☞ This is the 15100th article published by Metal Processing (mw1950pub).
3D printing is an emerging technology in the manufacturing industry, known as a “manufacturing technology with industrial revolution significance.” Today, the editor has organized the top ten 3D printing technologies, vividly presenting their principles through GIFs. The main technologies introduced are SLA, CLIP, 3DP, PolyJet, and FDM, as well as the principles of five metal 3D printing technologies: NPJ, SLM, SLS, LMD, and EBM.
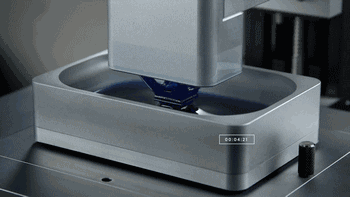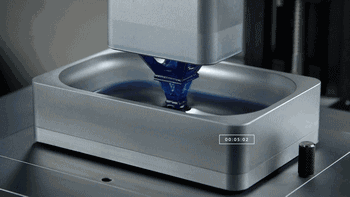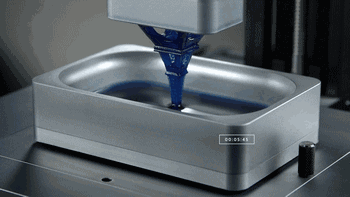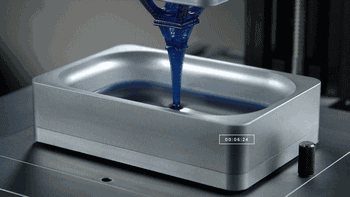
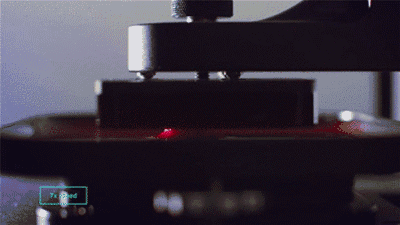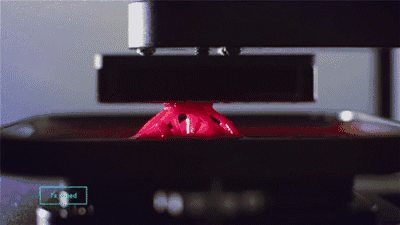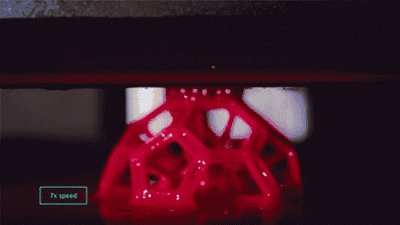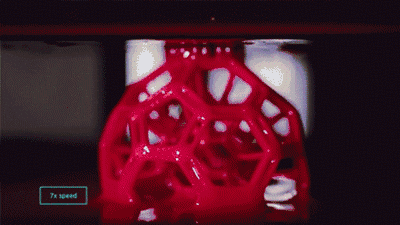
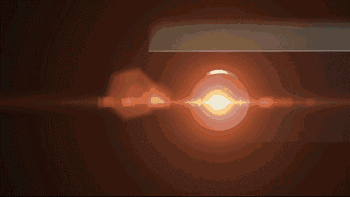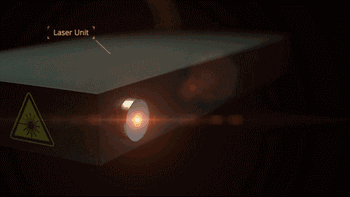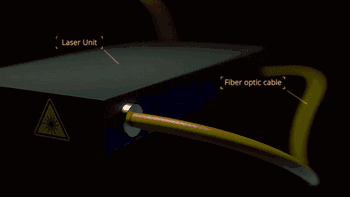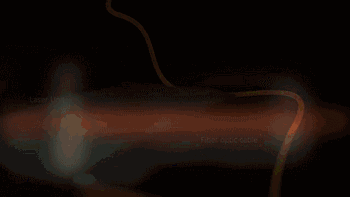
1. SLA (StereoLithography)
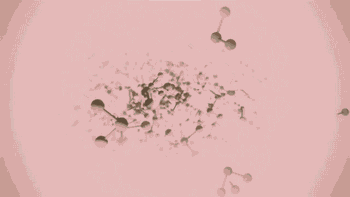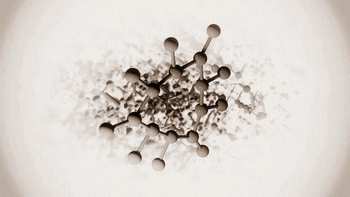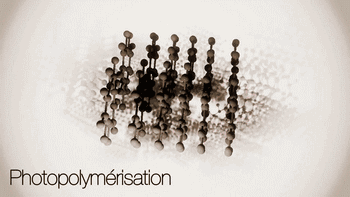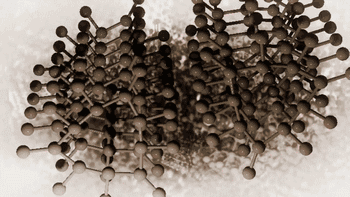
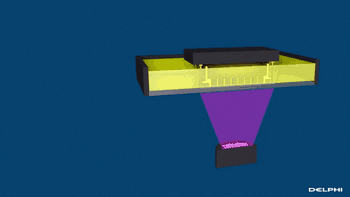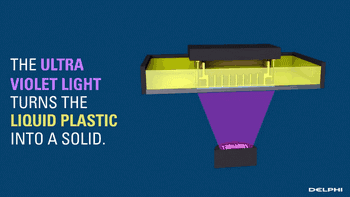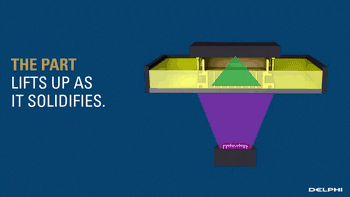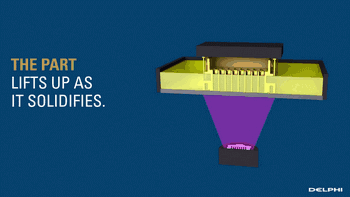
SLA, or Stereolithography, is a light curing molding technology that uses ultraviolet light to irradiate liquid photosensitive resin, causing a polymerization reaction to cure layer by layer and form a three-dimensional entity. The dimensional accuracy of the workpiece produced by SLA is high, making it one of the earliest commercialized 3D printing technologies.
