
Introduction
This article is the second installment of the “Detailed Explanation of iWAN” series.
In the previous article, Xiaopai introduced SD-WAN and explained the key application scenarios of the self-developed tunnel protocol iWAN by Panabit.
▶ Previous Article Recap: Still using traditional VPN? This article helps you understand SD-WAN
Today, we will talk about the new feature recently released for iWAN—Layer 2 Networking.

Compared to Layer 3 networking, iWAN’s Layer 2 networking has unique advantages in many scenarios. However, when it comes to Layer 2 networking, many may find it somewhat abstract. Don’t worry, today Xiaopai will break it down in detail to see what capabilities it has.
What Makes iWAN Layer 2 Networking Different
As mentioned earlier, the primary issue with wide area networks is how to connect network nodes that are dispersed across different geographical locations.
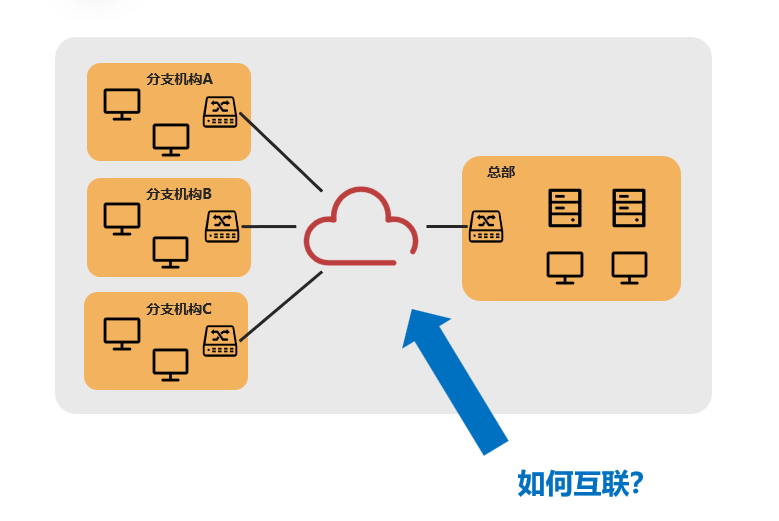
In simple terms, iWAN Layer 2 networking establishes a “virtual dedicated line” using iWAN tunnels between remote locations, allowing both sides to communicate as if they were on a local area network.
▎Layer 2 Networking VS Layer 3 Networking
At this point, many might ask: Didn’t the original iWAN, IPsec, and other Layer 3 networking methods also solve the problem of remote interconnection? Why do we need Layer 2?
The Layer 2 and Layer 3 we refer to here correspond to the data link layer and network layer of the OSI seven-layer model.
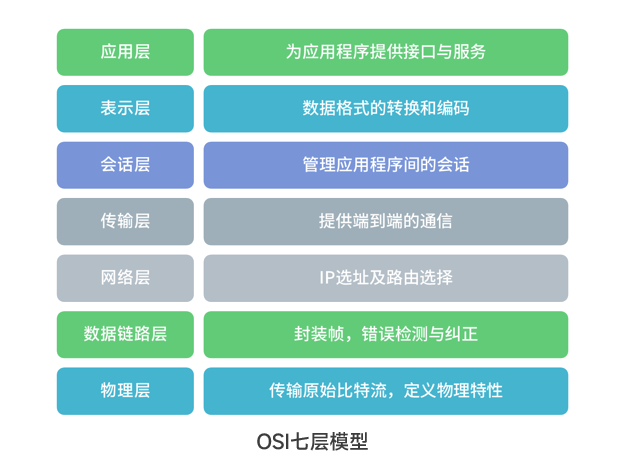
The working principle of Layer 3 networking is based on IP addresses for routing and forwarding, emphasizing “address lookup”; while Layer 2 networking is based on MAC addresses for addressing, emphasizing “direct connectivity”.
