2021 Advanced Control Technology Forum for Process Industry and Technical Exchange on Advanced Control, Optimization Control, and Intelligent Control in the Chemical Industry
As the neural center of modern large chemical plants, the DCS central control room (Central Control Room or Central Control Room) plays an important role, where all important control decisions are made.
What Does the Control Room Look Like?
The control room is generally a must-visit place for big shots or new employees, so it naturally has a higher degree of glossiness. However, it is important to know that the control room is a workplace where work efficiency is the top priority, occupational health is second, and grandeur and comfort are a distant third.

Traditional control consoles are rarely seen in modern factories unless they are very old.

Such control rooms only exist in science fiction movies; no one would use such control rooms in industry as they are not practical at all.
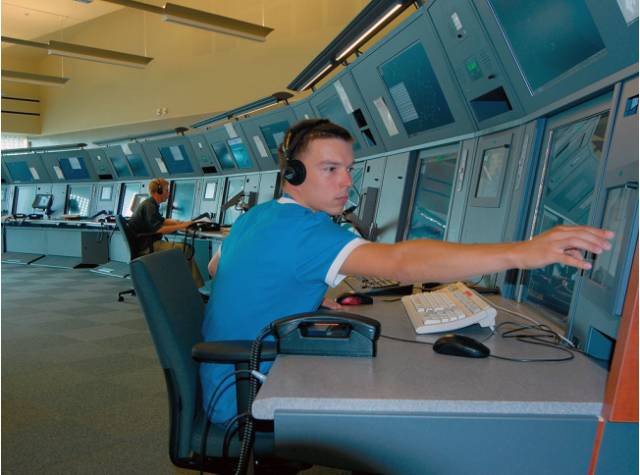

This extremely long control console is only suitable when each operator operates independently and in parallel; if close cooperation is needed, the distance is too far. This is an air traffic control console, which meets the requirements of independence and parallelism.

Zhenhai Refining and Chemical Monitors 8000 Control Points with Just 7 Employees
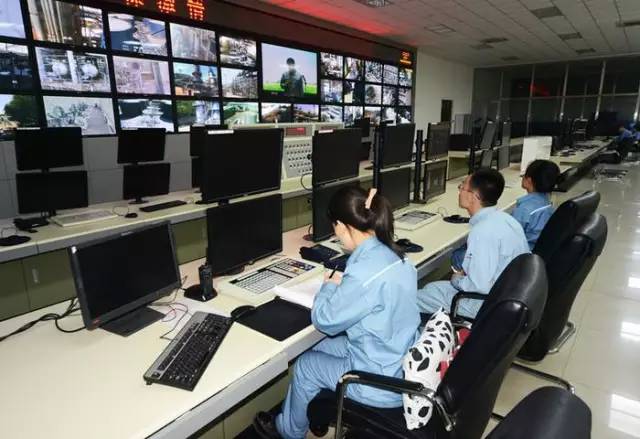

Yanshan Petrochemical Refinery No. 2 Central Control Room Achieves Black Screen Operation