The following is the SLA process engineering.
 Layer-by-layer Scanning Molding
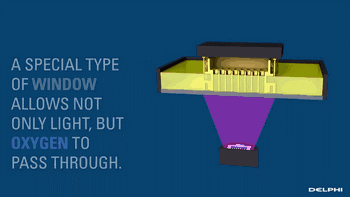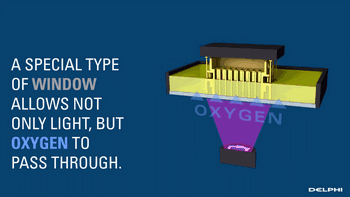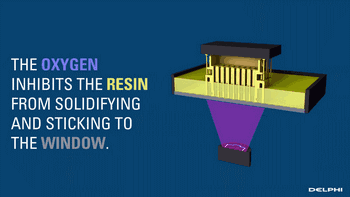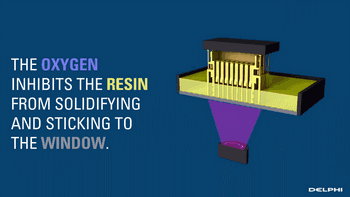
CLIP, or Continuous Liquid Interface Production, is a revolutionary 3D printing technology developed by Carbon 3D based on SLA technology, increasing the speed of 3D printing by 100 times.
CLIP projects from the bottom, curing the photosensitive resin, while the uncured parts maintain a stable liquid state by controlling oxygen to form a dead zone, suppressing the light curing reaction, thus ensuring the continuity of curing.
Oxygen Suppressing the Light Curing Process
Demonstration of the Light Curing Dead Zone
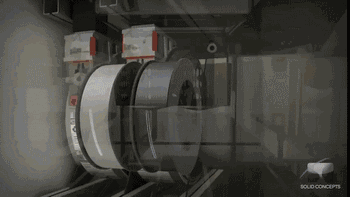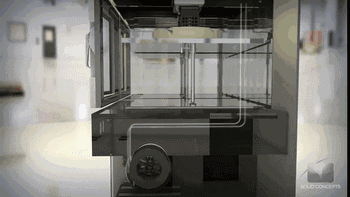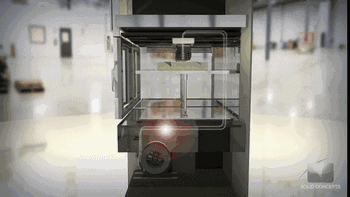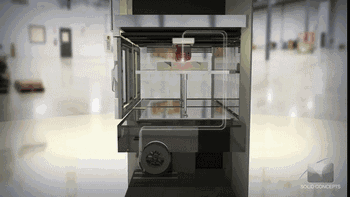
3. 3DP (Three-Dimensional Printing)
3DP, or Three-Dimensional Printing, is a rapid prototyping technology similar to traditional two-dimensional inkjet printing, where a binder (colored binder can print colored parts) is sprayed from a nozzle to bond powder on the platform, typically using gypsum powder as the forming material. Currently, 3DP technology is mainly applied in two areas: full-color 3D printing and sand mold casting.
