The Internet of Things (IoT) is a technology that connects objects to the internet through information sensing devices such as Bluetooth, RFID, infrared sensors, GPS, and laser scanners, according to agreed protocols. This connection enables objects to exchange information and communicate over the network, thereby achieving intelligent identification, positioning, tracking, monitoring, and management functions. The goal of IoT is to integrate various items, devices, and smart sensors from the real world into a unified internet architecture, constructing intelligent, digital, and networked systems to create a safer, more convenient, and efficient living and working environment for users. The concept of IoT also includes real-time information sharing and intelligent collection, transmission, processing, and execution between objects, which helps promote social development, such as improving traffic flow, optimizing energy use, and increasing medical efficiency.
In 2023, our hospital initiated the construction of an IoT platform project, aiming to achieve indoor positioning coverage across approximately 125,000 square meters of the hospital. Bluetooth positioning beacons and IoT base station hardware will be installed in the covered areas to achieve an average positioning accuracy of 1 to 3 meters. For the hospital’s atrium area, a Beacon PAD smart antenna array will be used for positioning coverage, and next-generation medical IoT platforms will be constructed using indoor positioning technology and high-precision 3D maps. Combining various special IoT tags used in different scenarios in the hospital, we will provide a smart medical application system for IoT in multiple scenarios. The success of the IoT project hinges on the realization of application scenarios and clinical perception.
To promote the application scenarios of the IoT platform, our hospital has established a key project team led by the responsible dean. The team members cover various departments including information, asset management, logistical support, nursing, and surgery, collaborating across four dimensions: authorization, training, consensus, and results. After discussions and practice, the project team reached a consensus that the key application scenarios include equipment positioning and efficiency analysis, equipment sharing, patient positioning and care systems (for checks, surgeries, treatments, etc.), intelligent delivery services, and emergency patient positioning and time collection systems.
By attaching non-invasive smart asset tags to medical equipment, we can bind IoT identifiers and manage asset classifications, allowing for automatic queries of real-time device locations, historical movement trajectories, one-click real-time inventory, and accurate differentiation of different device operational states (on, off, standby, running), and analyze operational data to monitor the equipment status and efficiency in a multi-dimensional manner, achieving refined management of devices. Additionally, the system connects seamlessly with the HIS system without requiring login, facilitating clinical use. As shown in Figure 1:
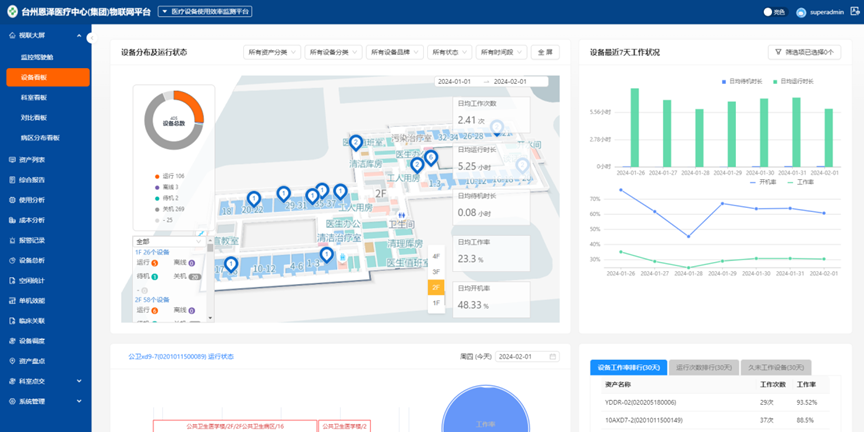
 Figure 1 Equipment Positioning and Efficiency Analysis System
Figure 1 Equipment Positioning and Efficiency Analysis System
A “sharing platform” module has been added to the asset management system, which includes functions such as “sharing appraisal,” “sharing management,” and “data statistics.” It fully integrates the asset management system with the IoT platform (binding asset codes and device MAC addresses), collecting the usage status and location of devices through the IoT platform. Various statuses (in use, idle, under maintenance) are clear at a glance, facilitating quick and effective selection for both supply and demand sides, reducing communication costs arising from shared devices in clinical settings, and improving sharing efficiency. The system categorizes asset sharing into idle sharing and rental sharing, with idle assets transferring ownership through “department transfer”; rental assets remain with the renting department, allowing the renting department limited usage rights for a certain period, achieved through “borrowing,” mainly for equipment such as ECG monitors, micro pumps, ventilators, and portable ultrasound devices.
Using medical IoT technology, special patients wear smart positioning wristbands or tags to achieve real-time positioning, tracking, historical trajectory playback, electronic fence alarms (stay alarms, boundary crossing alarms), one-click emergency alarms, vital sign monitoring, alarm analysis, and trajectory analysis within the hospital or controlled areas, assisting medical staff in viewing real-time patient locations and alarm information to promote timely rescue. Our hospital categorizes special patients into groups such as elderly patients with dementia, those going out for examinations (elderly patients), those going out for treatments (such as gastroscopy), and surgical patients. By wearing positioning wristbands, not only can we ensure the safety of patients, but we can also analyze the waiting times for examinations and treatments, facilitating subsequent improvements. At the same time, the hospital’s HIS system connects with the IoT platform, allowing medical staff to directly view key patient trajectories.
Based on the medical IoT platform, we are creating a “Didi Taxi” style intelligent delivery system, which mainly includes a delivery task reception and generation system, a delivery center dispatch system, and a PDA order-taking system (automated or manual). Care workers are equipped with order-taking PDAs, and the intelligent delivery system connects to the IoT platform, obtaining real-time positioning and historical trajectories of care workers. The system adopts the concept of “Didi Taxi,” achieving nearby order dispatch, intelligent order grabbing, and automatic task completion. Simultaneously, the platform seamlessly integrates with the hospital’s HIS, examination appointments, and surgical arrangements, enabling automatic and precise data collection in real time.
By equipping emergency patients with positioning wristbands, we can bind IoT identifiers and manage emergency classifications, allowing for real-time positioning and tracking of emergency patients’ flow. Information technology replaces the traditional manual filling method, automatically and seamlessly recording the required treatment steps and times, ensuring the recorded data is objective and accurate, monitoring the flow of critically ill patients, and providing precise location and timing information for rescue processes, thus saving rescue time. At the same time, the wristband features a “one-click record” function; during key treatment processes (when the system cannot obtain accurate timing), nurses can simply click the corresponding physical event button on the wristband, and the platform will automatically log what treatment the patient received indoors and when, ensuring timely, standardized, efficient, and thorough medical services for emergency patients.
Currently, under the continuous promotion of the project team, the five major application scenarios are gradually being implemented and continuously strengthening the application foundation. After more than a year of practice and experience summarization, the key to the success of the IoT platform project lies in the implementation of key application scenarios and the practice of lean management thinking. During the project implementation, clinical awareness is essential for sustainability and effectiveness. Additionally, special attention must be paid to information security during the project construction process, such as the security risks of IoT devices. In response to system security risks, the hospital has established a unified information security protection system, conducting annual evaluations to continuously improve security measures.
(Thanks to Yang Hai, Zhang Ruibiao, and Zheng Minxi for their contributions to this article)


