
With the development of the Internet era, coupled with the major transformations in modern society, traditional organizational structures can no longer adapt to the rapidly changing business environment, facing challenges and innovations in their respective industries. If there are no new organizational models or mechanisms to support them, due to organizational inertia and the inability to keep up with organizational capabilities, even if entrepreneurs have good strategic ideas and see the future development direction, it will be difficult to achieve the strategic goals of the enterprise. Therefore, understanding the trends in organizational structure innovation is of great significance for college students’ innovation and entrepreneurship. Next, let’s join Chuang Chuang in today’s entrepreneurship class about “Trends in Organizational Innovation in the Internet Era”!

Flattening of Organizational Forms

The flattening of organizational structure refers to reducing management levels, increasing management scope, enhancing employee autonomy, and improving the effectiveness of organizational information transmission. Currently, most enterprises adopt a hierarchical management structure, which has obvious drawbacks: first, low management efficiency due to multiple management levels, leading to slow information transmission; second, it obstructs contact with the market and customers, making it difficult to timely and effectively reflect market demands; third, it is not conducive to employee management and innovation, suppressing employee autonomy and not allowing individual characteristics to be well expressed.
Hierarchical Structure (right image)
 Flattening (left image)
Flattening (left image)
Therefore, organizations are gradually moving towards a flattening direction, which emphasizes the distribution of power, stressing that power should not be overly concentrated at the top, but rather more authority should be granted to the grassroots, allowing grassroots to enjoy more autonomy. The advantages of a flat organization mainly include four aspects:
1
Improved communication quality, increased communication efficiency, and facilitated work coordination between organizations.
2
Reduced organizational management costs, transforming from a pyramid to a flat structure, thus reducing intermediate management organizations.
3
Enhanced self-control levels; as employees gain more autonomy, they also need to strengthen their self-control.
4
Quick response to market demands with zero distance, allowing for faster aggregation of consumer and market information.
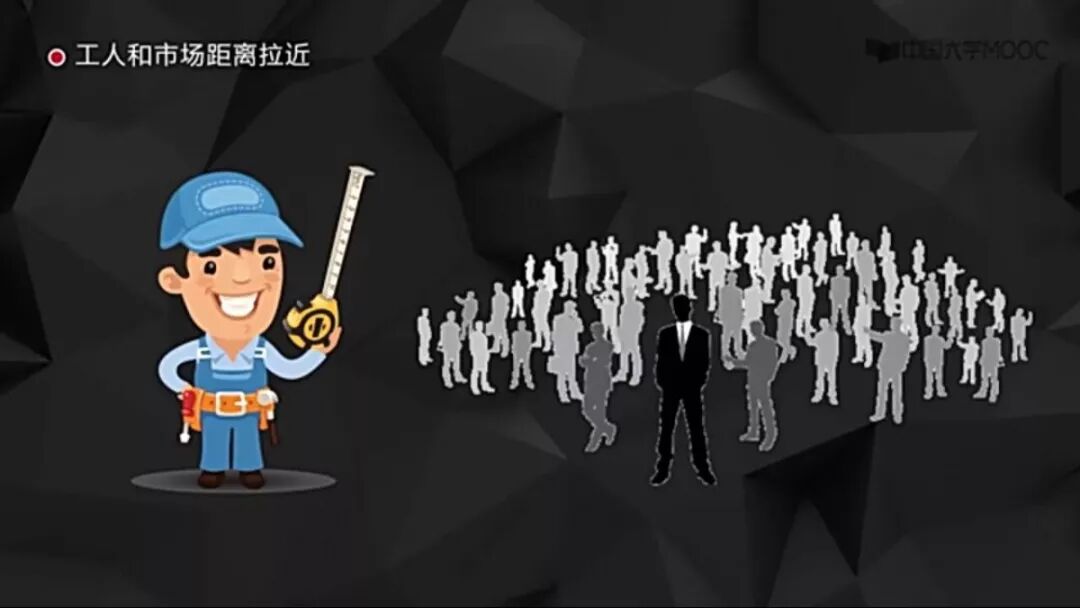


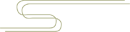
Of course, flattening also has its disadvantages: due to the large span of control, leaders cannot provide sufficient and effective guidance and supervision for each subordinate; each leader receives information from many subordinates, and the multitude of information may drown out the most important and valuable content, potentially affecting the timely utilization of information.
Virtualization of Organizational Structure

Virtualized organizations refer to organizational structures that are no longer based on property relations, linked by assets, or operated through authority, but rather are dynamic corporate alliances based on computer and information networks, with cooperative relationships as the connecting link, combining authority control with market equivalence exchange principles.

Virtual organizations mainly have the following characteristics:
1Adopt a franchising model2Integrate resources across enterprises and collaborate across time and space as the basic operational form3Construct a management mechanism driven by mutual benefits and win-win outcomes4Virtual organizations possess non-legal entity and non-physical characteristics5Virtual organizations are supported and carried by information and network technology

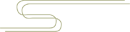
Its disadvantages include: first, it may be difficult to coordinate interests among member enterprises. Virtual enterprises are alliances composed of different companies, each with different interests, leading to complex “principal-agent” relationships. Secondly, communication of information between member enterprises may be challenging, and it may be difficult to form a consistent corporate culture among them. The original values and corporate cultures of the member enterprises may differ significantly, even conflicting.
Platformization of Organizational Structure

The Internet has spawned a new type of platform organization, emphasizing the so-called platform as an ecosystem that rapidly aggregates resources. Platform strategy transformation involves shifting from a clearly defined, closed hierarchical organizational system to a flat, open platform ecosystem, where employees and partners within the platform become resource integration units. Each unit on the platform can choose the most beneficial platform partners or resource support; the platform stimulates the enthusiasm of units and individuals, rapidly expanding its scale and influence.

The main characteristics of platform organizations include:
1Openness; comprehensive open interfaces are the primary means of interaction between platform organizations and the outside world2Functionality; establishing standard, simple, and user-friendly interfaces to modularize each functional unit3Scalability; enterprises within the system can influence each other, govern collaboratively, and cooperate4Interactivity; projects, products, and ideas are initiated from small fronts; the platform uses venture capital mechanisms and internal free market mechanisms to allocate resources
In summary, the development of enterprises cannot be separated from scientific management and innovation. Keeping pace with the times and promoting organizational innovation is an inevitable requirement of the era, the source of maintaining vitality for enterprises and driving the development of the entire economy, as well as the future trend of enterprise development. Because they each have their advantages, limitations, and characteristics, how should enterprises choose an organizational structure model? The key lies in the need to comprehensively analyze the various influencing factors that lead to differences in organizational models and their effectiveness, so as to seek commonalities in certain factors while fully considering the individuality of the enterprise, thus selecting the most suitable organizational structure for themselves.
Click below to read the original text to watch the class video directly!

Click to follow for more exciting content!!

Written and compiled by Long Yu
Image source: Internet