The following is the sand mold casting process using 3DP technology by Exone Company.
PolyJet is a polymer jetting technology, whose molding principle is similar to 3DP technology, but instead of a binder, it jets light-curing resin, which is cured after spraying using ultraviolet light.
PolyJet Molding Principle
PolyJet uses an array of nozzles, allowing it to jet different materials simultaneously, achieving multi-material and multi-color printing.
Array Nozzle Working Process
5. FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
FDM, or Fused Deposition Modeling, uses high temperature to melt materials, extruding them through a print head to form filaments that accumulate on the component platform. FDM is the simplest and most common 3D printing technology, typically used in desktop 3D printing devices.
The following is the working principle of FDM technology.
Material Extrusion Forming
Metal 3D printing technology can be directly used for rapid prototyping of metal parts, with broad industrial application prospects, and is a key development area for 3D printing technology both domestically and internationally. Below, we share the principles of five metal 3D printing technologies: NPJ, SLM, SLS, LMD, and EBM.
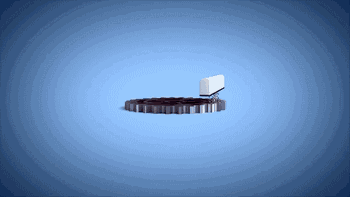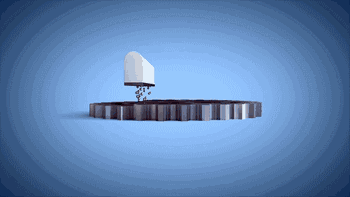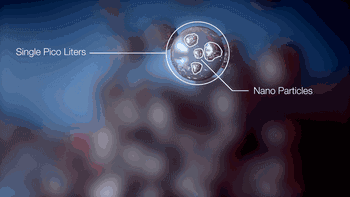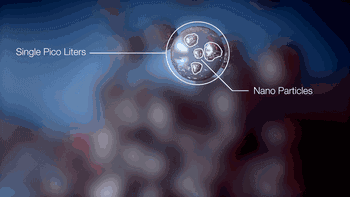
6. NPJ (Nano Particle Jetting)
NPJ technology is the latest metal 3D printing technology developed by the Israeli company Xjet. Compared to conventional laser 3D printing, it uses nano-liquid metal to deposit and form through inkjet, achieving a printing speed five times faster than ordinary laser printing, with excellent precision and surface roughness.
The following is the working process of Xjet equipment.
Metal Particle Refinement
Metal Particles Distributed in Droplets
Droplet Jetting Forming Process
Liquid Phase Discharge Process
7. SLM (Selective Laser Melting)
SLM, or Selective Laser Melting, is currently the most common technology in metal 3D printing. It uses a finely focused laser spot to rapidly melt pre-set metal powder, directly obtaining parts of any shape with complete metallurgical bonding, achieving a density of over 99%.
The laser scanning system is one of the key technologies of SLM. The following is a working diagram of the scanning system from SLM Solution Company.
Metal Powder Melting Process
In the metal 3D printing process, due to the complexity of the parts, support materials are usually required during printing. After the parts are completed, supports need to be removed, and the surface of the parts needs to be treated.
