“China Science and Technology Investment” by Luo Xiaofan
Introduction: The Internet has become the “fourth space” following territory, territorial waters, and airspace, becoming a strategic high ground for major power games. The report of the 20th National Congress proposed to accelerate the construction of a network power. Building a network power is an important measure to enhance the comprehensive international competitiveness of our country in the context of major changes in the world today.
The mobile Internet is an important component of our country’s new infrastructure and a crucial foundation for practicing network power. The construction of new infrastructures such as the Internet of Things, 5G, artificial intelligence, and industrial Internet provides significant support for building a network power.
The Internet of Things (IoT), as the name suggests, is the “internet connecting things to things,” encompassing two aspects: first, the IoT is a network that extends and expands based on the Internet; second, the user end of the IoT extends and expands to any item, achieving connectivity of all things.
The IoT is an infrastructure that realizes ubiquitous connections between people, machines, and things through sensing technology and network communication technology, providing services such as information perception, information transmission, and information processing. For example, applications of the IoT include autonomous driving, facial recognition, smart homes, smart healthcare, and so on, covering various aspects of our daily lives.
The IoT industry is currently a key industry supported and encouraged by national policies. The report of the 20th National Congress pointed out that we should accelerate the development of the IoT and build an efficient and smooth circulation system to reduce logistics costs. The innovative development and application of technologies such as IoT are of great significance for accelerating the construction of a network power and promoting high-quality development.
What is the current state of IoT development in our country? What opportunities and challenges will “connectivity of all things” bring? How should we further promote the high-quality development of the IoT in the future? This article will focus on the current development status and policy system of the IoT industry in our country, sorting out the challenges it faces and the future policy trends.
1. The Wave of IoT is Surging
As the third wave of information development following computers and the internet, the IoT has become an important part of the national science and technology development strategy and is one of the dominant forces in future strategic emerging industries.
At the first Mobile IoT Conference (2022) held in November this year, Zhao Ce, Deputy Director of the Information and Communication Development Department of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, stated that China’s mobile IoT development has made significant achievements, mainly reflected in four aspects.
First, network construction has reached a new level, establishing the world’s largest mobile IoT network. As of the end of September, the number of NB-IoT, 4G, and 5G base stations nationwide reached 756,000, 5.962 million, and 2.22 million, respectively.
Second, user scale has achieved a new breakthrough. As of the end of September, the number of mobile IoT connections in China reached 1.75 billion, an increase of 350 million from the beginning of the year, accounting for over 70% of the total number of mobile IoT connections globally.
Third, integrated applications have opened new spaces, forming four primary applications: vehicle networking, public services, retail services, and smart homes, as well as three applications with tens of millions of users: smart agriculture, intelligent manufacturing, and smart logistics.
Fourth, the industry ecosystem is shaping new advantages. The industrial scale continues to grow, and the innovation and R&D capabilities are continuously enhanced. Domestic mobile IoT chip and module companies are refining their efforts and breaking through, gaining a certain advantage in the global market.
In August of this year, the number of mobile IoT connections in China reached 1.698 billion, surpassing the number of mobile phone users (1.678 billion) for the first time, making China the first country among major economies to achieve “more things than people.” This means that mobile IoT has become a new engine driving the digital transformation of the economy and society, promoting high-quality development in the information and communication industry, and continuously enhancing industrial strength.
2. Favorable Policies Are Frequently Implemented
In recent years, our country has placed great emphasis on the development of the IoT, which has been included in the national development strategy. To promote the healthy and orderly development of the IoT in our country, multiple policies and incentive measures have been successively introduced at the national and local levels in terms of industrial strategic planning, technical standards research, funding, and engineering projects.
As early as the 12th Five-Year Plan period, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued the “12th Five-Year Plan for IoT Development,” stating that China should seize opportunities, clarify directions, highlight key points, and accelerate the cultivation and growth of the IoT.
During the 13th Five-Year Plan, the IoT was listed as one of China’s strategic emerging industries, accelerating the development of the IoT itself while gradually attempting to shift to the “IoT+” business model. In 2017, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued a notice on comprehensively promoting the construction and development of mobile IoT (NB-IoT), proposing quantitative indicators for network construction and user development for the first time.
In the post-2020 14th Five-Year Plan period, China began to deeply promote the comprehensive development of the IoT. In 2020, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued a notice on deeply promoting the comprehensive development of mobile IoT, clearly requiring the acceleration of mobile IoT network construction and strengthening research on standards and technologies.
In September 2021, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and eight other departments jointly issued the “Three-Year Action Plan for the Construction of New IoT Infrastructure (2021-2023)” (hereinafter referred to as the “Action Plan”), which specifies that by the end of 2023, new IoT infrastructure should be initially established in major domestic cities, strengthening the foundation for modern social governance, industrial digital transformation, and upgrading of consumer spending.
