume less power, and can be bent, the organic materials oxidize, resulting in a relatively short lifespan and color burn-in issues. Additionally, due to high costs and technical complexity, they are mostly suitable for small screens, such as smartphone displays.
2 Mini LED and Micro LED: What’s the difference?
After understanding the basic differences between LCD, LED, and OLED, let’s look at the advanced display technologies Mini LED, Micro LED, and Micro OLED.
The most intuitive difference between Mini LED and Micro LED is the size of the LED crystals, but conceptually, there are some differences. Mini LED is formally known as “Sub-Millimeter Light Emitting Diode”, while Micro LED refers to “Micro Light Emitting Diode”. The crystal size of the two is generally divided by 100 μm, approximately 0.1 mm.
 Micro LED technology structure (Source: Technology News Report)
Micro LED technology structure (Source: Technology News Report)
Mini LED is seen as a transitional phase to Micro LED, an improved version based on traditional LED backlighting, used as a backlight source for LCD panels. Micro LED, on the other hand, is a new generation of display technology that miniaturizes and matrices the LED backlight, aiming to drive inorganic self-emitting (self-emitting) individually, extending product lifespan and even outperforming OLED, regarded by the industry as the next generation of display technology.
Currently, Mini LED technology is mainly used in “Multi-Zone Backlight Displays” and “Large RGB Small Pitch Displays”. The “Multi-Zone Backlight Control” feature in Mini LED technology achieves zone dimming, enhancing the high contrast and high resolution of the image, achieving HDR effects similar to OLED displays. Another technology uses Mini LED chips to create large screens with pixel pitch less than 1.0 mm, improving the resolution of LED displays and creating new mainstream specifications for display screens.
As for Micro LED, it will bring technological breakthroughs. Its applications are not limited to backlighting, as the Micro LED crystals are at a level indistinguishable to the naked eye, allowing the R, G, and B primary color crystals to be combined into a single pixel, transforming the concept of “one pixel” without the need for filters and liquid crystal layers. This technological characteristic is completely different from the light-emitting structure of past LCD displays, which will bring a new revolution to the LCD industry.
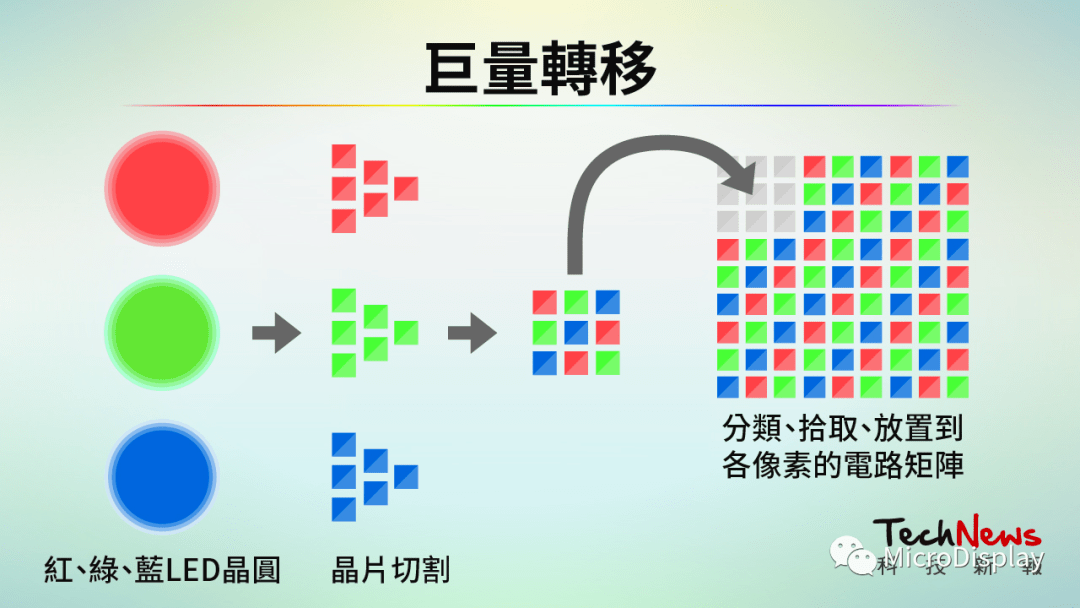 Mass transfer aims to place the crystals accurately onto the circuit matrix, which is very difficult in practice. (Source: Technology News Report)
Mass transfer aims to place the crystals accurately onto the circuit matrix, which is very difficult in practice. (Source: Technology News Report)
In addition to potentially creating a new landscape for the LCD industry, the future applications of Micro LED are vast, including AR/VR devices, automotive screens, and high-resolution wearable products. However, Micro LED technology faces many challenges that need to be addressed, from the initial bottlenecks in epitaxy technology, mass transfer yield, packaging and testing issues, to subsequent detection and maintenance, all of which are significant challenges affecting the mass production of Micro LED.