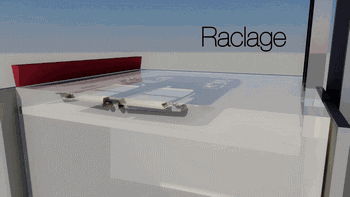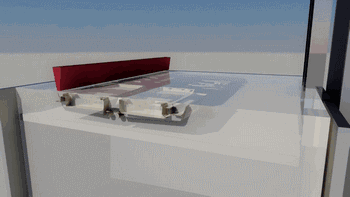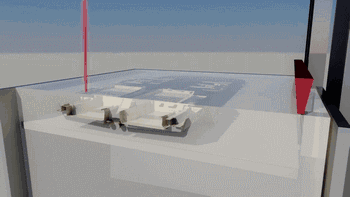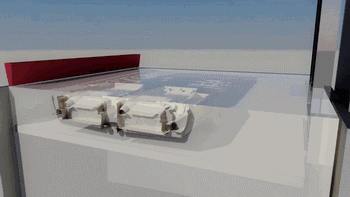
8. SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)
SLS, or Selective Laser Sintering, is similar to SLM technology, with the main difference being the power of the laser, which is typically used for 3D printing of polymer materials.
The following is the process of preparing plastic parts using SLS.
Model Layering and Slicing
Layer-by-layer Scanning Molding
CLIP, or Continuous Liquid Interface Production, is a revolutionary 3D printing technology developed by Carbon 3D based on SLA technology, increasing the speed of 3D printing by 100 times.
CLIP projects from the bottom, curing the photosensitive resin, while the uncured parts maintain a stable liquid state by controlling oxygen to form a dead zone, suppressing the light curing reaction, thus ensuring the continuity of curing.
Oxygen Suppressing the Light Curing Process
Demonstration of the Light Curing Dead Zone
3. 3DP (Three-Dimensional Printing)
3DP, or Three-Dimensional Printing, is a rapid prototyping technology similar to traditional two-dimensional inkjet printing, where a binder (colored binder can print colored parts) is sprayed from a nozzle to bond powder on the platform, typically using gypsum powder as the forming material. Currently, 3DP technology is mainly applied in two areas: full-color 3D printing and sand mold casting.
The following is the sand mold casting process using 3DP technology by Exone Company.
PolyJet is a polymer jetting technology, whose molding principle is similar to 3DP technology, but instead of a binder, it jets light-curing resin, which is cured after spraying using ultraviolet light.
PolyJet Molding Principle
PolyJet uses an array of nozzles, allowing it to jet different materials simultaneously, achieving multi-material and multi-color printing.
Array Nozzle Working Process
5. FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
FDM, or Fused Deposition Modeling, uses high temperature to melt materials, extruding them through a print head to form filaments that accumulate on the component platform. FDM is the simplest and most common 3D printing technology, typically used in desktop 3D printing devices.
The following is the working principle of FDM technology.
Material Extrusion Forming
Metal 3D printing technology can be directly used for rapid prototyping of metal parts, with broad industrial application prospects, and is a key development area for 3D printing technology both domestically and internationally. Below, we share the principles of five metal 3D printing technologies: NPJ, SLM, SLS, LMD, and EBM.
6. NPJ (Nano Particle Jetting)
NPJ technology is the latest metal 3D printing technology developed by the Israeli company Xjet. Compared to conventional laser 3D printing, it uses nano-liquid metal to deposit and form through inkjet, achieving a printing speed five times faster than ordinary laser printing, with excellent precision and surface roughness.
The following is the working process of Xjet equipment.
Metal Particle Refinement
Metal Particles Distributed in Droplets
Droplet Jetting Forming Process
Liquid Phase Discharge Process
7. SLM (Selective Laser Melting)
SLM, or Selective Laser Melting, is currently the most common technology in metal 3D printing. It uses a finely focused laser spot to rapidly melt pre-set metal powder, directly obtaining parts of any shape with complete metallurgical bonding, achieving a density of over 99%.
The laser scanning system is one of the key technologies of SLM. The following is a working diagram of the scanning system from SLM Solution Company.
Metal Powder Melting Process
In the metal 3D printing process, due to the complexity of the parts, support materials are usually required during printing. After the parts are completed, supports need to be removed, and the surface of the parts needs to be treated.
8. SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)
SLS, or Selective Laser Sintering, is similar to SLM technology, with the main difference being the power of the laser, which is typically used for 3D printing of polymer materials.