The “Action Plan” proposed four major actions and 12 key tasks: first, to carry out innovation capability enhancement actions, focusing on breakthroughs in key core technologies, promoting technological integration and innovation, and building a collaborative innovation mechanism. Second, to carry out industrial ecosystem cultivation actions, focusing on nurturing diversified subjects and strengthening industrial agglomeration development. Third, to carry out integrated application innovation actions, focusing on social governance, industry applications, and consumer spending in three major application fields, continuously enriching multi-scenario applications. Fourth, to carry out support system optimization actions, focusing on improving network deployment, standard systems, public services, and security guarantees to enhance the development environment.
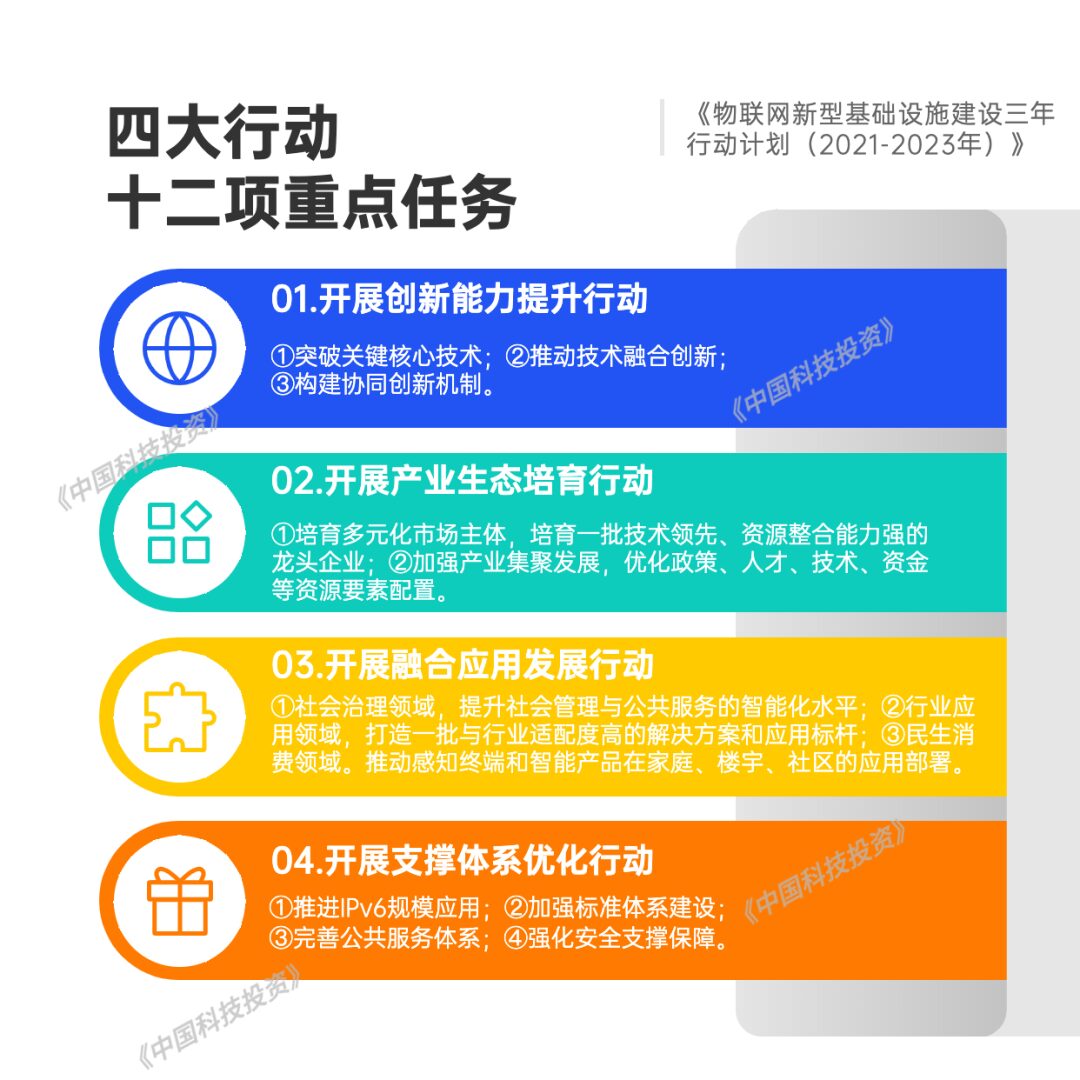
At the same time, the “Action Plan” lists specific guidelines for the implementation of various tasks in a column format. To ensure the implementation of the four major actions, the “Action Plan” specifies five guarantee measures, including optimizing collaborative governance mechanisms, improving statistical and evaluation mechanisms, enhancing talent training systems, increasing financial and tax support, and deepening international exchanges and cooperation.