Maoming Petrochemical Control Room Hall
The Development of Industrial Production Control Systems
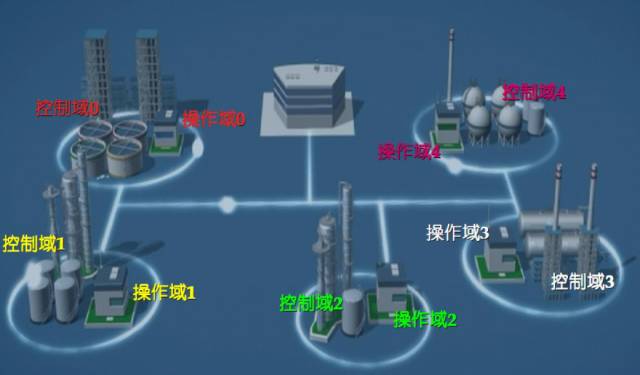
Basic Control Framework of the System
Let’s understand how the industrial production control system has developed step by step.
1. The Primitive Manual Control Stage
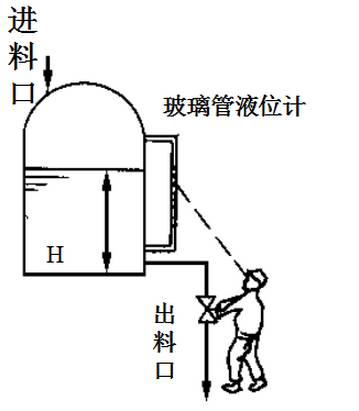
The most primitive control method was to add a little more if it was too much and to add a little less if it was too little…
To replace human labor, reduce labor intensity, improve work efficiency, and ensure the safe production of large and complex industries, improvements were made towards automation.
2. Conventional Instrument Control
Unit Combination Instruments
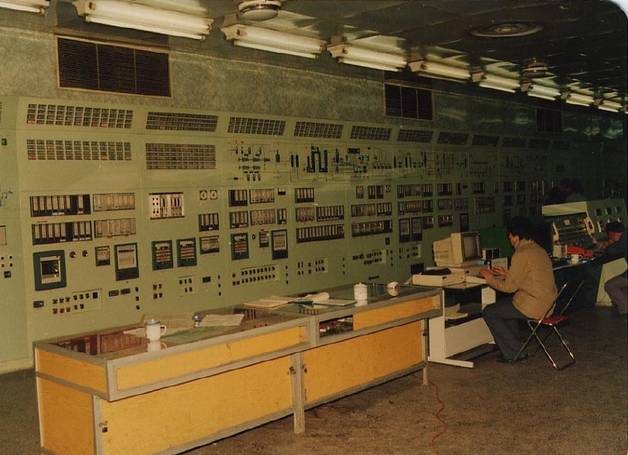

Central Control Room Using Conventional Instruments
As the scale of production processes continues to expand, the number of central control instruments increases, and the requirements for operators to monitor and operate processes become higher, conventional instruments become inadequate.
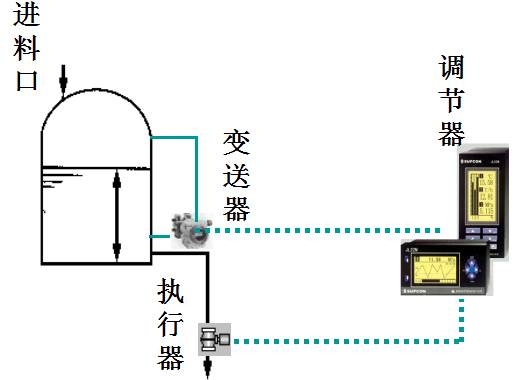
3. Computer Centralized Control
How to minimize the hazards caused by computer failures and disperse the dangers has become the primary issue to be solved by applying computer control systems.
The requirements for centralized and integrated operation and supervision necessitate corresponding data communication links for control and operation at the plant, workshop, and production line levels, requiring not only a large volume of data transmission but also high-speed data transmission rates.
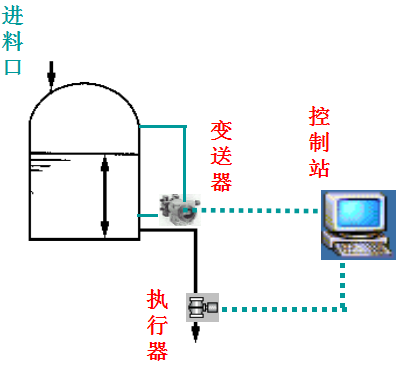
4. DCS Control System
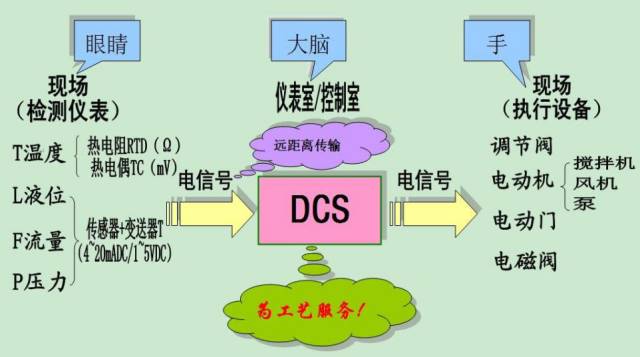
DCS, commonly known as the “Industrial Brain”
DCS Objects Are Distributed → Control Is Distributed