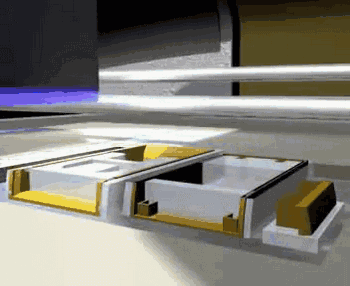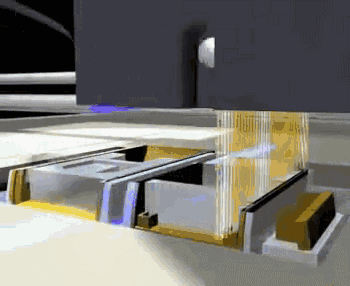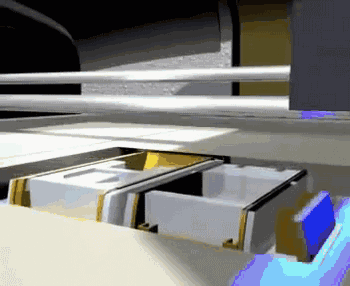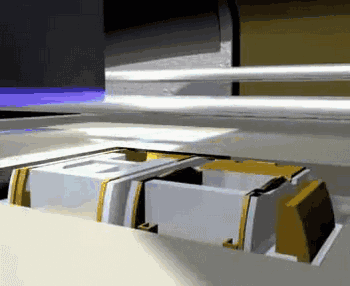
The following is the process of preparing plastic parts using SLS.
Model Layering and Slicing
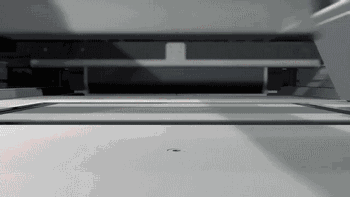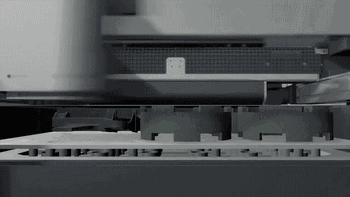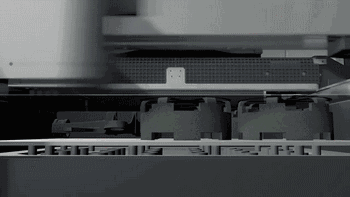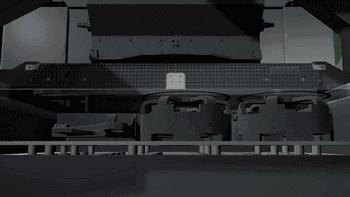
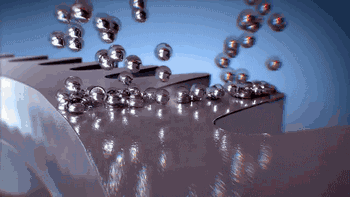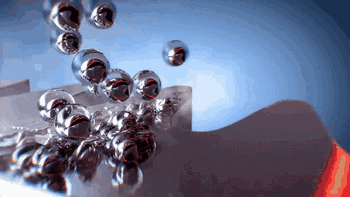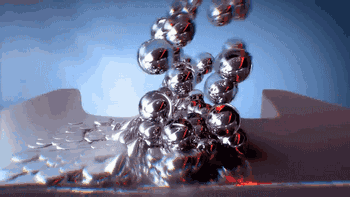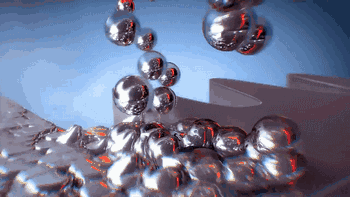
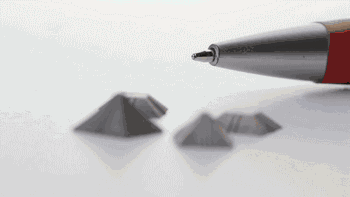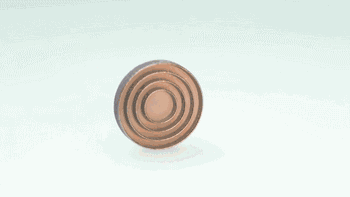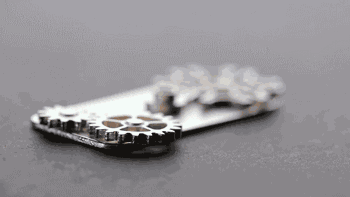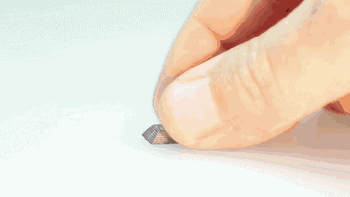
 Removing the Parts
Removing the Parts
 Post-processing
SLS can also be used to manufacture metal or ceramic parts, but the resulting parts have a lower density and require post-sintering treatment to be usable.
