
The necessity for digital transformation in oilfields is now widely acknowledged. Emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence, and cloud computing are almost household terms for every oil professional. The IoT is referred to as the third wave of global development following computers and the internet.
Although IoT technology has seen extensive application and development, the global application of IoT is still in its infancy. Different countries have varying levels of understanding and research into IoT technology, leading to many challenges in the development of basic fields and skills.

01
Birth and Debut

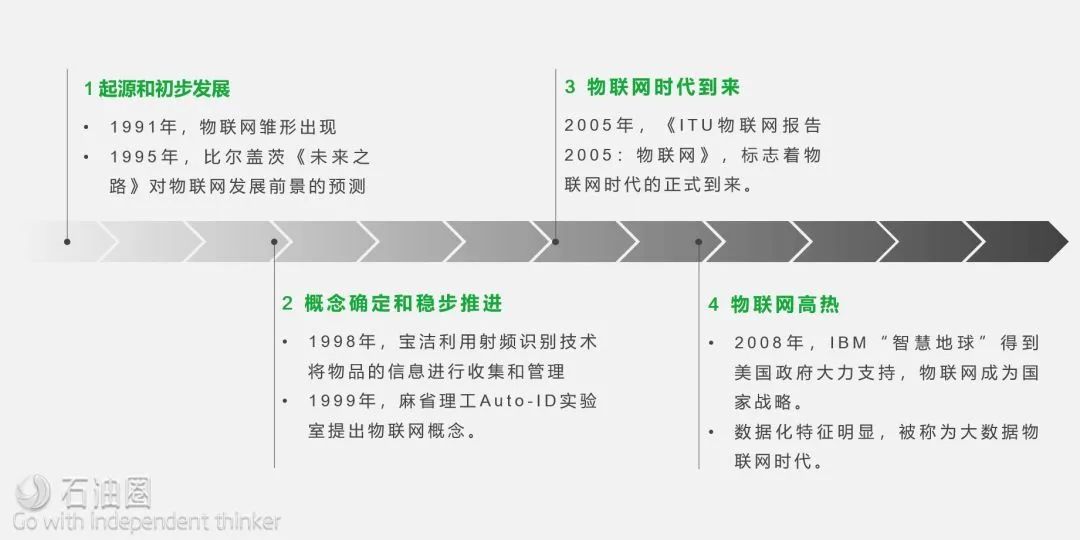
So far, the development of IoT can be summarized into four important stages:
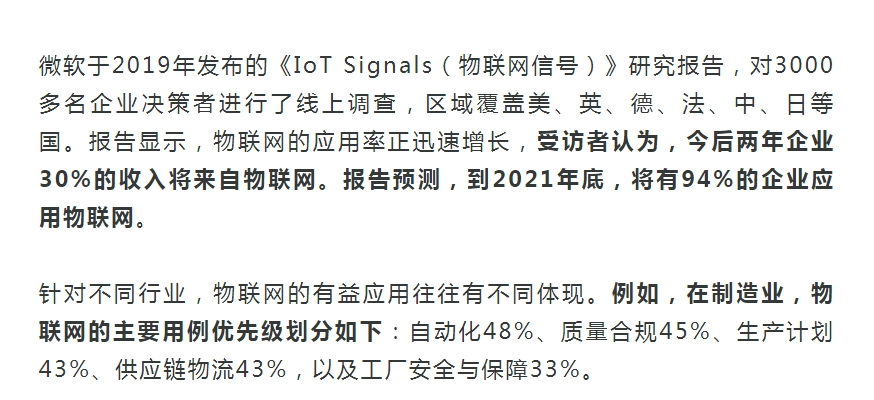