Although it seems like there isn’t much difference, Layer 3 networking can indeed meet the vast majority of remote connection needs, but in practical applications, Layer 3’s “identity” still has some limitations:
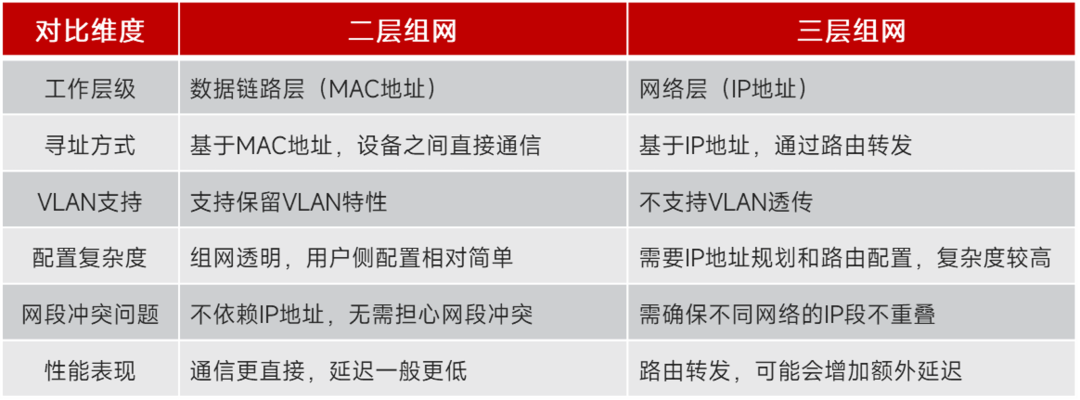
For example, Layer 3 networking requires planning for routing and IP addresses, which is more complex; whereas Layer 2 networking is more “foolproof”, directly pulling remote devices into a local area network, making configuration easier.
Additionally, if both ends of the network require the same IP segment (for example, overlapping network segments at two branch points), Layer 3 networking will lead to IP conflicts, whereas Layer 2 networking does not have this issue.
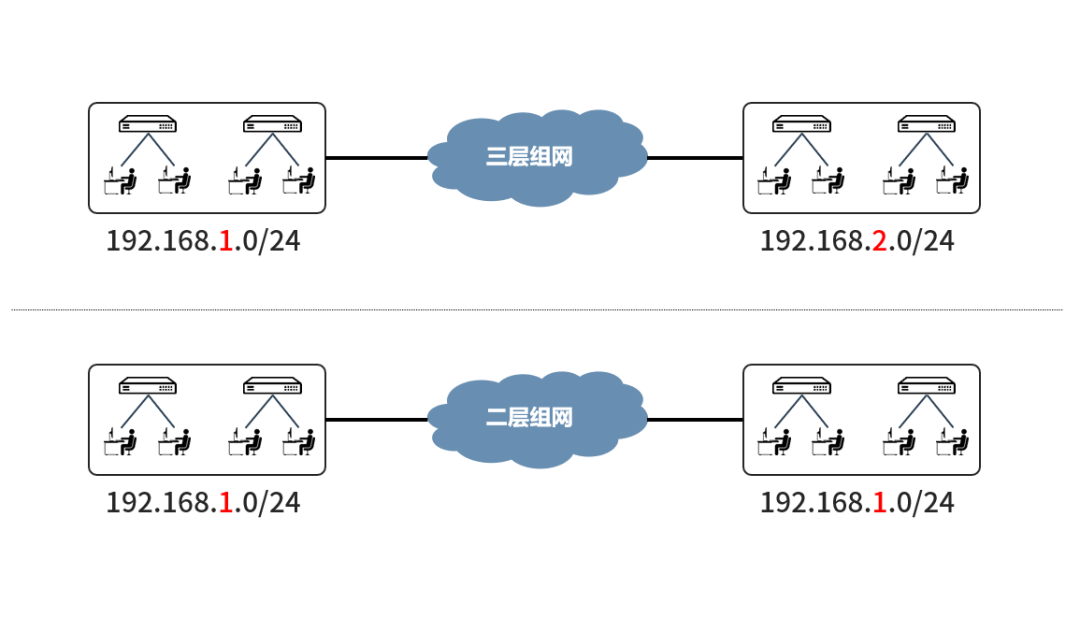
Below is a detailed comparison between Layer 2 and Layer 3 networking:
▎iWAN Layer 2 Networking
Of course, we are not saying that one is superior to the other; Layer 2 networking cannot replace Layer 3 networking, but can serve as a complement to Layer 3 networking, providing options for scenarios that require more flexibility and transparency.
The principle of iWAN Layer 2 networking is actually quite simple: it establishes a Layer 2 network tunnel (iWAN) based on the Layer 3 network, achieving cross-layer, cross-region Layer 2 network interconnection.
In Layer 2 networking, we can think of the iWAN server as a virtual L2 switch, forwarding based on MAC address addressing, enabling Layer 2 network switching for remote terminals.
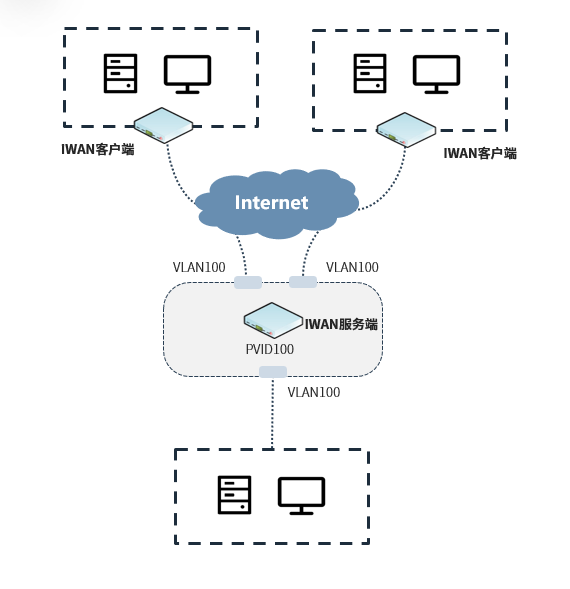
In summary, three keywords can encapsulate its core characteristics:
Lower Cost:
No need to pull additional physical lines, saving dedicated line costs, and it is easy to expand.
VLAN Support:
Can maintain the VLAN characteristics of Layer 2 networks, achieving security isolation.
Transparent Direct Connection:
Networking is more direct, without worrying about IP address and other high-level protocol issues.
In a nutshell, it can be summarized as: achieving more powerful remote Layer 2 interconnection capabilities in a simpler way!
How to Use iWAN Layer 2 Networking?
Having discussed the theory, let’s look at a few typical scenarios to see where it can be applied.
▎Direct Interconnection Between Headquarters and Branches
First and foremost is the interconnection between headquarters and branches. A lot has already been discussed regarding this, so I won’t elaborate further. In summary, through iWAN Layer 2 networking, business access between headquarters and various branches is as convenient as if they were on the same local area network.
▎Layer 2 Dedicated Line Backup
One major advantage of iWAN Layer 2 networking is that it can provide a more cost-effective dedicated line backup solution.
As the saying goes, the business line is the lifeline. Many users invest heavily in dedicated lines for critical business, but if the dedicated line encounters issues, the repair process is slow, and business recovery cannot keep pace. Therefore, at least one backup line is needed to ensure uninterrupted business.
The so-called backup line is like a spare tire; it is usually not used but can come in handy only when the main line is down. Since dedicated lines are already expensive, I believe not many people would want to spend the same amount again to buy a line that is not used regularly (please ignore if money is not an issue).