Post-processing
SLS can also be used to manufacture metal or ceramic parts, but the resulting parts have a lower density and require post-sintering treatment to be usable.
 SLS Manufacturing of Metal Parts
9. LMD (Laser Metal Deposition)
LMD, or Laser Metal Deposition, has many names, as different research institutions independently study and name it. Common names include: LENS, DMD, DLF, LRF, etc. The main difference from SLM is that its powder is gathered to the work table through a nozzle and melted with the laser at a point, obtaining a deposited overlay entity after cooling.
The following is the working process of LENS technology.
SLS Manufacturing of Metal Parts
9. LMD (Laser Metal Deposition)
LMD, or Laser Metal Deposition, has many names, as different research institutions independently study and name it. Common names include: LENS, DMD, DLF, LRF, etc. The main difference from SLM is that its powder is gathered to the work table through a nozzle and melted with the laser at a point, obtaining a deposited overlay entity after cooling.
The following is the working process of LENS technology.
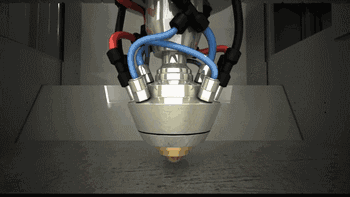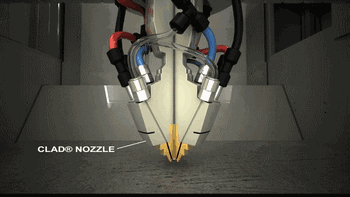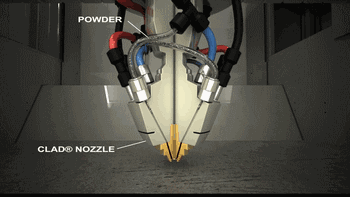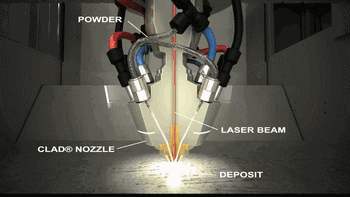 Coaxial Powder Feeding
Coaxial Powder Feeding
 Building Process
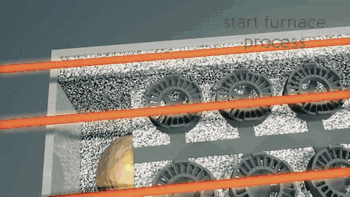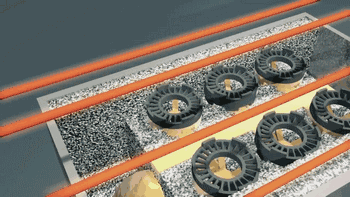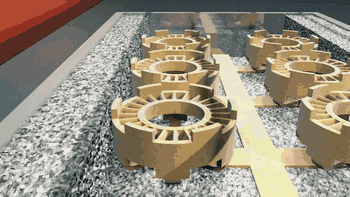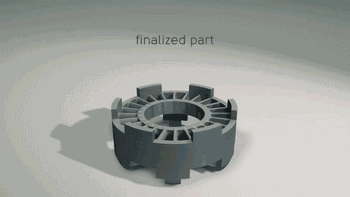
10. EBM (Electron Beam Melting)
EBM, or Electron Beam Melting, has a process very similar to SLM, with the difference being that the energy source used in EBM is an electron beam. The electron beam output energy of EBM is typically an order of magnitude larger than the laser output power of SLM, and the scanning speed is also much higher than that of SLM. Therefore, during the construction process, the entire build platform needs to be preheated to prevent excessive residual stress caused by high temperatures during the molding process. The following is the working process of EBM.
Building Process
10. EBM (Electron Beam Melting)
EBM, or Electron Beam Melting, has a process very similar to SLM, with the difference being that the energy source used in EBM is an electron beam. The electron beam output energy of EBM is typically an order of magnitude larger than the laser output power of SLM, and the scanning speed is also much higher than that of SLM. Therefore, during the construction process, the entire build platform needs to be preheated to prevent excessive residual stress caused by high temperatures during the molding process. The following is the working process of EBM.