3 The Next Generation of OLED Technology: Micro OLED Innovations
Micro OLED, also known as silicon-based OLED (OLED on silicon), combines semiconductor technology with OLED technology to achieve a lighter, thinner, and lower energy-consuming technology, with promising applications in AR/VR. But how does it differ from the previously mentioned Micro LED?
Before that, it is essential to clarify what OLED is and whether Micro OLED is merely a miniaturized version of OLED.
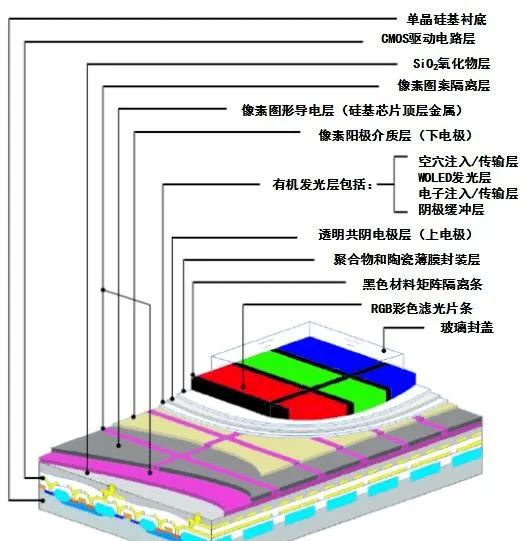 Micro OLED technology
Micro OLED technology
OLED technology has been developed for a long time, with most materials being organic. It does not require a backlight module, as each pixel can emit light independently in a specific color and can be turned on and off individually. Therefore, it not only has excellent and deep blacks and good contrast but also consumes less power than traditional LED and LCD displays.
 Numerous OLED pixels (Source: Shutterstock)
Numerous OLED pixels (Source: Shutterstock)
Currently, OLED technology has also been applied in smartphones and television displays. Micro OLED, although it only adds “Micro” to the name and originates from OLED, is a more complex display technology with a distinctly different market positioning, specifically targeting the AR/VR display field.
Micro OLED primarily uses light-emitting fluorescent organic materials between two layers of electrodes. When current passes through, it emits monochromatic light, which is then filtered to generate the desired color. The Micro OLED light source module is created by depositing OLED onto a substrate, while the main silicon-based OLED is deposited onto a silicon substrate (semiconductor wafer). In addition to having the self-emitting advantages of OLED, the panel thickness and volume are thinner, smaller, and consume less energy than before. Coupled with short response times and high luminous efficiency, it is easier to achieve high PPI (pixels per inch).
This precisely meets the needs of AR/VR head-mounted displays, display mirrors, etc. Although AR/VR technology has been around for many years, the technology itself is not yet perfected, and the actual experience often faces issues such as dizziness, low resolution, and large, expensive devices. To solve the dizziness problem, the panel resolution needs to be increased from the current 500 PPI to 2000 PPI.
This is where the market for Micro OLED lies. Although it may not be as bright and has varying degrees of aging issues like OLED, it has significant advantages in small sizes. As the application of AR/VR displays expands from gaming and military to medical, education, and retail, the market grows, and the demand for display quality, latency, and other requirements increases. The new generation of display technology with high resolution, brightness, contrast, and response speed can seize development opportunities. Currently, Micro OLED has already been applied in military, industrial, medical, and commercial smart glasses.