Let me briefly explain from the perspective of the protocol stack: dedicated lines can be roughly divided into Layer 2 dedicated lines and Layer 3 dedicated lines. Layer 3 dedicated lines generally refer to MPLS VPN, which is more high-end. Most of what we refer to as dedicated lines still refers to Layer 2 dedicated lines.
Layer 2 dedicated lines are equivalent to the operator providing a “virtual cable” between remote locations, directly pulling the devices from both locations into the same local area network.
Does this description sound similar to the description of iWAN Layer 2 networking? That’s right, it is precisely based on this characteristic that iWAN can become an ideal choice for Layer 2 dedicated line backup.
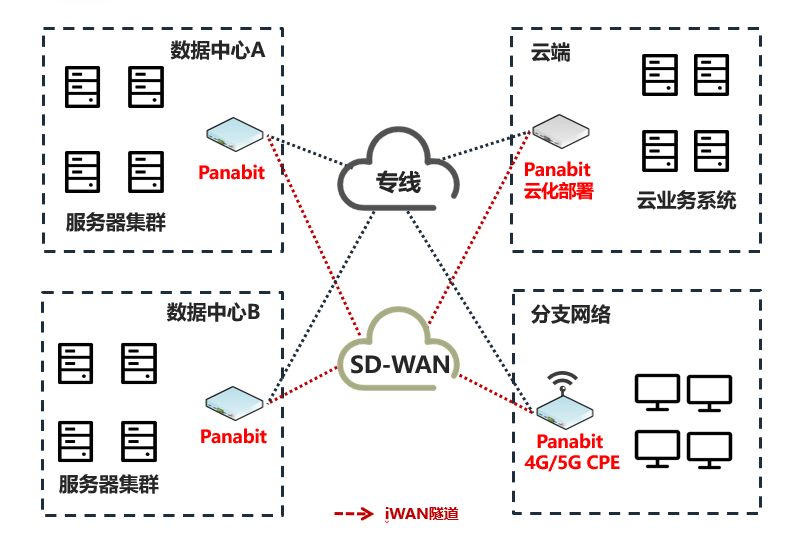
Users with existing Layer 2 dedicated lines (such as MSTP, etc.) do not need to make major changes to their current network architecture. They can establish a virtual Layer 2 tunnel through iWAN, seamlessly compatible with existing dedicated lines
Whether it’s fiber, ADSL, or 4G/5G wireless networks, they can all serve as flexible backup channels, achieving low-cost backup
When the original dedicated line fails, quickly switch to the iWAN backup line, ensuring business continuity
Through iWAN Layer 2 networking, it is possible to achieve a more cost-effective dedicated line backup, especially suitable for users who have already deployed dedicated lines but are worried about backup lines.
▎Other Scenarios
In addition to direct connections between headquarters and branches and dedicated line backups, iWAN Layer 2 networking can unlock more scenarios:
Specific Business Support
For certain specific businesses that rely on Layer 2 communication, it meets their remote networking needs, such as some industrial control systems, video conferencing, video surveillance, etc.
Data Center Interconnection
Establishing a large Layer 2 network between data centers, achieving effects similar to VxLAN.
Flexible Adaptation to Various Network Needs
Complementing iWAN Layer 3 networking, it provides more flexible solutions in the face of complex hybrid network scenarios.
Conclusion
To help everyone understand more intuitively, let’s briefly compare iWAN Layer 2 networking with other technologies:
● PK Traditional Dedicated Lines:
No need to pull extra lines, lower costs, and greater expansion capabilities and flexibility.
● PK Layer 3 Networking:
Retains Layer 2 features such as VLAN, reduces complex routing configurations, and makes networking more transparent.
● PK Other Layer 2 VPNs:
Based on self-developed tunnel protocols, higher transmission efficiency, while supporting centralized management of SaaS cloud platforms, saving time and effort for maintenance.
In summary, iWAN Layer 2 networking brings not just a “virtual dedicated line” but a more free and efficient way of network connectivity.
In the next article, Xiaopai will introduce another advanced capability of iWAN—Segment Routing. Stay tuned!
Previous Highlights



Follow More Official Platforms

Official Video Account
@Beijing Panabit
Scan to Follow

Official Douyin Account
@Beijing Panabit
Open Douyin and Scan to Follow

Official Bilibili Account
@Beijing Panabit
Search and Follow on Bilibili

Official Weibo Account
@Panabit
Search and Follow on Weibo
Enjoy Connecting with the World