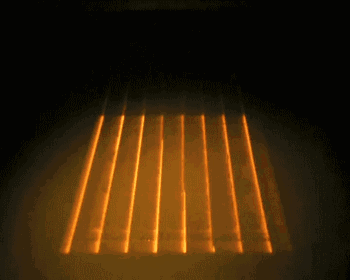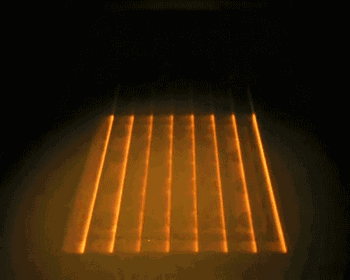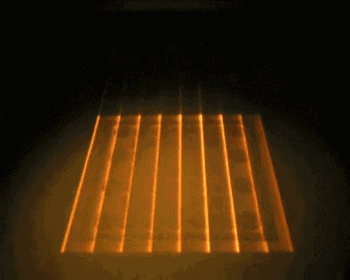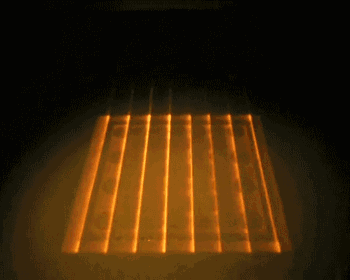 Overall Preheating
Overall Preheating
 Forming Process
Forming Process
 Changes of Powder During Melting
Changes of Powder During Melting
Follow the Metal Processing video account for an industrial media with attitude.
☞ Source: Mufeng Machinery ☞ Article edited by: xp ☞ Media cooperation: 010-88379790-801 ☞The only submission website for Metal Processing Magazine: http://tougao.mw1950.cn/
Statement: If there are any copyright issues with the videos, images, or text used in this article, please inform us immediately. We will confirm the copyright based on the proof materials you provide and pay remuneration according to national standards or delete the content immediately!






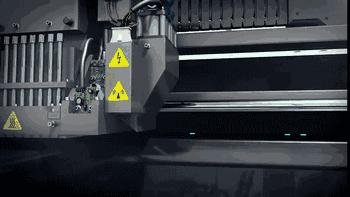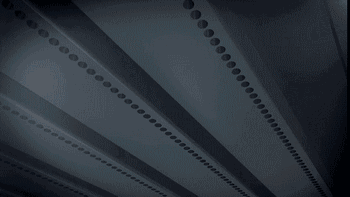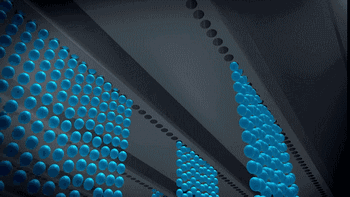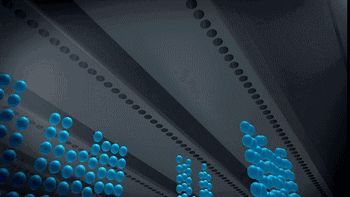















 Removing the Parts
Removing the Parts Post-processing
Post-processing SLS Manufacturing of Metal Parts
SLS Manufacturing of Metal Parts Coaxial Powder Feeding
Coaxial Powder Feeding Building Process
Building Process Overall Preheating
Overall Preheating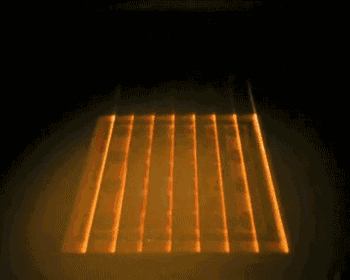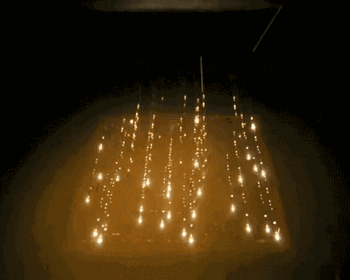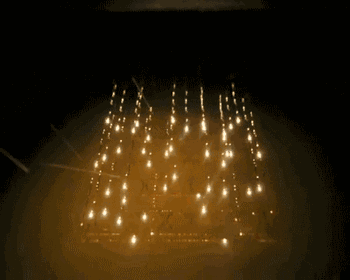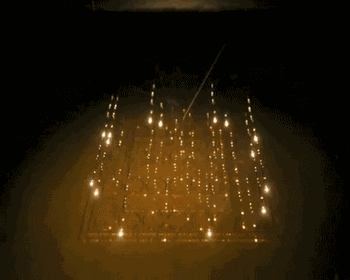
 Forming Process
Forming Process Changes of Powder During Melting
Changes of Powder During Melting