Centralized Management:

DCS Concept
DCS is short for Distributed Control System; in the domestic automatic control field, it is also known as a centralized control system.
The main characteristics of DCS can be summed up in one sentence: “Distributed Control, Centralized Management”.
DCS typically uses several controllers (process stations) to control numerous control points in a production process, with controllers connected via a network for data exchange.
Production control operations are performed using computer operator stations that connect to controllers via a network to collect production data and convey operational instructions.
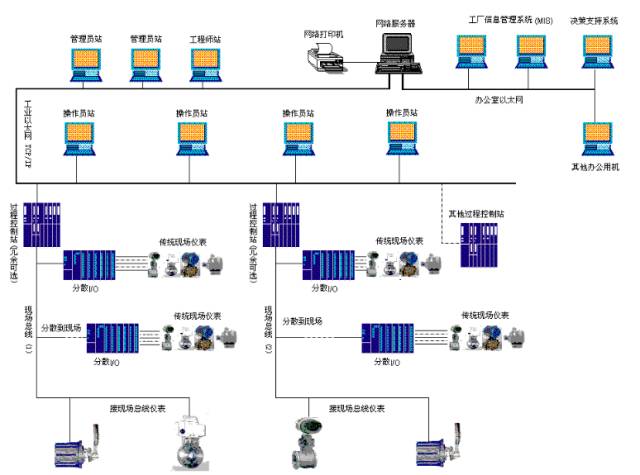
DCS Structural Composition
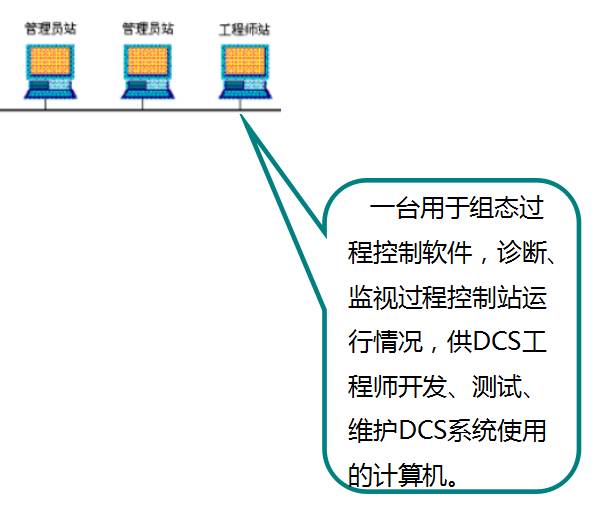
Structurally, DCS includes process level, operation level, and management level.
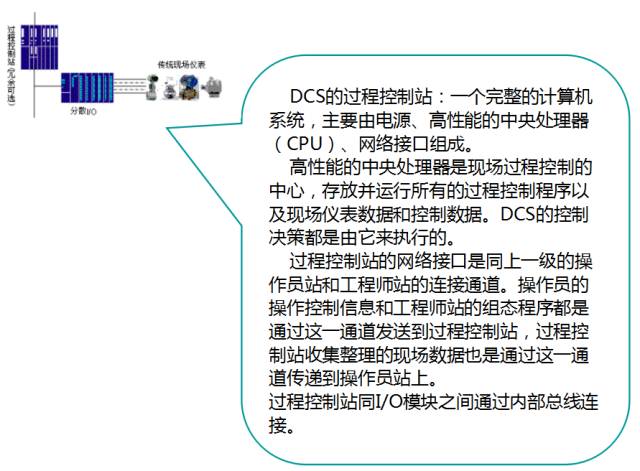
Process Level:Composed of process control stations, I/O units, and field instruments, it is the main implementation part of the system control function.
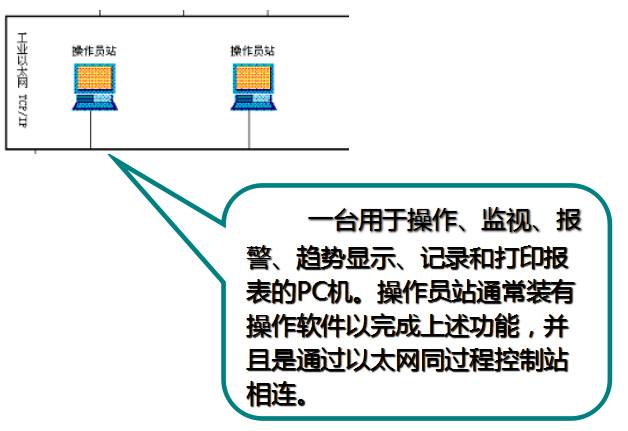
Operation Level:Operator stations and engineer stations complete system operation monitoring and configuration maintenance.
The management level mainly refers to the factory management information system (MIS or ERP system), which serves as a higher-level application of DCS.
DCS Operation Beginner’s Guide (Taking Central Control DCS System as an Example)
DCS operations are generally simple and convenient, making them easy to learn. For process operators, there is no need to explain complex computer principles and internal structures; the focus should be on teaching them practical usage methods and operational requirements.
Function Introduction
The computer monitoring system integrates functions such as field signal acquisition, dynamic display, automatic control, remote operation of electrical equipment (pumps), and interlocking control. The following functions can be realized on the computer operation and monitoring screen:
Toolbar Introduction