4 Micro OLED or Micro LED? Don’t get confused!
When mentioning Micro OLED, another advanced display technology with a similar name, “Micro LED”, is often referenced. However, although both aim for ultra-high precision, high resolution, high reliability, and fast response times, their processes and applications are entirely different, with only partial overlap in the markets of Micro LED and Micro OLED.
Micro LED is defined as having a size of less than 75 μm, without a sapphire substrate. In terms of process, Micro LED also uses different epitaxy technologies, integrating a high-density array of tiny LEDs on the chip. Its application fields are vast, ranging from wearable devices, head-mounted displays, AR/VR, to phototherapy technologies. Because Micro LED uses inorganic materials, it has higher brightness and is more stable than OLED, which uses organic materials.
Currently, the biggest challenge for Micro LED is how to accurately transfer millions of tiny LEDs onto the backplane (mass transfer) and the subsequent detection and packaging technologies, which involve significant investment costs.
In contrast, Micro OLED is not necessarily limited to 75 μm in size. The OLED process defines the size of each pixel. Micro OLED primarily uses deposition technology, focusing on how to accurately and uniformly deposit organic materials, which are easily affected by oxygen and water, onto the substrate. Vacuum deposition machines and precise Fine Metal Masks (FMM) will be key points in the process.
Currently, several manufacturers are developing Micro OLED, mainly because silicon-based Micro OLED technology combines integrated circuit design processes (CMOS process) with OLED technology, using single-crystal silicon as the active driving backplane. For example, Nikkei Asia reported in March that Apple has approached its long-term chip supply partner TSMC to jointly develop the ultra-advanced display technology Micro OLED.
In addition, China and South Korea have not overlooked this area. Since 2018, BOE Technology Group has been developing Micro OLED in partnership with Kunming BOE Display Technology in Yunnan. ELEC research indicates that BOE plans to launch commercial Micro OLED displays in the second half of 2021, targeting the AR/VR field, with deposition equipment developed in collaboration with South Korea’s Sunic Systems.
South Korean display and semiconductor equipment manufacturer APS Holdings also revealed in May that the South Korean government has approached them to lead a Micro OLED display project, and APS will collaborate with other developers to create 4000 PPI AR glasses by 2024.
In 2020, French Micro OLED also announced it received €8 million in growth investment from two pan-European high-tech investors, Cipio Partners and Ventech, to promote the development of integrated AR modules.
The market direction for Micro OLED is clear, with significant advantages in small sizes. Its application range is not as broad as OLED or Micro LED, making it one of the research hotspots in recent years. Many manufacturers have invested in enhancing manufacturing capabilities to meet the demands of different fields, which will be a significant driver for AR/VR and other human-machine devices in the next decade. In fact, several Micro OLED products were showcased at the 2020 display exhibition, with PPI exceeding 3000.
It is expected that by 2024, the global microdisplay market will reach 50 million units, including AR/VR, smart glasses, head-mounted displays, and heads-up displays.
Source: MicroDisplay, Technology News Report
If there is any infringement, please contact us for removal.
–
END
–
 About SDIAThe Shenzhen Flat Panel Display Industry Association was established in January 2005by more than 30 leading enterprises in the industry.In 2009, the Touch Screen Branch was established,making it one of the earliest optoelectronic display industry associations in China,with members covering both domestic and international.It is currently one of the largest, most influential, and most active optoelectronic display industry organizations in China.
About SDIAThe Shenzhen Flat Panel Display Industry Association was established in January 2005by more than 30 leading enterprises in the industry.In 2009, the Touch Screen Branch was established,making it one of the earliest optoelectronic display industry associations in China,with members covering both domestic and international.It is currently one of the largest, most influential, and most active optoelectronic display industry organizations in China. Secretariat Hotline: Minister Liu 13027903795Yearbook/Brochure Advertising: Minister He 18617177787Submission/Complaint Email: [email protected]
Secretariat Hotline: Minister Liu 13027903795Yearbook/Brochure Advertising: Minister He 18617177787Submission/Complaint Email: [email protected]