In September 2022, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued a notice on organizing the collection of typical application cases for mobile IoT in 2022, focusing on intelligent home, connected vehicles, and smart wearables in the field of intelligent living applications, as well as digital applications in smart agriculture, smart factories, and smart healthcare, and intelligent governance applications in smart firefighting, environmental monitoring, and smart metering, collecting outstanding cases to promote the development of mobile IoT applications.
3. Challenges Facing IoT Development
First, the absence of standards hinders development. Currently, there is no unified IoT application standard internationally, and the situation is even more pronounced domestically. The IoT industry involves multiple enterprises across various fields, with significant industry spans, and the requirements and user demands differ greatly across industries. As a result, it is challenging for applications of the IoT to form unified standards between industries and enterprises. The lack of unified standards leads to the inability of IoT projects to interoperate, which undoubtedly increases the difficulty of wide-area, full-process, and full-network applications in the IoT field, hindering the long-term development of the IoT.
Second, core technologies need breakthroughs. Core technology is a key factor determining whether the IoT industry can develop in the long term. China’s IoT industry faces issues such as being relatively young and lacking technological innovation capabilities. Currently, there is still a significant gap between China and developed countries in core technologies in the IoT field, such as RFID key technologies, computing and service technologies, and network communication technologies, which are mainly controlled by Western developed countries.
Third, information security needs urgent resolution. As billions of devices connect to the IoT providing innovative and interconnected new services, the number of fraud and attack behaviors in the entire ecosystem has increased, posing a particularly significant impact on user privacy and the security of the underlying network environment. If this is not taken seriously, network security issues such as “hacker intrusion and data leakage” will not only infringe on the interests of individuals and enterprises but also pose threats to national society.
Fourth, large-scale applications are still pending. Currently, a series of pilot and demonstration projects have been carried out in various fields such as smart grids, intelligent transportation, smart logistics, smart homes, environmental protection, industrial automation, healthcare, precision agriculture, financial services, public safety, and national defense. However, overall, China’s IoT is still in the exploratory and partially demonstrative development stage, with most technologies remaining at the theoretical and experimental stages. Only when the IoT achieves large-scale applications can it provide a practical use for its technology and industry, fulfilling its role as an important engine for economic and social development.
4. Future Policy Trends
In early 2022, the State Council officially released the “14th Five-Year Plan for Digital Economy Development” (hereinafter referred to as the “Plan”). As a crucial support for the future digital economy, the construction of new IoT infrastructure is also a key focus of the Plan regarding the development direction, infrastructure, access capabilities, and application scenarios of the IoT.
First, it clearly lists the fields and directions that the IoT needs to focus on for development, including promoting technological innovations such as sensors, network slicing, and high-precision positioning, developing cloud services and edge computing in a coordinated manner, and nurturing industries such as vehicle networking, medical IoT, and home IoT.
Second, regarding infrastructure, it encourages IoT sensing facilities to be used as public infrastructure for smart cities. Currently, “digital twin cities” are becoming a global hotspot for smart city construction. Through massive IoT sensing terminals in systems such as transportation, energy, security, and environmental protection, the real operating status of real cities can be perceived in real-time, creating a virtual image of real cities, supporting various applications such as urban monitoring and prediction, and achieving intelligent management and regulation of cities.
Third, in terms of access capabilities, it aims to build access capabilities that support the integration of fixed and mobile networks and the combination of broadband and narrowband. Access capability is a core foundational capability of the IoT, possessing infrastructure attributes. The so-called fixed-mobile integration refers to the integrated development of fixed networks and mobile networks, which means promoting further in-depth cooperation between mobile networks and fixed networks to form a robust “access-backhaul” network system. The “broadband-narrowband combination” is viewed from the perspective of the access resources supported by IoT nodes. In recent years, the access infrastructure of the IoT in China has continuously promoted a reasonable layout of broadband and narrowband combinations, including the commercial use of 5G networks, which brings eMBB capabilities to meet the requirements for broadband and high-speed IoT access capabilities; promoting the construction of NB-IoT networks, with the current number of NB-IoT base stations expected to exceed 1 million, forming basic narrowband access capabilities.
Fourth, regarding application scenarios, it encourages the application of the IoT in municipal public facilities and buildings. For a long time, urban public utilities have been the main application scenarios for the IoT. For example, at present, water meters and gas meters have become the largest devices connected by NB-IoT. Of course, merely achieving intelligent meter reading is far from enough; the goal is to promote the widespread and in-depth application of the IoT throughout the entire industry, using intelligent meter reading as an opportunity.