 System Overview:Introduces the product functions, characteristics, and scale of the company.
System Overview:Introduces the product functions, characteristics, and scale of the company.
 Alarm Overview:When parameters trigger an alarm, the alarm information is automatically logged onto the alarm screen, recording up to 1000 historical alarm messages. By checking the alarm overview screen, historical alarm situations can be obtained.
Alarm Overview:When parameters trigger an alarm, the alarm information is automatically logged onto the alarm screen, recording up to 1000 historical alarm messages. By checking the alarm overview screen, historical alarm situations can be obtained.
 System Overview:The system retrieval directory. From here, you can view system flow diagrams, trend curves, data overviews, control groups, etc., and can directly enter selected flow diagrams, trend curves, data overviews, control groups from the overview screen; you can also pop up a specific dynamic parameter gauge from the overview screen to check detailed information about that parameter.
System Overview:The system retrieval directory. From here, you can view system flow diagrams, trend curves, data overviews, control groups, etc., and can directly enter selected flow diagrams, trend curves, data overviews, control groups from the overview screen; you can also pop up a specific dynamic parameter gauge from the overview screen to check detailed information about that parameter.
 Control Group:Information regarding adjustable or modifiable parameters can be reviewed, and modifications can be made if operational permissions allow. You can also directly enter adjustment screens from the control group screen. Function: Place related instruments on the same screen for simultaneous operation.
Control Group:Information regarding adjustable or modifiable parameters can be reviewed, and modifications can be made if operational permissions allow. You can also directly enter adjustment screens from the control group screen. Function: Place related instruments on the same screen for simultaneous operation.
 Adjustment Screen:Click this button to view the adjustment screen for the selected position number;
Adjustment Screen:Click this button to view the adjustment screen for the selected position number;
 Trend Chart:The trend curve screen: allows you to review the record curves of relevant parameters. Each page of the trend curve screen can record the changing trends of up to 8 parameters. Each curve can be reviewed individually for clearer examination. The time scale can be moved left and right to review the current values of parameters at a specific time within the allowed recording length (i.e., to review historical data), and the parameter recording time interval can be set according to user needs.
Trend Chart:The trend curve screen: allows you to review the record curves of relevant parameters. Each page of the trend curve screen can record the changing trends of up to 8 parameters. Each curve can be reviewed individually for clearer examination. The time scale can be moved left and right to review the current values of parameters at a specific time within the allowed recording length (i.e., to review historical data), and the parameter recording time interval can be set according to user needs.
 Flow Diagram:The process flow screen, which serves as the main monitoring and operation interface for the system, allows for monitoring and controlling on-site functions.
Flow Diagram:The process flow screen, which serves as the main monitoring and operation interface for the system, allows for monitoring and controlling on-site functions.
 Report Screen:The report screen displays real-time data in report form, including important system data and on-site data for system status checks or process analysis.
Report Screen:The report screen displays real-time data in report form, including important system data and on-site data for system status checks or process analysis.
 Data Overview:Each page of the data overview screen can display up to 32 dynamic parameters. You can select a page of the data overview screen to review the dynamic changes of multiple parameters.