Data Source: Microsoft IoT Signals Research Report
Regarding the use cases and value of IoT in the oil and gas industry, a Deloitte report hypothesized that if a large oil company producing 270 million barrels annually could fully apply IoT technology, its production costs could be reduced by at least over $500 million.
For example.
In the oil and gas production sector, automating thousands of wells in different regions (comparable to a large oil company with over 50,000 wells) and monitoring multiple devices at each well (if a single-stage pump fails, the oil company faces daily losses of $100,000 to $300,000), would make production the largest potential beneficiary of IoT applications in oil and gas.
In the oil and gas development process, smart sensors, machine-to-machine connections, and big data analytics can increase active drilling time, while supply chains relying on mobile networks and big data can reduce cost inflation and alleviate delays in new projects.
For oil and gas exploration, advancements in seismic data acquisition (4D, microseismic) and computing power have improved exploration and development companies’ understanding of geology by providing more and better data. However, greater opportunities lie in processing existing seismic data faster and converting it into surface models.
02
Skills and Expertise
The most basic function of IoT is to provide “ubiquitous connectivity and online services,” which can be subdivided into four functions: information acquisition, information transmission, information processing, and information application.
For the oil and gas industry, the typical functions of IoT technology can be summarized into the following scenarios.
(1) Operation Monitoring
For various stages in the exploration and development process, automatic collection of specialized operational data is one of the main functions of IoT technology. This function allows engineering technicians to achieve real-time monitoring of the construction process, aiding in the rapid analysis and resolution of various engineering issues encountered during operations.
(2) Material Management
Intelligent management of specialized equipment, vehicles, and other materials can enhance the overall management and service levels of enterprises and business units, achieving refined management and reducing management and service costs.
(3) Design Optimization
Based on real-time collection, analysis, and processing of on-site operational data, combined with various management data such as materials, construction design plans can be comprehensively optimized, improving design efficiency and quality.
(4) Condition Warning
Real-time condition diagnosis and prediction for various construction processes and equipment can provide warnings and alerts for potential engineering events and operational risks, reducing risks and improving efficiency.
(5) Remote Command
Combining advanced communication technologies like 5G, tightly connecting construction sites and bases allows for remote scheduling and command, coordinating solutions for complex situations on-site.
For instance.

RTOC completed its design scheme at the end of August 2014, officially entered the trial operation phase in June 2015, completed overall environment and software/hardware acceptance in December 2015, and went online and officially operated by the end of March 2016. As of June 2019, PetroChina’s RTOC had monitored over 1,400 active drilling operations and utilized real-time monitoring, warning software, and specialized tools to detect over 100 various anomalies, including sensor abnormalities, equipment failures, and well leaks/overflows.
03
Key Technologies
The “EU IoT Strategic Research Roadmap” white paper published by the European Union lists 13 key technologies, with the technical system framework diagram as follows:
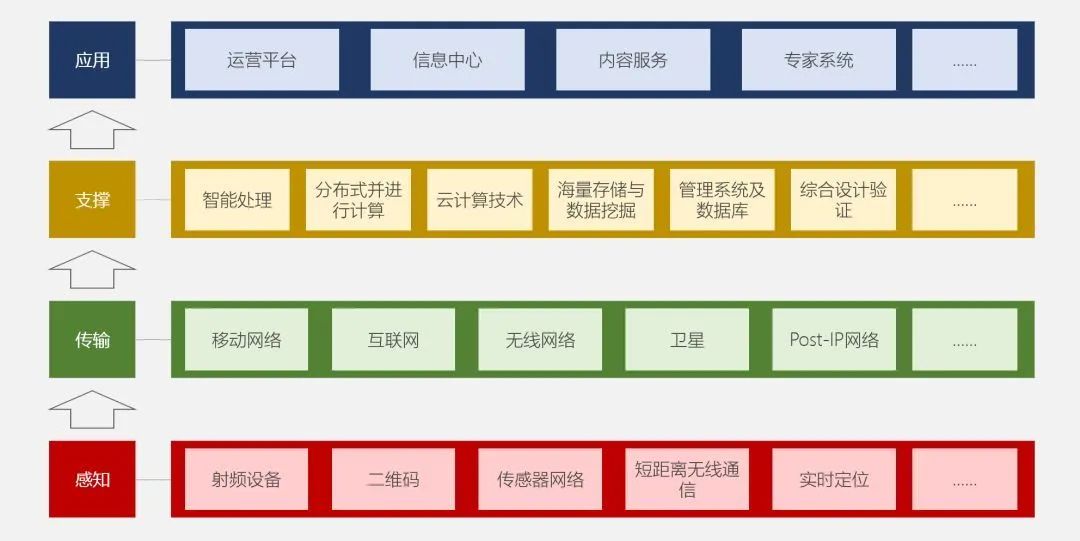
The IoT technology system architecture


04
Representative Works
Data collection is the foundation and prerequisite for analysis. The IoT utilizes sensor technology and communication technology to collect equipment status data, enabling functions such as intelligent identification, positioning, tracking, and management.
Currently, almost all large and medium-sized oil companies and oil service companies globally have made varying degrees of progress in digital transformation and have gained significant results in IoT applications.
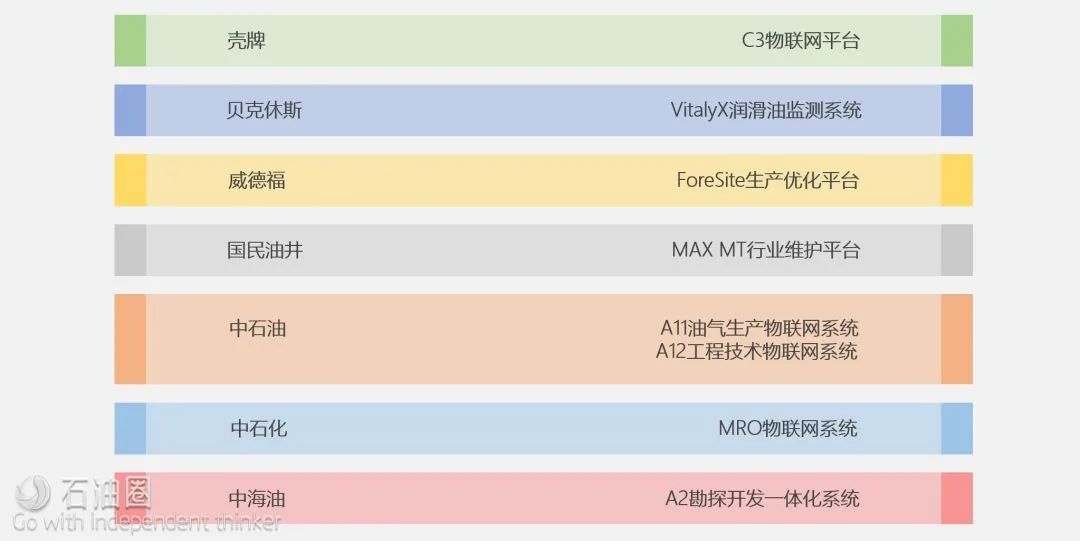
Overview of IoT technology applications in some oil and oil service companies
This briefly introduces PetroChina’s A11 system.

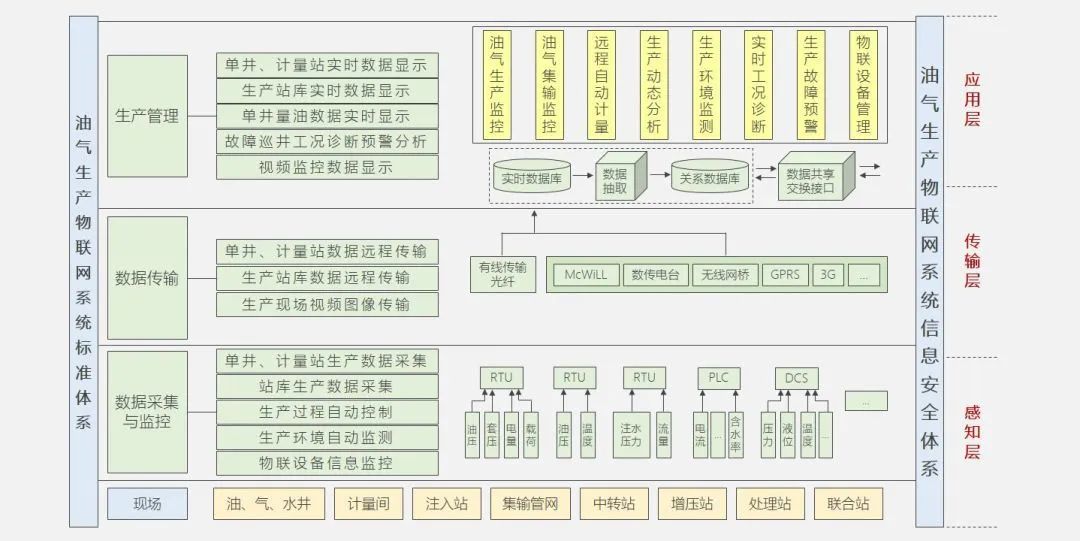
A11 Functional Architecture Diagram
The construction goals of A11 can mainly be summarized as: designing and implementing a unified platform, establishing and enforcing a set of standard specifications, and building a number of demonstration projects.

A11 Construction Route and Goals
05
Conclusion
The strategic significance of digital oilfields is self-evident. In the process of achieving digital oilfields, IoT technology, with its advantages in technical architecture, industry maturity, and development potential, has vast application potential in oilfield production environments. However, the application of IoT in the construction of digital oilfields still faces numerous issues, such as technical standards, security, protocols, IP address problems, and terminal issues, all of which need further exploration and resolution.