Data Overview:Each page of the data overview screen can display up to 32 dynamic parameters. You can select a page of the data overview screen to review the dynamic changes of multiple parameters.
 System Status:Click to pop up the screen for fault diagnosis, which displays the remote diagnostics of the hardware and software operation of the control station. Process information is used to display background service information.
System Status:Click to pop up the screen for fault diagnosis, which displays the remote diagnostics of the hardware and software operation of the control station. Process information is used to display background service information.
 Previous Page:Go to the previous page.
Previous Page:Go to the previous page.
 Next Page:Go to the next page.
Next Page:Go to the next page.
 Turn Page:Turn to any current page.
Turn Page:Turn to any current page.
 Backward:Go back to the previous screen.
Backward:Go back to the previous screen.
 Forward:Advance to the next screen after the current one.
Forward:Advance to the next screen after the current one.
 User Login:Operational login and permission settings: ensuring system security.
User Login:Operational login and permission settings: ensuring system security.
 Mute:Click this button to silence the alarm sound.
Mute:Click this button to silence the alarm sound.
 Operation Record Overview:Records all operations on the monitoring screen for operators to review. The operation record overview is displayed in two ways: position operation records and system operation records.
Operation Record Overview:Records all operations on the monitoring screen for operators to review. The operation record overview is displayed in two ways: position operation records and system operation records.
 System Services:Displays information about the software version, copyright, usage rights, etc., and allows for system service settings.
System Services:Displays information about the software version, copyright, usage rights, etc., and allows for system service settings.
 Find I/O Position Number:This function is used to quickly find the I/O position number in the monitoring software.
Find I/O Position Number:This function is used to quickly find the I/O position number in the monitoring software.
 Print:Used to print the current monitoring screen.
Print:Used to print the current monitoring screen.
 Popup Alarm: Used for particularly important alarms; once an alarm occurs, the system will immediately pop up an alarm dialog box.
Popup Alarm: Used for particularly important alarms; once an alarm occurs, the system will immediately pop up an alarm dialog box.
 Exit System:Used to exit the AdvanTrol monitoring software.
Exit System:Used to exit the AdvanTrol monitoring software.
Source: Internet
Recent Training
2021 Advanced Control Technology Forum for Process Industry and Technical Exchange Meeting on Advanced Control, Optimization Control, and Intelligent Control in the Chemical Industry


Chiral Separation Technology (PPT Available Upon Request)
Chemical Process Intensification Technology (PPT Available Upon Request)
Summary of Good Organic Chemistry Reaction Mechanisms (143 PPT Slides)
In-depth Analysis of the Technical Gap in Ren Zhengfei’s View, Why Do We Hate Chemistry?
Synthesis Route Design and Synthesis Methods
Animated Explanation of the Principles of Four Major Spectra (IR, MS, NMR, UV)
The Experimental Operating Experience of a Shanghai Organic Institute Doctor That Cannot Be Bought (Complete Version)
Reactor Structure and Working Principle Diagram
PPT|| Pilot Scale-Up and Production Process Regulations
Copyright Statement
Disclaimer: The copyright of the article belongs to the original author. If there are any issues related to the content, copyright, or others, please contact us for deletion! The content of the article represents the author’s personal views and does not reflect the endorsement or support of this public account. This public account holds the final interpretation right of this statement.
